Karuzela wyświetla przewijaną listę elementów, które dynamicznie dostosowują się do rozmiaru okna. Używaj karuzel, aby prezentować kolekcję powiązanych treści. Elementy karuzeli zawierają przede wszystkim treści wizualne, ale mogą też zawierać krótki tekst, który dostosowuje się do rozmiaru elementu.
Dostępne są 4 układy karuzeli, które pasują do różnych przypadków użycia:
- Wielokrotne przeglądanie: obejmuje produkty o różnych rozmiarach. Zalecany do przeglądania wielu elementów naraz, np. zdjęć.
- Nieograniczony: zawiera elementy o jednym rozmiarze, które przepływają poza krawędź ekranu. Można go dostosować, aby wyświetlać więcej tekstu lub innych elementów interfejsu nad lub pod każdym elementem.
- Główny: wyróżnia jedno duże zdjęcie, na którym skupia się uwaga, i pokazuje mały element, który zapowiada następną treść. Zalecany do wyróżniania treści, na których chcesz się skupić, np. miniatur filmów lub programów.
- Pełny ekran: wyświetla po jednym dużym elemencie od krawędzi do krawędzi i przewija się w pionie. Zalecany w przypadku treści, które są wyższe niż szersze.
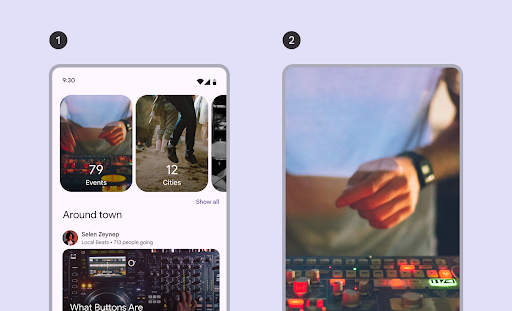
Na tej stronie dowiesz się, jak wdrożyć układy karuzeli z wieloma przeglądarkami i bez kontenera. Więcej informacji o typach układu znajdziesz w wytycznych dotyczących karuzeli w Material 3.
Powierzchnia interfejsu API
Aby zaimplementować karuzele z wieloma przeglądarkami i bez kontenera, użyj komponentów HorizontalMultiBrowseCarousel i HorizontalUncontainedCarousel. Te funkcje kompozycyjne mają te kluczowe parametry:
state: instancjaCarouselState, która zarządza bieżącym indeksem elementów i pozycją przewijania. Utwórz ten stan za pomocą wartościrememberCarouselState { itemCount }, gdzieitemCountto łączna liczba elementów w karuzeli.itemSpacing: określa ilość pustego miejsca między sąsiednimi elementami w karuzeli.contentPadding: stosuje dopełnienie wokół obszaru treści karuzeli. Użyj tego, aby dodać odstęp przed pierwszym lub po ostatnim elementem albo aby zapewnić marginesy dla elementów w obszarze przewijania.content: funkcja typu „composable”, która przyjmuje indeks liczby całkowitej. Użyj tej lambdy, aby zdefiniować interfejs każdego elementu w karuzeli na podstawie jego indeksu.
Te funkcje kompozycyjne różnią się sposobem określania rozmiaru elementu:
itemWidth(w przypadkuHorizontalUncontainedCarousel): określa dokładną szerokość każdego elementu w nieograniczonym karuzeli.preferredItemWidth(w przypadkuHorizontalMultiBrowseCarousel): sugeruje idealną szerokość elementów w karuzeli z wieloma przeglądarkami, umożliwiając wyświetlanie wielu elementów, jeśli jest na to miejsce.
Przykład: karuzela z wieloma przeglądarkami
Ten fragment kodu implementuje karuzelę z wieloma przeglądarkami:
@Composable fun CarouselExample_MultiBrowse() { data class CarouselItem( val id: Int, @DrawableRes val imageResId: Int, val contentDescription: String ) val items = remember { listOf( CarouselItem(0, R.drawable.cupcake, "cupcake"), CarouselItem(1, R.drawable.donut, "donut"), CarouselItem(2, R.drawable.eclair, "eclair"), CarouselItem(3, R.drawable.froyo, "froyo"), CarouselItem(4, R.drawable.gingerbread, "gingerbread"), ) } HorizontalMultiBrowseCarousel( state = rememberCarouselState { items.count() }, modifier = Modifier .fillMaxWidth() .wrapContentHeight() .padding(top = 16.dp, bottom = 16.dp), preferredItemWidth = 186.dp, itemSpacing = 8.dp, contentPadding = PaddingValues(horizontal = 16.dp) ) { i -> val item = items[i] Image( modifier = Modifier .height(205.dp) .maskClip(MaterialTheme.shapes.extraLarge), painter = painterResource(id = item.imageResId), contentDescription = item.contentDescription, contentScale = ContentScale.Crop ) } }
Najważniejsze informacje o kodzie
- Definiuje
CarouselItemklasę danych, która strukturyzuje dane każdego elementu w karuzeli. - Tworzy i zapamiętuje
ListobiektówCarouselItem, które są wypełnione zasobami obrazów i opisami. - Używa funkcji kompozycyjnej
HorizontalMultiBrowseCarousel, która jest przeznaczona do wyświetlania wielu elementów w karuzeli.- Stan karuzeli jest inicjowany za pomocą zmiennej
rememberCarouselState, której przypisywana jest łączna liczba elementów. - Elementy mają atrybut
preferredItemWidth(w tym przypadku186.dp), który sugeruje optymalną szerokość każdego elementu. Karuzela używa tego parametru, aby określić, ile elementów może się zmieścić na ekranie jednocześnie. - Parametr
itemSpacingdodaje niewielką przerwę między elementami. - Ostatnia lambda
HorizontalMultiBrowseCarouseliteruje poCarouselItems. W każdej iteracji pobiera element o indeksieii renderuje dla niego funkcję kompozycyjnąImage. Modifier.maskClip(MaterialTheme.shapes.extraLarge)stosuje do każdego obrazu wstępnie zdefiniowaną maskę kształtu, nadając mu zaokrąglone rogi.contentDescriptionpodaje opis obrazu obsługujący ułatwienia dostępu.
- Stan karuzeli jest inicjowany za pomocą zmiennej
Wynik
Na ilustracji poniżej widać wynik działania powyższego fragmentu kodu:

Przykład: nieograniczony karuzel
Poniższy fragment kodu implementuje nieograniczony karuzel:
@Composable fun CarouselExample() { data class CarouselItem( val id: Int, @DrawableRes val imageResId: Int, val contentDescription: String ) val carouselItems = remember { listOf( CarouselItem(0, R.drawable.cupcake, "cupcake"), CarouselItem(1, R.drawable.donut, "donut"), CarouselItem(2, R.drawable.eclair, "eclair"), CarouselItem(3, R.drawable.froyo, "froyo"), CarouselItem(4, R.drawable.gingerbread, "gingerbread"), ) } HorizontalUncontainedCarousel( state = rememberCarouselState { carouselItems.count() }, modifier = Modifier .fillMaxWidth() .wrapContentHeight() .padding(top = 16.dp, bottom = 16.dp), itemWidth = 186.dp, itemSpacing = 8.dp, contentPadding = PaddingValues(horizontal = 16.dp) ) { i -> val item = carouselItems[i] Image( modifier = Modifier .height(205.dp) .maskClip(MaterialTheme.shapes.extraLarge), painter = painterResource(id = item.imageResId), contentDescription = item.contentDescription, contentScale = ContentScale.Crop ) } }
Najważniejsze informacje o kodzie
- Kompozycja
HorizontalUncontainedCarouseltworzy układ karuzeli.- Parametr
itemWidthustawia stałą szerokość każdego elementu w karuzeli.
- Parametr
Wynik
Na ilustracji poniżej widać wynik działania powyższego fragmentu kodu:

