يعمل العنصر القابل للإنشاء Card كحاوية Material Design لواجهة المستخدم.
تعرض البطاقات عادةً جزءًا واحدًا متماسكًا من المحتوى. في ما يلي بعض الأمثلة على الحالات التي يمكنك فيها استخدام بطاقة:
- منتج في تطبيق تسوّق
- خبر في تطبيق للأخبار
- رسالة في تطبيق للتواصل
والتركيز على عرض جزء واحد من المحتوى هو ما يميّز
Card عن الحاويات الأخرى. على سبيل المثال، يوفّر Scaffold بنية عامة لشاشة كاملة. البطاقة هي بشكل عام عنصر أصغر في واجهة المستخدم ضمن تخطيط أكبر، بينما يوفّر مكوّن التخطيط، مثل Column أو Row، واجهة برمجة تطبيقات أبسط وأكثر عمومية.

التنفيذ الأساسي
يتشابه سلوك Card إلى حد كبير مع سلوك الحاويات الأخرى في Compose. يمكنك تحديد محتوى هذا العنصر من خلال استدعاء عناصر أخرى قابلة للإنشاء بداخله. على سبيل المثال، لنفترض أنّ Card يتضمّن طلبًا إلى Text في المثال البسيط التالي:
@Composable
fun CardMinimalExample() {
Card() {
Text(text = "Hello, world!")
}
}
عمليات التنفيذ المتقدّمة
اطّلِع على المرجع لمعرفة تعريف واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الخاص بـ Card. ويحدّد هذا الملف عدة معلَمات تتيح لك تخصيص مظهر المكوّن وسلوكه.
في ما يلي بعض المَعلمات الرئيسية التي يجب ملاحظتها:
elevation: تضيف هذه السمة ظلًا إلى المكوّن، ما يجعله يبدو مرتفعًا عن الخلفية.colors: تستخدم النوعCardColorsلضبط اللون التلقائي لكل من الحاوية وأي عناصر فرعية.enabled: إذا مرّرت القيمةfalseلهذه المَعلمة، ستظهر البطاقة على أنّها غير مفعّلة ولن تستجيب لإدخالات المستخدم.-
onClick: لا يقبلCardعادةً أحداث النقرات. وبالتالي، فإنّ الحمل الزائد الأساسي الذي يجب ملاحظته هو الحمل الذي يحدّد المَعلمةonClick. يجب استخدام هذا التحميل الزائد إذا كنت تريد أن يستجيب تنفيذك للدالةCardلعمليات الضغط التي يجريها المستخدم.
يوضّح المثال التالي كيفية استخدام هذه المَعلمات، بالإضافة إلى مَعلمات شائعة أخرى، مثل shape وmodifier.
بطاقة ممتلئة
في ما يلي مثال على كيفية تنفيذ بطاقة مملوءة.
المفتاح هنا هو استخدام السمة colors لتغيير لون التعبئة.
@Composable fun FilledCardExample() { Card( colors = CardDefaults.cardColors( containerColor = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.surfaceVariant, ), modifier = Modifier .size(width = 240.dp, height = 100.dp) ) { Text( text = "Filled", modifier = Modifier .padding(16.dp), textAlign = TextAlign.Center, ) } }
تظهر عملية التنفيذ هذه على النحو التالي:

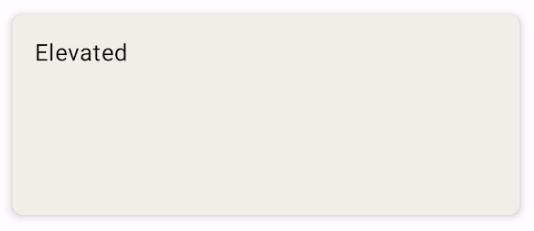
بطاقة بارزة
يوضّح المقتطف التالي كيفية تنفيذ بطاقة مرتفعة. استخدِم الدالة البرمجية القابلة للإنشاء ElevatedCard المخصّصة.
يمكنك استخدام السمة elevation للتحكّم في مظهر الارتفاع والظل الناتج.
@Composable fun ElevatedCardExample() { ElevatedCard( elevation = CardDefaults.cardElevation( defaultElevation = 6.dp ), modifier = Modifier .size(width = 240.dp, height = 100.dp) ) { Text( text = "Elevated", modifier = Modifier .padding(16.dp), textAlign = TextAlign.Center, ) } }
تظهر عملية التنفيذ هذه على النحو التالي:
بطاقة ذات حدود خارجية
في ما يلي مثال على بطاقة ذات حدود خارجية. استخدِم الدالة البرمجية المركبة
OutlinedCard المخصّصة.
@Composable fun OutlinedCardExample() { OutlinedCard( colors = CardDefaults.cardColors( containerColor = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.surface, ), border = BorderStroke(1.dp, Color.Black), modifier = Modifier .size(width = 240.dp, height = 100.dp) ) { Text( text = "Outlined", modifier = Modifier .padding(16.dp), textAlign = TextAlign.Center, ) } }
تظهر عملية التنفيذ هذه على النحو التالي:

القيود
لا تتضمّن البطاقات إجراءات التمرير أو الإغلاق، ولكن يمكن دمجها في عناصر قابلة للإنشاء توفّر هذه الميزات. على سبيل المثال، لتنفيذ ميزة "التمرير السريع للإغلاق" على بطاقة، يجب دمجها مع العنصر القابل للإنشاء SwipeToDismiss. لدمج
التمرير، استخدِم أدوات تعديل التمرير، مثل verticalScroll. يمكنك الاطّلاع على مستندات
Scroll لمزيد من المعلومات.
