共有要素の遷移は、コンテンツが相互に一貫しているコンポーザブル間をシームレスに遷移する方法です。ナビゲーションによく使用され、ユーザーが画面間を移動する際に、異なる画面を視覚的に接続できます。
たとえば、次の動画では、スナックの画像とタイトルが一覧ページから詳細ページに共有されていることがわかります。
Compose には、共有要素の作成に役立つ高レベル API がいくつかあります。
SharedTransitionLayout: 共有要素のトランジションを実装するために必要な最も外側のレイアウト。SharedTransitionScopeを提供します。共有要素修飾子を使用するには、コンポーザブルがSharedTransitionScope内にある必要があります。Modifier.sharedElement(): 別のコンポーザブルと一致させる必要があるコンポーザブルをSharedTransitionScopeに通知する修飾子。Modifier.sharedBounds(): このコンポーザブルの境界を、トランジションが発生するコンテナの境界として使用する必要があることをSharedTransitionScopeに示す修飾子。sharedElement()とは対照的に、sharedBounds()は視覚的に異なるコンテンツ向けに設計されています。
Compose で共有要素を作成する際に重要なコンセプトは、オーバーレイとクリッピングとの連携です。この重要なトピックについて詳しくは、クリッピングとオーバーレイのセクションをご覧ください。
基本的な使用方法
このセクションでは、小さい「リスト」アイテムから大きい詳細アイテムに移行する次のトランジションを構築します。

Modifier.sharedElement() を使用する最適な方法は、AnimatedContent、AnimatedVisibility、または NavHost と組み合わせて使用することです。これにより、コンポーザブル間の切り替えが自動的に管理されます。
出発点は、共有要素を追加する前の MainContent と DetailsContent コンポーザブルを含む既存の基本的な AnimatedContent です。
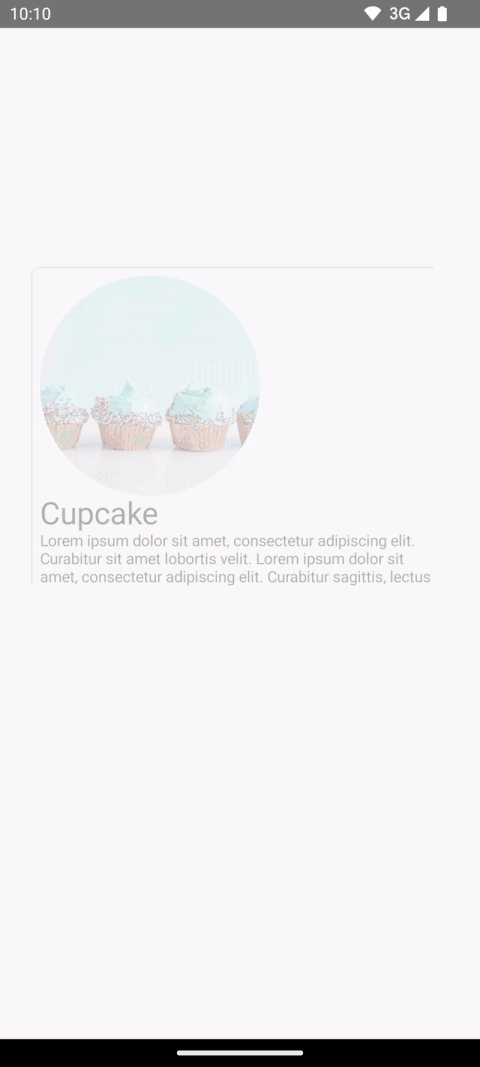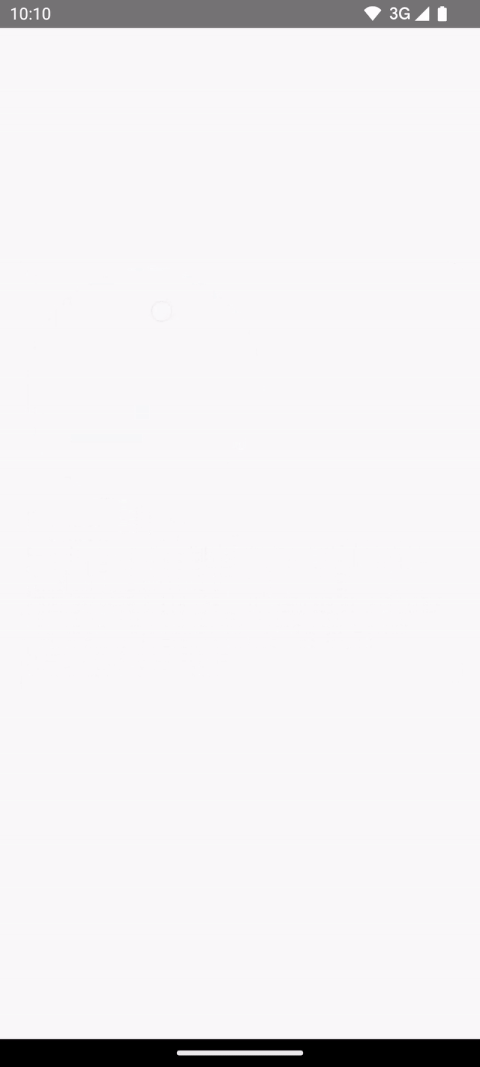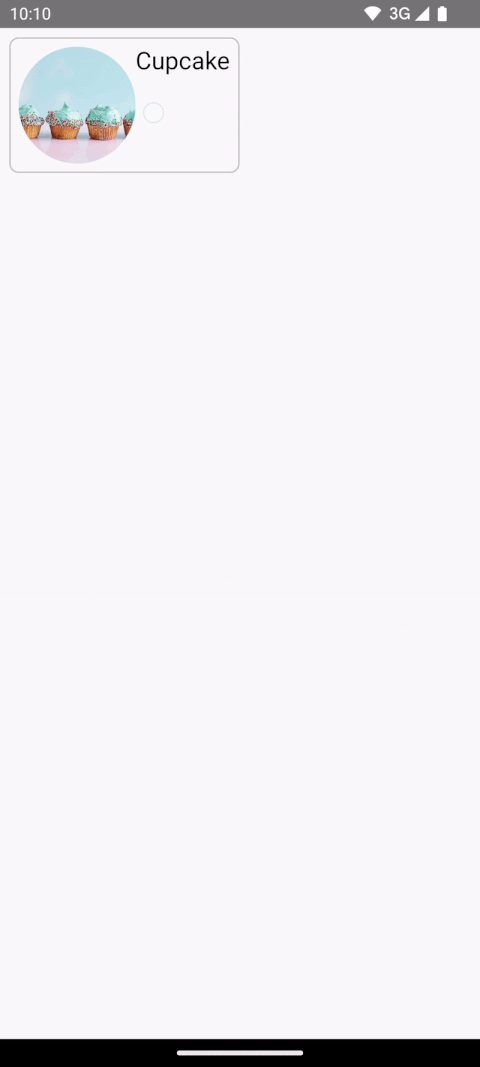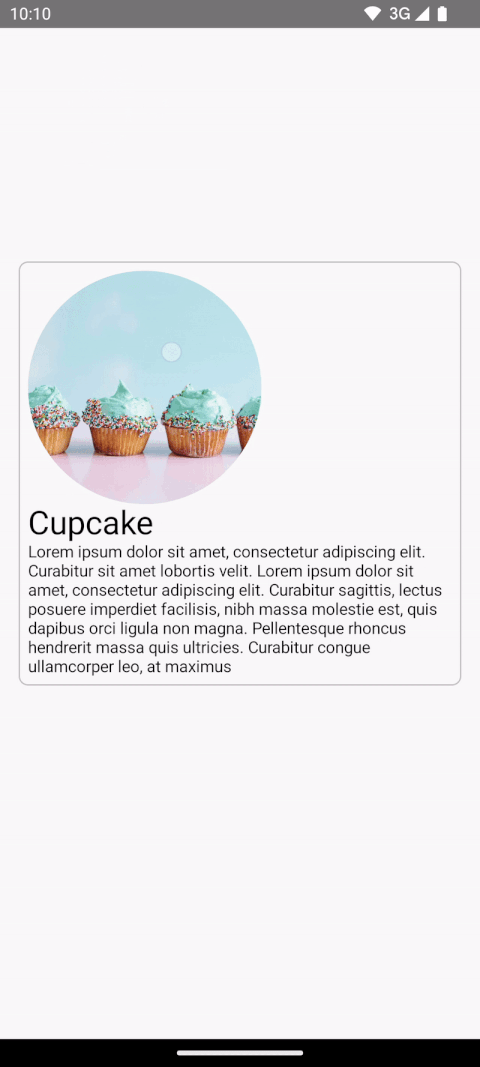
AnimatedContent を開始します。共有要素が 2 つのレイアウト間でアニメーション化されるようにするには、
AnimatedContentコンポーザブルをSharedTransitionLayoutで囲みます。SharedTransitionLayoutとAnimatedContentのスコープはMainContentとDetailsContentに渡されます。var showDetails by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } SharedTransitionLayout { AnimatedContent( showDetails, label = "basic_transition" ) { targetState -> if (!targetState) { MainContent( onShowDetails = { showDetails = true }, animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedContent, sharedTransitionScope = this@SharedTransitionLayout ) } else { DetailsContent( onBack = { showDetails = false }, animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedContent, sharedTransitionScope = this@SharedTransitionLayout ) } } }
一致する 2 つのコンポーザブルのコンポーザブル修飾子チェーンに
Modifier.sharedElement()を追加します。SharedContentStateオブジェクトを作成し、rememberSharedContentState()で記憶します。SharedContentStateオブジェクトは、共有される要素を決定する一意のキーを保存しています。コンテンツを識別する一意のキーを指定し、記憶するアイテムにrememberSharedContentState()を使用します。AnimatedContentScopeは、アニメーションの調整に使用される修飾子に渡されます。@Composable private fun MainContent( onShowDetails: () -> Unit, modifier: Modifier = Modifier, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope, animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope ) { Row( // ... ) { with(sharedTransitionScope) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.cupcake), contentDescription = "Cupcake", modifier = Modifier .sharedElement( rememberSharedContentState(key = "image"), animatedVisibilityScope = animatedVisibilityScope ) .size(100.dp) .clip(CircleShape), contentScale = ContentScale.Crop ) // ... } } } @Composable private fun DetailsContent( modifier: Modifier = Modifier, onBack: () -> Unit, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope, animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope ) { Column( // ... ) { with(sharedTransitionScope) { Image( painter = painterResource(id = R.drawable.cupcake), contentDescription = "Cupcake", modifier = Modifier .sharedElement( rememberSharedContentState(key = "image"), animatedVisibilityScope = animatedVisibilityScope ) .size(200.dp) .clip(CircleShape), contentScale = ContentScale.Crop ) // ... } } }
共有要素の一致が発生したかどうかに関する情報を取得するには、rememberSharedContentState() を変数に抽出し、isMatchFound をクエリします。
これにより、次の自動アニメーションが作成されます。

コンテナ全体の背景色とサイズは、デフォルトの AnimatedContent 設定が使用されていることに気づくかもしれません。
共有境界と共有要素
Modifier.sharedBounds() は Modifier.sharedElement() と同様です。ただし、修飾子は次の点で異なります。
sharedBounds()は、視覚的に異なるが、状態間で同じ領域を共有する必要があるコンテンツ用です。一方、sharedElement()は、コンテンツが同じであることを想定しています。sharedBounds()では、2 つの状態間の移行中に、画面に出入りするコンテンツが表示されますが、sharedElement()では、変換境界内でターゲット コンテンツのみがレンダリングされます。Modifier.sharedBounds()には、AnimatedContentの動作と同様に、コンテンツの切り替え方法を指定するためのenterパラメータとexitパラメータがあります。sharedBounds()の最も一般的なユースケースはコンテナ変換パターンですが、sharedElement()のユースケースの例はヒーロー トランジションです。Textコンポーザブルを使用する場合は、斜体と太字の切り替えや色の変更などのフォント変更をサポートするために、sharedBounds()を使用することをおすすめします。
前の例で、2 つの異なるシナリオの Row と Column に Modifier.sharedBounds() を追加すると、2 つの境界を共有して遷移アニメーションを実行し、互いに拡大できるようになります。
@Composable private fun MainContent( onShowDetails: () -> Unit, modifier: Modifier = Modifier, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope, animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope ) { with(sharedTransitionScope) { Row( modifier = Modifier .padding(8.dp) .sharedBounds( rememberSharedContentState(key = "bounds"), animatedVisibilityScope = animatedVisibilityScope, enter = fadeIn(), exit = fadeOut(), resizeMode = SharedTransitionScope.ResizeMode.scaleToBounds() ) // ... ) { // ... } } } @Composable private fun DetailsContent( modifier: Modifier = Modifier, onBack: () -> Unit, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope, animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope ) { with(sharedTransitionScope) { Column( modifier = Modifier .padding(top = 200.dp, start = 16.dp, end = 16.dp) .sharedBounds( rememberSharedContentState(key = "bounds"), animatedVisibilityScope = animatedVisibilityScope, enter = fadeIn(), exit = fadeOut(), resizeMode = SharedTransitionScope.ResizeMode.scaleToBounds() ) // ... ) { // ... } } }
スコープについて理解する
Modifier.sharedElement() を使用するには、コンポーザブルが SharedTransitionScope にある必要があります。SharedTransitionLayout コンポーザブルは SharedTransitionScope を提供します。共有する要素を含む UI 階層の同じ最上位ポイントに配置してください。
一般に、コンポーザブルは AnimatedVisibilityScope 内に配置する必要があります。これは通常、AnimatedContent を使用してコンポーザブルを切り替える場合、AnimatedVisibility を直接使用する場合、または NavHost コンポーザブル関数によって提供されます(可視性を手動で管理する場合を除く)。複数のスコープを使用するには、必要なスコープを CompositionLocal に保存するか、Kotlin のコンテキスト レシーバを使用するか、スコープをパラメータとして関数に渡します。
追跡するスコープが複数ある場合や、階層が深くネストされている場合は、CompositionLocals を使用します。CompositionLocal を使用すると、保存して使用するスコープを正確に選択できます。一方、コンテキスト レシーバを使用すると、階層内の他のレイアウトが提供されたスコープを誤ってオーバーライドする可能性があります。たとえば、複数のネストされた AnimatedContent がある場合、スコープがオーバーライドされる可能性があります。
val LocalNavAnimatedVisibilityScope = compositionLocalOf<AnimatedVisibilityScope?> { null } val LocalSharedTransitionScope = compositionLocalOf<SharedTransitionScope?> { null } @Composable private fun SharedElementScope_CompositionLocal() { // An example of how to use composition locals to pass around the shared transition scope, far down your UI tree. // ... SharedTransitionLayout { CompositionLocalProvider( LocalSharedTransitionScope provides this ) { // This could also be your top-level NavHost as this provides an AnimatedContentScope AnimatedContent(state, label = "Top level AnimatedContent") { targetState -> CompositionLocalProvider(LocalNavAnimatedVisibilityScope provides this) { // Now we can access the scopes in any nested composables as follows: val sharedTransitionScope = LocalSharedTransitionScope.current ?: throw IllegalStateException("No SharedElementScope found") val animatedVisibilityScope = LocalNavAnimatedVisibilityScope.current ?: throw IllegalStateException("No AnimatedVisibility found") } // ... } } } }
また、階層が深くネストされていない場合は、スコープをパラメータとして渡すこともできます。
@Composable fun MainContent( animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope ) { } @Composable fun Details( animatedVisibilityScope: AnimatedVisibilityScope, sharedTransitionScope: SharedTransitionScope ) { }
AnimatedVisibility と共有された要素
前の例では、AnimatedContent で共有要素を使用する方法を示しましたが、共有要素は AnimatedVisibility でも機能します。
たとえば、この遅延グリッドの例では、各要素が AnimatedVisibility でラップされています。アイテムをクリックすると、コンテンツが UI からダイアログのようなコンポーネントに引き出されるような視覚効果が適用されます。
var selectedSnack by remember { mutableStateOf<Snack?>(null) } SharedTransitionLayout(modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()) { LazyColumn( // ... ) { items(listSnacks) { snack -> AnimatedVisibility( visible = snack != selectedSnack, enter = fadeIn() + scaleIn(), exit = fadeOut() + scaleOut(), modifier = Modifier.animateItem() ) { Box( modifier = Modifier .sharedBounds( sharedContentState = rememberSharedContentState(key = "${snack.name}-bounds"), // Using the scope provided by AnimatedVisibility animatedVisibilityScope = this, clipInOverlayDuringTransition = OverlayClip(shapeForSharedElement) ) .background(Color.White, shapeForSharedElement) .clip(shapeForSharedElement) ) { SnackContents( snack = snack, modifier = Modifier.sharedElement( sharedContentState = rememberSharedContentState(key = snack.name), animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedVisibility ), onClick = { selectedSnack = snack } ) } } } } // Contains matching AnimatedContent with sharedBounds modifiers. SnackEditDetails( snack = selectedSnack, onConfirmClick = { selectedSnack = null } ) }
AnimatedVisibility と共有される要素。修飾子の順序
Modifier.sharedElement() と Modifier.sharedBounds() では、Compose の他の部分と同様に、修飾子のチェーンの順序が重要です。サイズに影響する修飾子の配置が正しくないと、共有要素のマッチング中に予期しない視覚的なジャンプが発生する可能性があります。
たとえば、2 つの共有要素でパディング修飾子の位置を変えると、アニメーションの見た目が異なります。
var selectFirst by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val key = remember { Any() } SharedTransitionLayout( Modifier .fillMaxSize() .padding(10.dp) .clickable { selectFirst = !selectFirst } ) { AnimatedContent(targetState = selectFirst, label = "AnimatedContent") { targetState -> if (targetState) { Box( Modifier .padding(12.dp) .sharedBounds( rememberSharedContentState(key = key), animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedContent ) .border(2.dp, Color.Red) ) { Text( "Hello", fontSize = 20.sp ) } } else { Box( Modifier .offset(180.dp, 180.dp) .sharedBounds( rememberSharedContentState( key = key, ), animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedContent ) .border(2.dp, Color.Red) // This padding is placed after sharedBounds, but it doesn't match the // other shared elements modifier order, resulting in visual jumps .padding(12.dp) ) { Text( "Hello", fontSize = 36.sp ) } } } }
一致した境界 |
一致しない境界: 共有要素のアニメーションが少しずれて表示されることに注目してください。これは、誤った境界に合わせてサイズ変更する必要があるためです。 |
|---|---|
共有要素修飾子の前に使用される修飾子は、共有要素修飾子に制約を提供します。この制約は、初期境界とターゲット境界、そして境界アニメーションを導出するために使用されます。
共有要素修飾子の後に使用される修飾子は、前の制約を使用して、子要素のターゲット サイズを測定して計算します。共有要素修飾子は、一連のアニメーション化された制約を作成して、子を初期サイズからターゲット サイズに徐々に変換します。
ただし、アニメーションに resizeMode = ScaleToBounds() を使用する場合や、コンポーザブルに Modifier.skipToLookaheadSize() を使用する場合は除きます。この場合、Compose はターゲット制約を使用して子をレイアウトし、レイアウト サイズ自体を変更する代わりに、スケール ファクタを使用してアニメーションを実行します。
一意キー
複雑な共有要素を扱う場合は、文字列以外のキーを作成することをおすすめします。文字列はマッチングでエラーが発生しやすいためです。一致させるには、各キーが一意である必要があります。たとえば、Jetsnack には次のような共有要素があります。
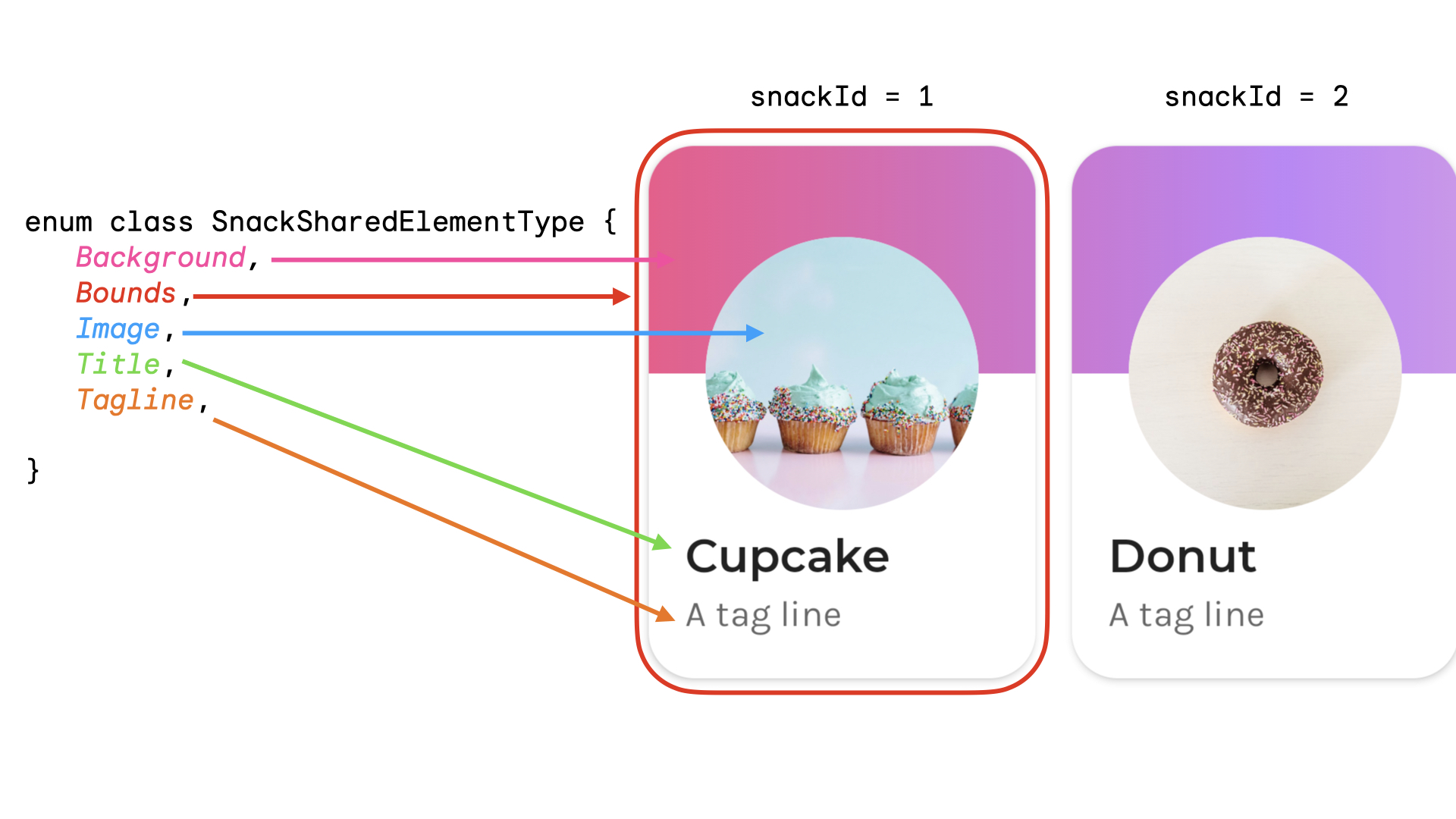
共有要素の型を表す列挙型を作成できます。この例では、スナックカード全体がホーム画面の複数の異なる場所(たとえば、「人気」セクションと「おすすめ」セクション)に表示されることもあります。共有される共有要素の snackId、origin(「人気」 / 「おすすめ」)、type を含むキーを作成できます。
data class SnackSharedElementKey( val snackId: Long, val origin: String, val type: SnackSharedElementType ) enum class SnackSharedElementType { Bounds, Image, Title, Tagline, Background } @Composable fun SharedElementUniqueKey() { // ... Box( modifier = Modifier .sharedElement( rememberSharedContentState( key = SnackSharedElementKey( snackId = 1, origin = "latest", type = SnackSharedElementType.Image ) ), animatedVisibilityScope = this@AnimatedVisibility ) ) // ... }
データクラスは hashCode() と isEquals() を実装するため、キーに推奨されます。
共有要素の表示を手動で管理する
AnimatedVisibility または AnimatedContent を使用していない場合は、共有要素の公開設定を自分で管理できます。Modifier.sharedElementWithCallerManagedVisibility() を使用して、アイテムを表示するかどうかを決定する独自の条件を指定します。
var selectFirst by remember { mutableStateOf(true) } val key = remember { Any() } SharedTransitionLayout( Modifier .fillMaxSize() .padding(10.dp) .clickable { selectFirst = !selectFirst } ) { Box( Modifier .sharedElementWithCallerManagedVisibility( rememberSharedContentState(key = key), !selectFirst ) .background(Color.Red) .size(100.dp) ) { Text(if (!selectFirst) "false" else "true", color = Color.White) } Box( Modifier .offset(180.dp, 180.dp) .sharedElementWithCallerManagedVisibility( rememberSharedContentState( key = key, ), selectFirst ) .alpha(0.5f) .background(Color.Blue) .size(180.dp) ) { Text(if (selectFirst) "false" else "true", color = Color.White) } }
現時点における制約
これらの API にはいくつかの制限があります。特に重要なのは次のとおりです。
- Views と Compose 間の相互運用性はサポートされていません。これには、
DialogやModalBottomSheetなど、AndroidViewをラップするコンポーザブルが含まれます。 - 次のものについては、自動アニメーションのサポートはありません。
- 共有画像コンポーザブル:
ContentScaleはデフォルトではアニメーション化されません。設定された終了ContentScaleにスナップします。
- シェイプのクリッピング - シェイプ間の自動アニメーション(アイテムの遷移時に正方形から円にアニメーションするなど)は、組み込みでサポートされていません。
- サポートされていないケースでは、
sharedElement()の代わりにModifier.sharedBounds()を使用し、アイテムにModifier.animateEnterExit()を追加します。
- 共有画像コンポーザブル:
