ریلها دسترسی به مقصدها را در برنامههایی که روی دستگاههایی با صفحه نمایش بزرگ اجرا میشوند، فراهم میکنند. شما باید از ریلهای ناوبری برای موارد زیر استفاده کنید:
- مقاصد سطح بالا که باید در هر کجای برنامه قابل دسترسی باشند
- سه تا هفت مقصد اصلی
- طرحبندی تبلت یا دسکتاپ
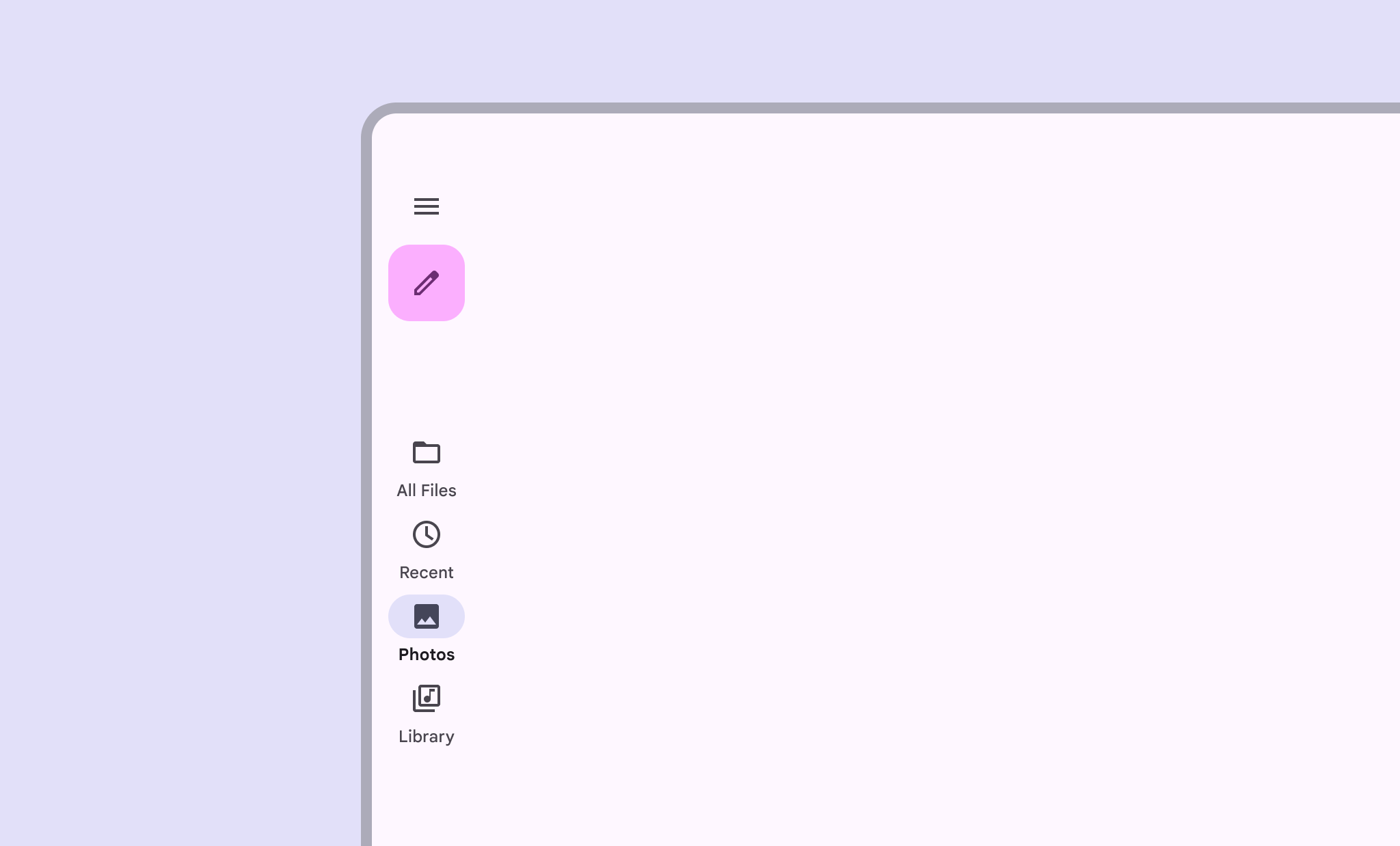
این صفحه به شما نشان میدهد که چگونه ریلها را در برنامه خود با صفحات مرتبط و ناوبری اولیه نمایش دهید.
سطح API
برای پیادهسازی یک ریل در برنامه خود، از NavigationRail Composable به همراه NavigationRailItem استفاده کنید. NavigationRailItem نشاندهنده یک آیتم ریل واحد در ستون ریل است.
NavigationRailItem شامل پارامترهای کلیدی زیر است:
-
selected: تعیین میکند که آیا آیتم ریلی فعلی از نظر بصری برجسته شده است یا خیر. -
onClick(): یک تابع لامبدا الزامی که عملی را که باید هنگام کلیک کاربر روی آیتم ریلی انجام شود، تعریف میکند. این جایی است که معمولاً رویدادهای ناوبری را مدیریت میکنید، وضعیت آیتم ریلی انتخاب شده را بهروزرسانی میکنید یا محتوای مربوطه را بارگذاری میکنید. -
label: متن درون آیتم ریلی را نمایش میدهد. اختیاری است. -
icon: یک آیکون را درون آیتم ریلی نمایش میدهد. اختیاری است.
مثال: ناوبری مبتنی بر ریل
قطعه کد زیر یک نوار ناوبری پیادهسازی میکند تا کاربران بتوانند بین صفحات مختلف یک برنامه حرکت کنند:
@Composable fun NavigationRailExample(modifier: Modifier = Modifier) { val navController = rememberNavController() val startDestination = Destination.SONGS var selectedDestination by rememberSaveable { mutableIntStateOf(startDestination.ordinal) } Scaffold(modifier = modifier) { contentPadding -> NavigationRail(modifier = Modifier.padding(contentPadding)) { Destination.entries.forEachIndexed { index, destination -> NavigationRailItem( selected = selectedDestination == index, onClick = { navController.navigate(route = destination.route) selectedDestination = index }, icon = { Icon( destination.icon, contentDescription = destination.contentDescription ) }, label = { Text(destination.label) } ) } } AppNavHost(navController, startDestination) } }
نکات کلیدی
-
NavigationRailیک ستون عمودی از آیتمهای ریلی را نمایش میدهد که هر آیتم مربوط به یکDestinationاست. -
val navController = rememberNavController()یک نمونه ازNavHostControllerایجاد و به خاطر میسپارد، که ناوبری را درون یکNavHostمدیریت میکند. -
var selectedDestination by rememberSaveable { mutableIntStateOf(startDestination.ordinal) }وضعیت آیتم ریلی انتخاب شده فعلی را مدیریت میکند.-
startDestination.ordinalاندیس عددی (موقعیت) ورودی شمارشیDestination.SONGSرا برمیگرداند.
-
- وقتی روی یک آیتم ریلی کلیک میشود،
navController.navigate(route = destination.route)برای پیمایش به صفحه مربوطه فراخوانی میشود. - لامبدا
onClickمربوط بهNavigationRailItemوضعیتselectedDestinationرا بهروزرسانی میکند تا آیتم ریلی کلیکشده به صورت بصری هایلایت شود. - این تابع،
AppNavHostcomposable را فراخوانی میکند وnavControllerوstartDestinationرا برای نمایش محتوای واقعی صفحه انتخاب شده ارسال میکند.
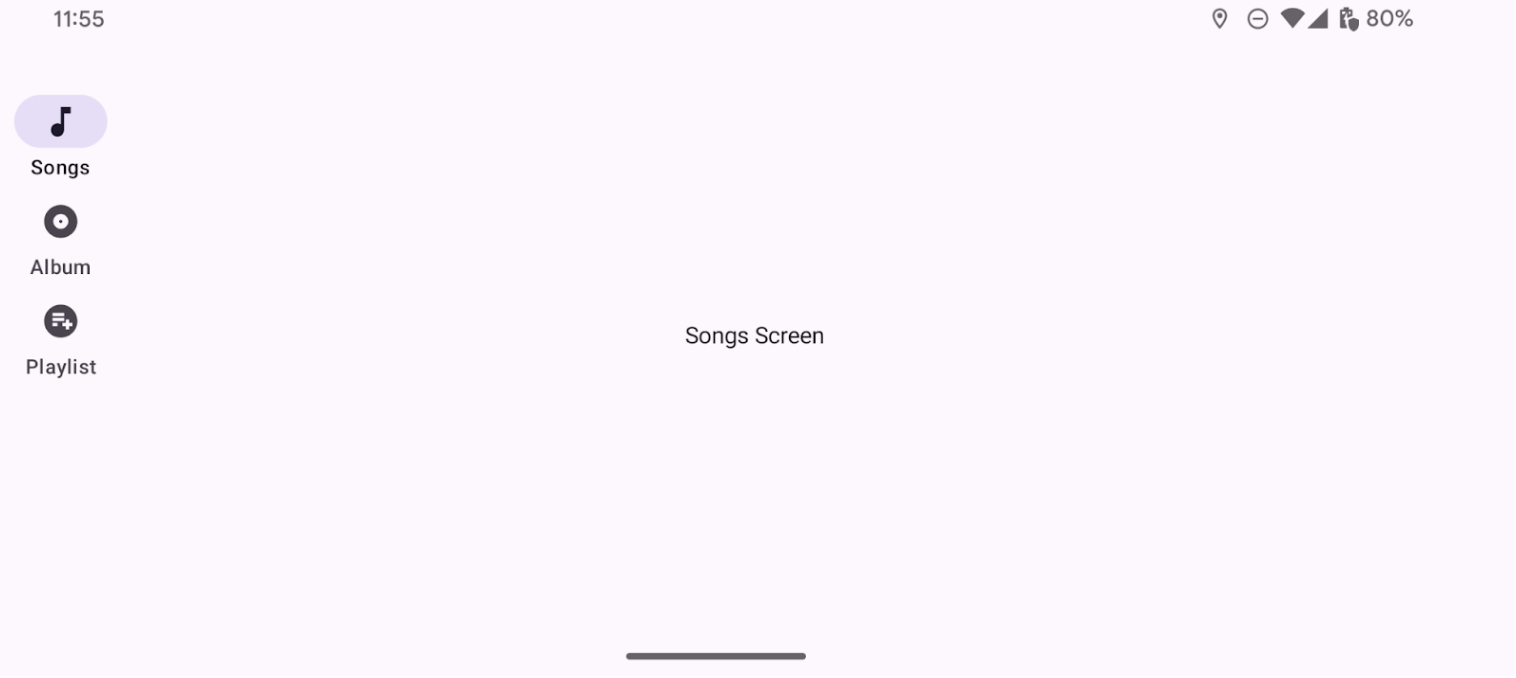
نتیجه
تصویر زیر نتیجهی قطعه کد قبلی را نشان میدهد: