فحص
تتوفّر عدة أدوات لمساعدتك في فحص المحتوى بسرعة من ناحية تسهيل الاستخدام:
- مجموعة أدوات تسهيل الاستخدام من Android: تتضمّن "قائمة تسهيل الاستخدام" و"سماع الاختيار" و "الوصول عبر مفتاح التحويل" وTalkBack، وهي تقدّم إحصاءات عن كيفية عمل ميزات الدلالات في تطبيقك لمستخدمي هذه التقنيات. ننصحك بشدة بإجراء الاختبار باستخدام التقنيات المساعِدة في Android، لأنّها أفضل طريقة لفهم التجربة التي سيحظى بها المستخدمون الذين لديهم احتياجات تسهيل الاستخدام.
- أداة فحص التنسيق: تتيح لك فحص الدلالات لكل عنصر مؤلف وتصحيح أخطائها، كما تساعد في تحديد أي معلومات غير متوفّرة أو غير صحيحة.
- تطبيق Accessibility Scanner: يفحص شاشتك ويقدّم اقتراحات لتحسين إمكانية استخدامها من خلال تحديد بعض المشاكل الشائعة.
تصحيح الأخطاء
بين ميزة "الإنشاء" ونظام الدلالات وخدمات تسهيل الاستخدام في Android، قد تواجه سلوكيات تسهيل الاستخدام غير المتوقّعة التي يصعب تتبُّعها. يمكن أن تساعدك السمات الدلالية في فهم سبب سلوك المكوّنات بهذه الطريقة.
يمكنك تصحيح أخطاء سلوك تسهيل الاستخدام باستخدام أداة فحص التنسيق في IDE لنظام Android أو أداة TreeDebug في إعدادات المطوّرين في TalkBack أو أداة ComposeTestRule
printToLog. يمكن أن تقدّم كل هذه الأدوات معلومات عن العقد
(وخصائصها) التي توفّرها خدمات تسهيل الاستخدام من خلال أداة Compose.
يستخدم المثال التالي أداة Layout Inspector لتصحيح أخطاء شاشة تتضمّن ثلاثة عناصر، حيث لا يتم اختيار العنصر الأول عند تفعيل خدمات تسهيل الاستخدام، ولا يتضمّن العنصر الثاني أي ملاحظات مرتبطة بالإجراءات المتعلّقة به. يمكنك فحص السمات الدلالية للعثور على المشاكل المحتمَلة.
تحتوي شجرة المكوّنات في "أداة فحص التنسيق" على معلومات عن حدود العنصر ومعلماته والمعلومات الدلالية الأخرى المرتبطة به. في الشجرة، يتم التعرّف على جميع العناصر الثلاثة:
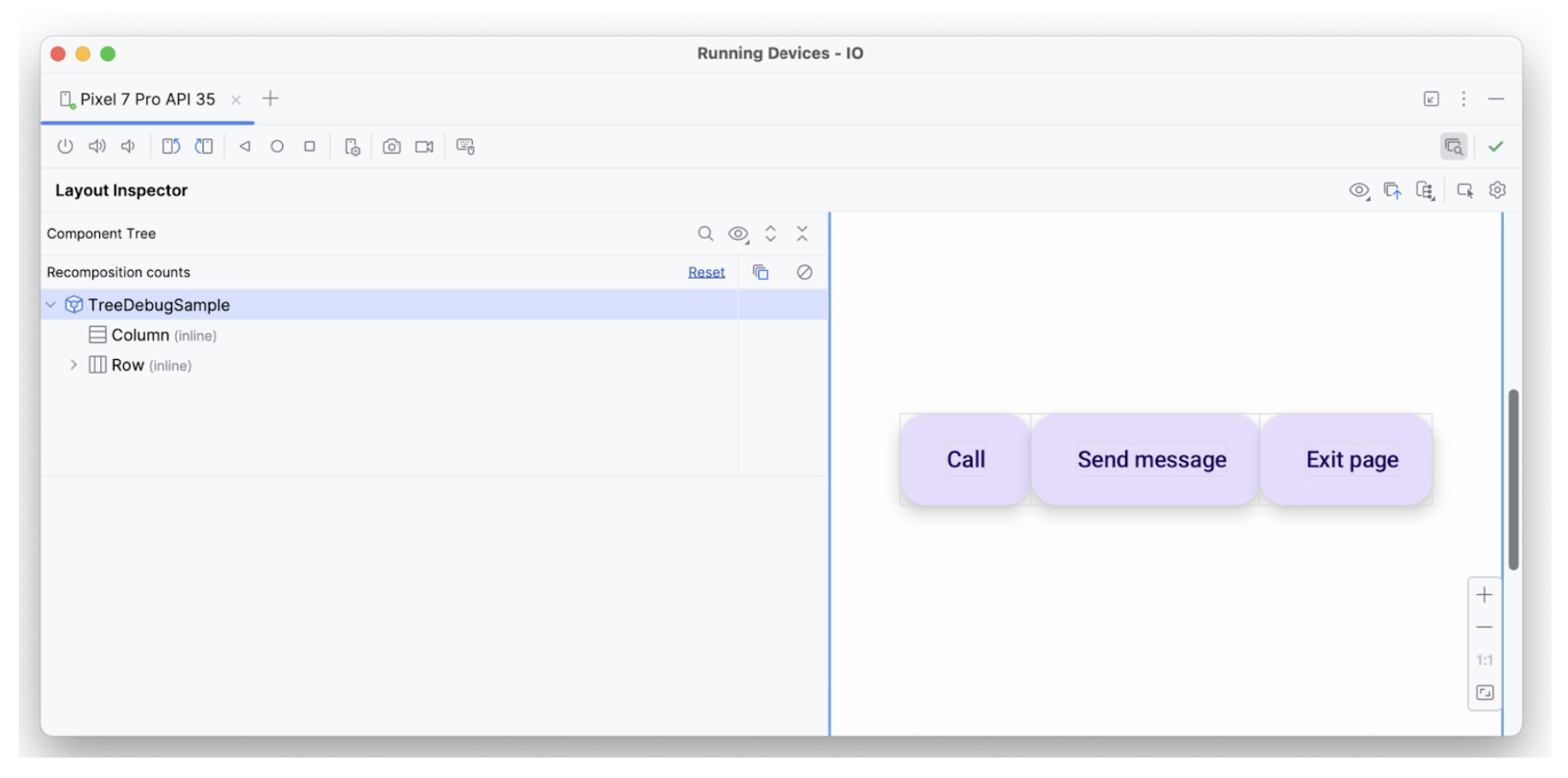
تم تطبيق السمة hideFromAccessibility على العنصر الأول. يشير ذلك
إلى أنّه قد تم وضع علامة على العنصر على أنّه مخفي في مكان ما في شجرة الدلالات
، أو أنّه محجوب بواسطة بعض العناصر الزخرفية التي تظهر فوقه.
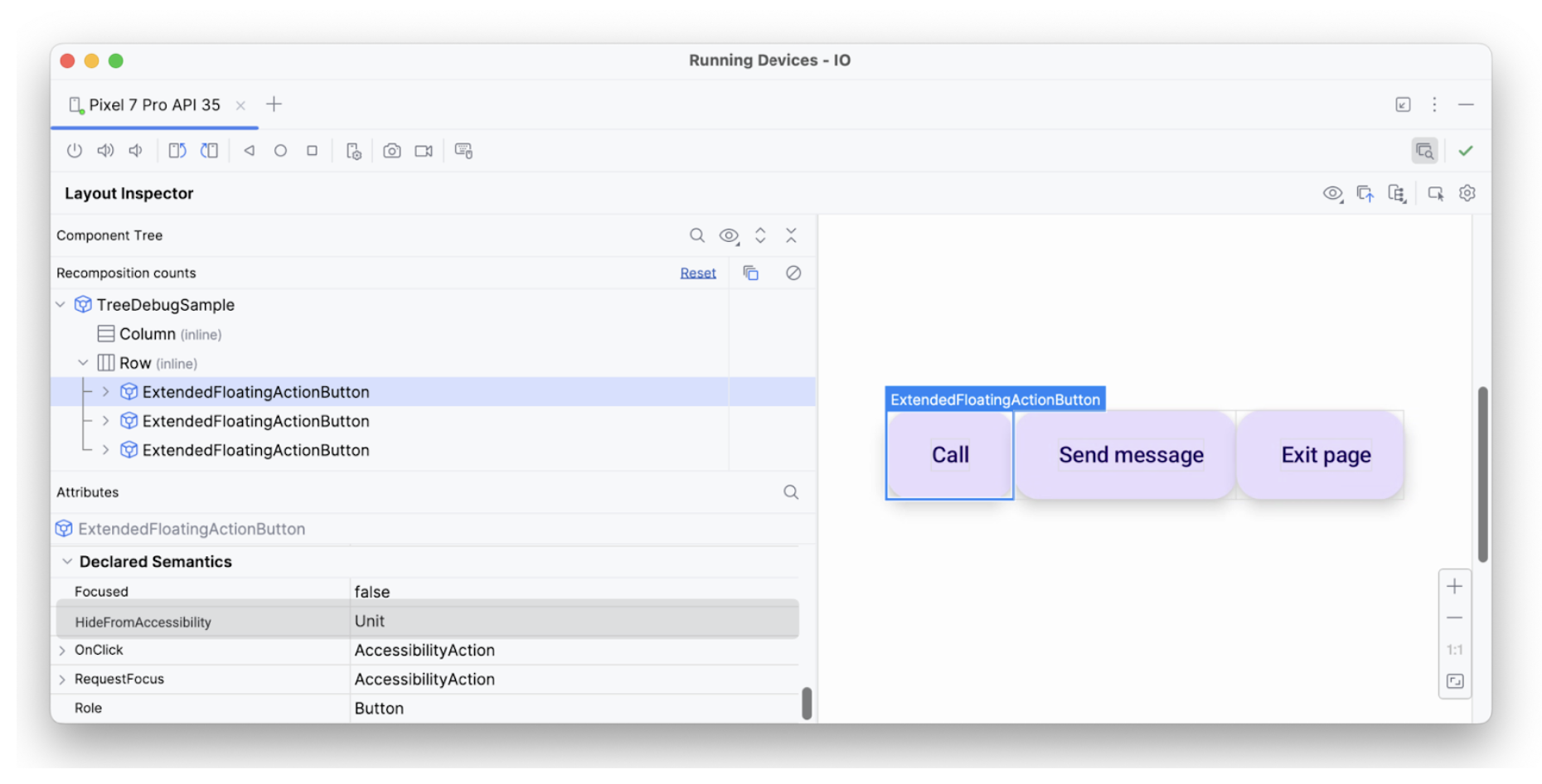
hideFromAccessibilityيحتوي العنصر الثاني على سمة focus، ولكن ليس لديه onClick مثل العنصر السابق. لذلك، قد لا يتوفّر مُعدِّل clickable في مكان ما، وهو السبب الذي قد يؤدي إلى عدم إعلان خدمة تسهيل الاستخدام، مثل TalkBack، عن بعض إشارات الإجراء للمستخدم:
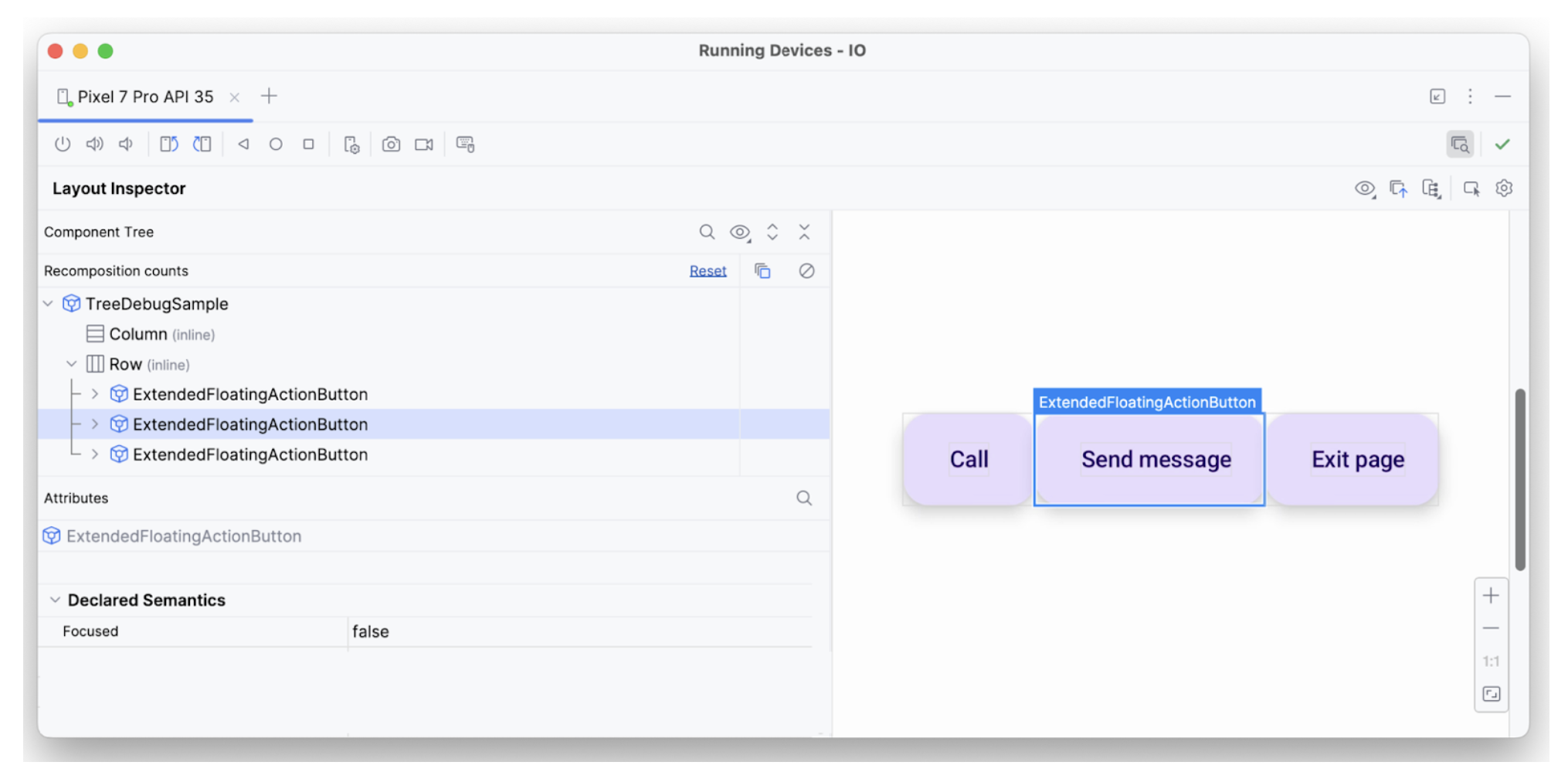
focusedيحتوي عنصر النص الثالث على جميع السمات اللازمة، فهو قابل للتركيز، ويحتوي على onClick، وتم تطبيق دلالات إضافية أخرى عليه، ولهذا السبب يتم تفسيره على النحو المتوقّع.
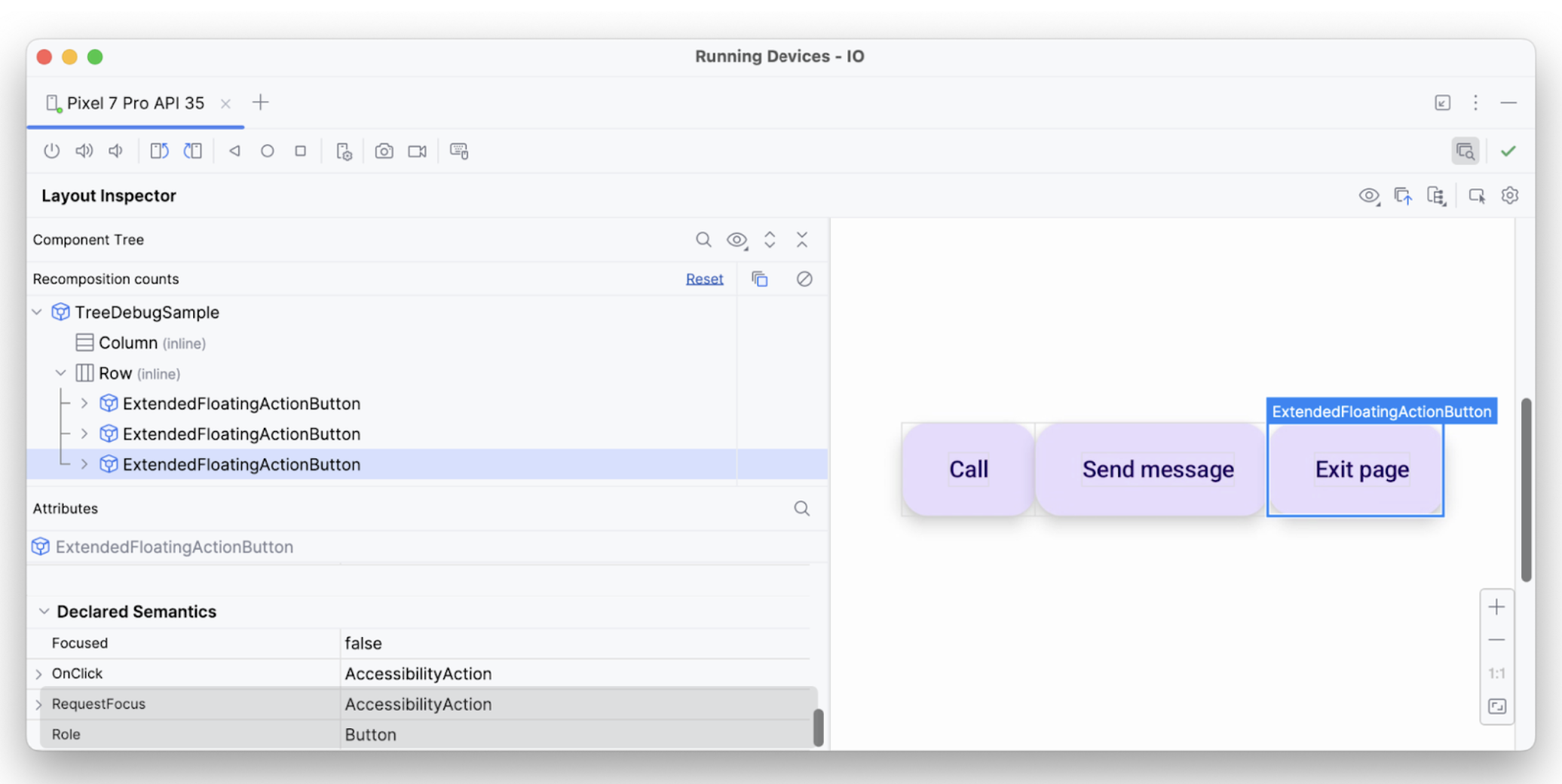
بهذه الطريقة، يمكنك استخدام أدوات تصحيح الأخطاء للتحقيق من سبب عدم تنفيذ خدمات تسهيل الاستخدام لإعلانات أو اختيارات معيّنة.
أفلام مُقترَحة لك
- ملاحظة: يتم عرض نص الرابط عندما تكون لغة JavaScript غير مفعّلة.
- تسهيل الاستخدام في ميزة "الإنشاء"
- [Material Design 2 في ميزة "الإنشاء"][19]
- اختبار تنسيق ميزة "الإنشاء"
