בדיקה
יש כמה כלים שיעזרו לכם לבדוק במהירות את התוכן מבחינת נגישות:
- Android Accessibility Suite: כולל את תפריט הנגישות, 'הקראה', 'גישה באמצעות מתג' ו-TalkBack, שמספקים תובנות לגבי האופן שבו הסמנטיקה של האפליקציה פועלת למשתמשים בטכנולוגיות האלה. מומלץ מאוד לבדוק את האתר באמצעות טכנולוגיות העזרה של Android, כי זו הדרך הטובה ביותר להבין איך המשתמשים שלכם עם צרכים של נגישות יחוו את האתר.
- Layout Inspector: מאפשר לבדוק ולתקן באגים בסמינטיקה של כל רכיב, ולזהות מידע חסר או שגוי.
- אפליקציית Accessibility Scanner: סורקת את המסך ומציגה הצעות לשיפור הנגישות שלו על ידי זיהוי של כמה מלכודות נפוצות.
ניפוי באגים
בין Compose, מערכת הסמנטיקה ושירותי הנגישות של Android, יכול להיות שתתקלו בהתנהגויות לא צפויות שקשורות לנגישות שקשה לעקוב אחריהן. מאפיינים סמנטיים יכולים לעזור לכם להבין למה הרכיבים מתנהגים בצורה מסוימת.
אתם יכולים לנפות באגים בבעיות שקשורות להתנהגות הנגישות באמצעות כלי לבדיקת הפריסה ב-Android Studio, באמצעות TreeDebug בהגדרות למפתחים של TalkBack או באמצעות printToLog של ComposeTestRule. כל הכלים האלה יכולים לספק מידע על צמתים (ועל המאפיינים שלהם) שנחשפים לשירותי נגישות על ידי Compose.
בדוגמה הבאה נעשה שימוש בכלי לבדיקת הפריסה כדי לנפות באגים במסך עם שלושה רכיבים, כאשר כששירותי הנגישות מופעלים, הרכיב הראשון לא נבחר, ולרכיב השני אין משוב על פעולה שמשויכת אליו. אפשר לבדוק את המאפיינים הסמנטיים כדי למצוא בעיות פוטנציאליות.
עץ הרכיבים בכלי לבדיקת הפריסה מכיל מידע על גבולות, פרמטרים ומידע סמנטי אחר שמשויך לאלמנט. בעץ, כל שלושת הרכיבים מזוהים:
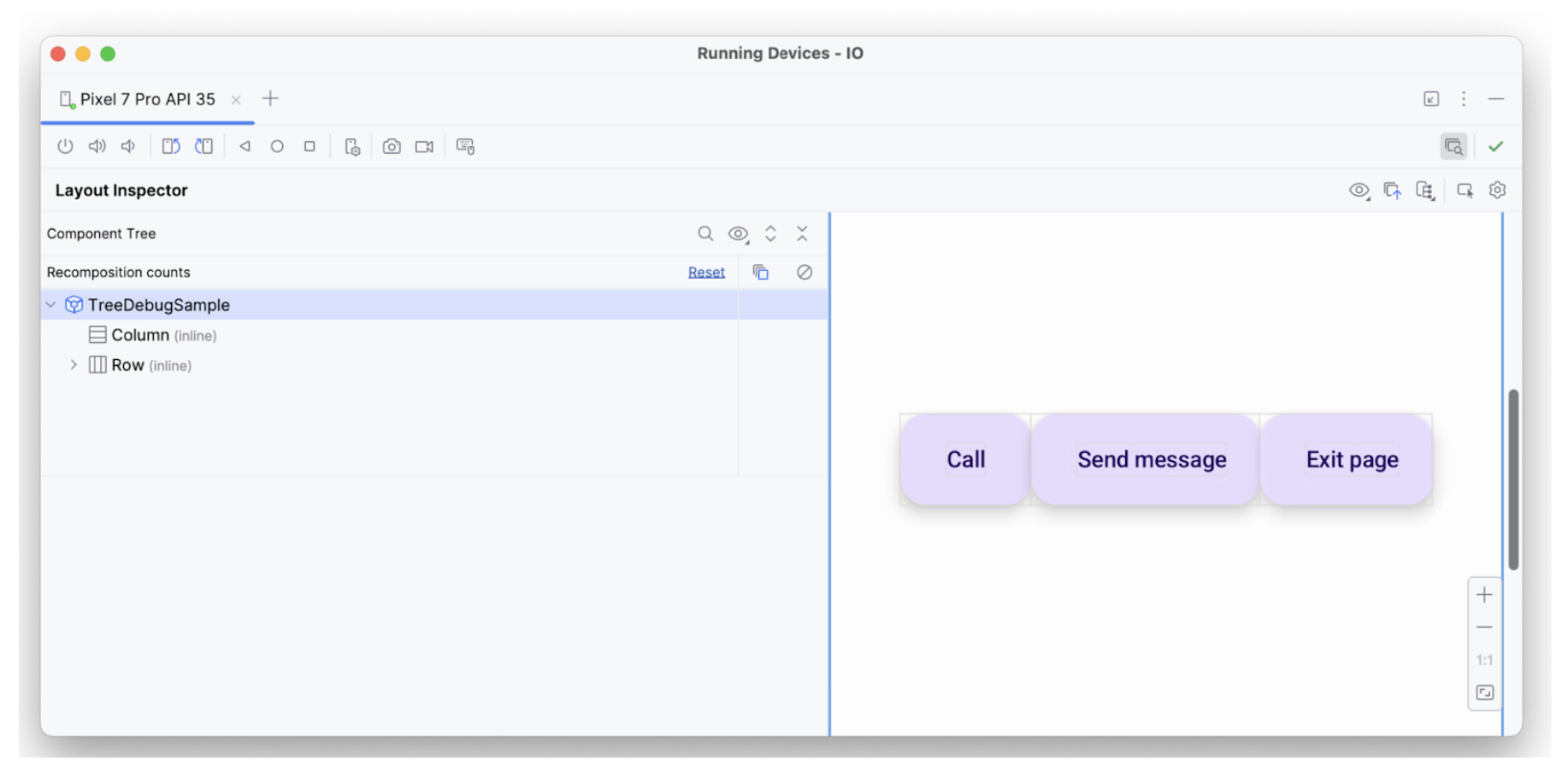
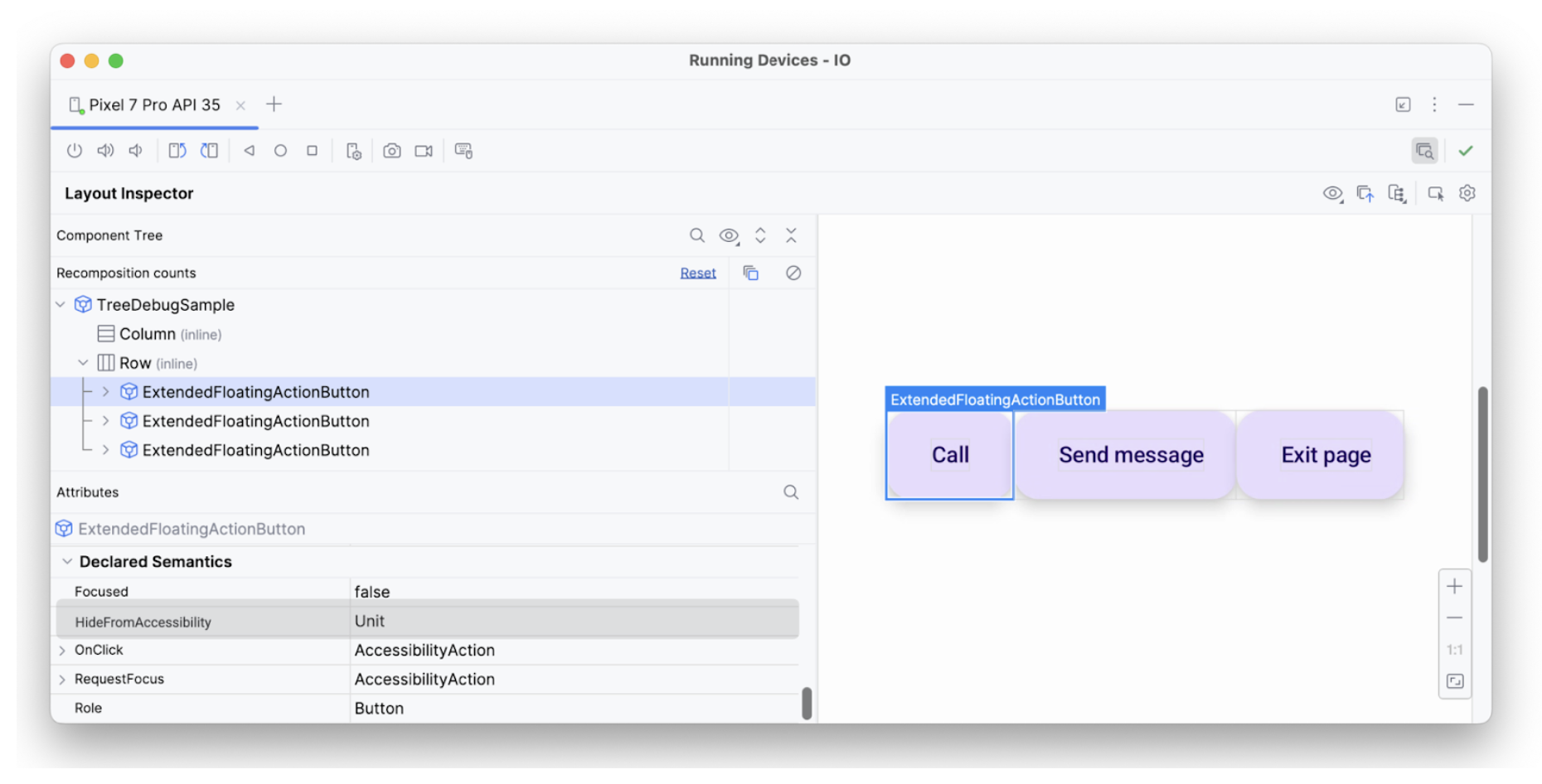
המאפיין hideFromAccessibility מיושם על הרכיב הראשון. המשמעות היא שהאלמנט עשוי להיות מסומן כמוסתר במקום כלשהו בעץ הסמנטיקה, או שהוא מוסתר על ידי שכבת-על דקורטיבית כלשהי.
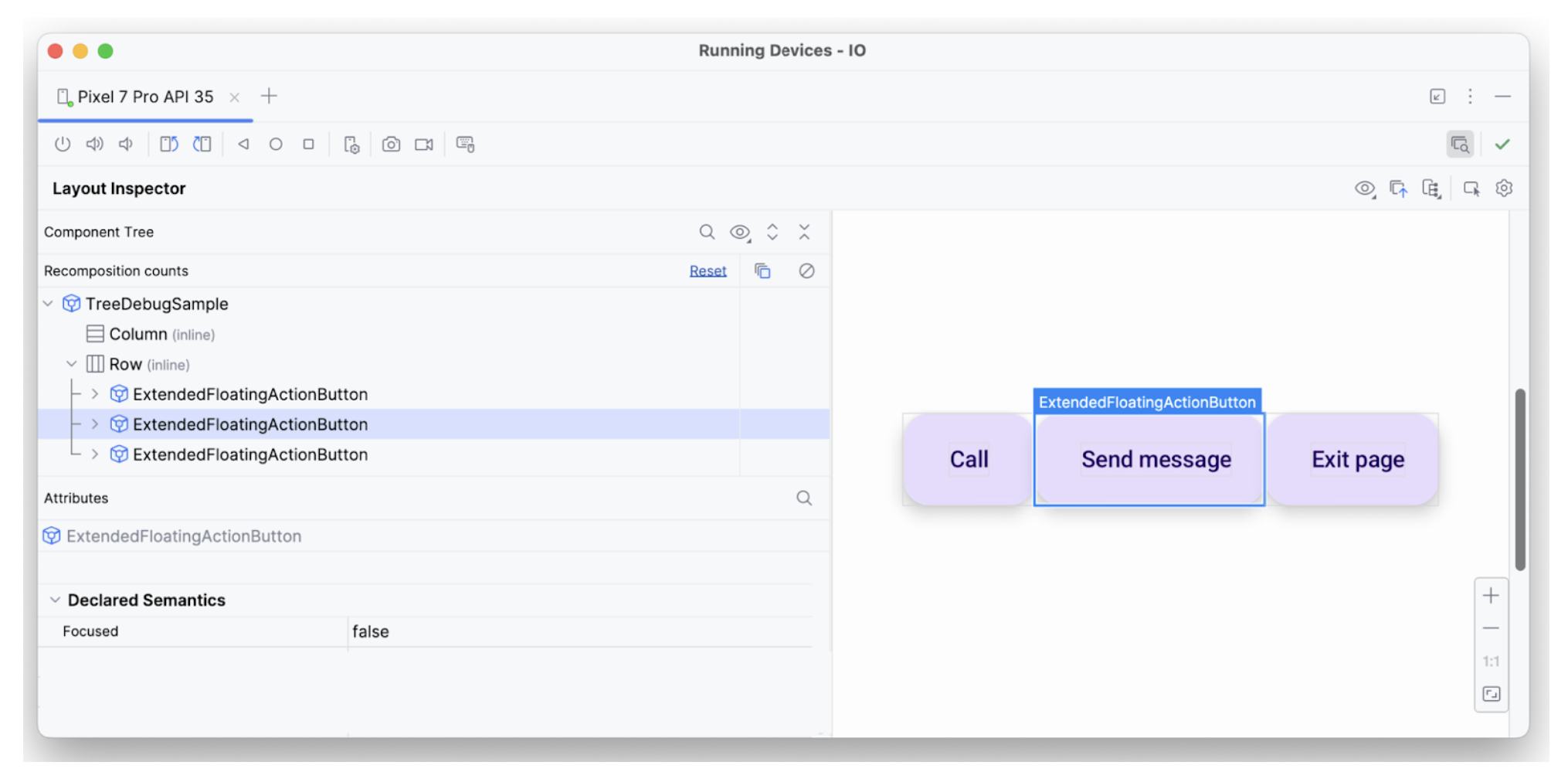
hideFromAccessibility.לרכיב השני יש מאפיין focus, אבל אין לו onClick כמו לרכיב הקודם. לכן, יכול להיות שחסרה פונקציית שינוי מסוג clickable במקום כלשהו, ולכן שירות נגישות כמו TalkBack לא מודיע למשתמש על אות פעולה כלשהו:
focused.לרכיב הטקסט השלישי יש את כל המאפיינים הנדרשים – אפשר להתמקד בו, יש לו onClick ונוספו לו סמנטיקה נוספת – ולכן הוא מפורש כצפוי.
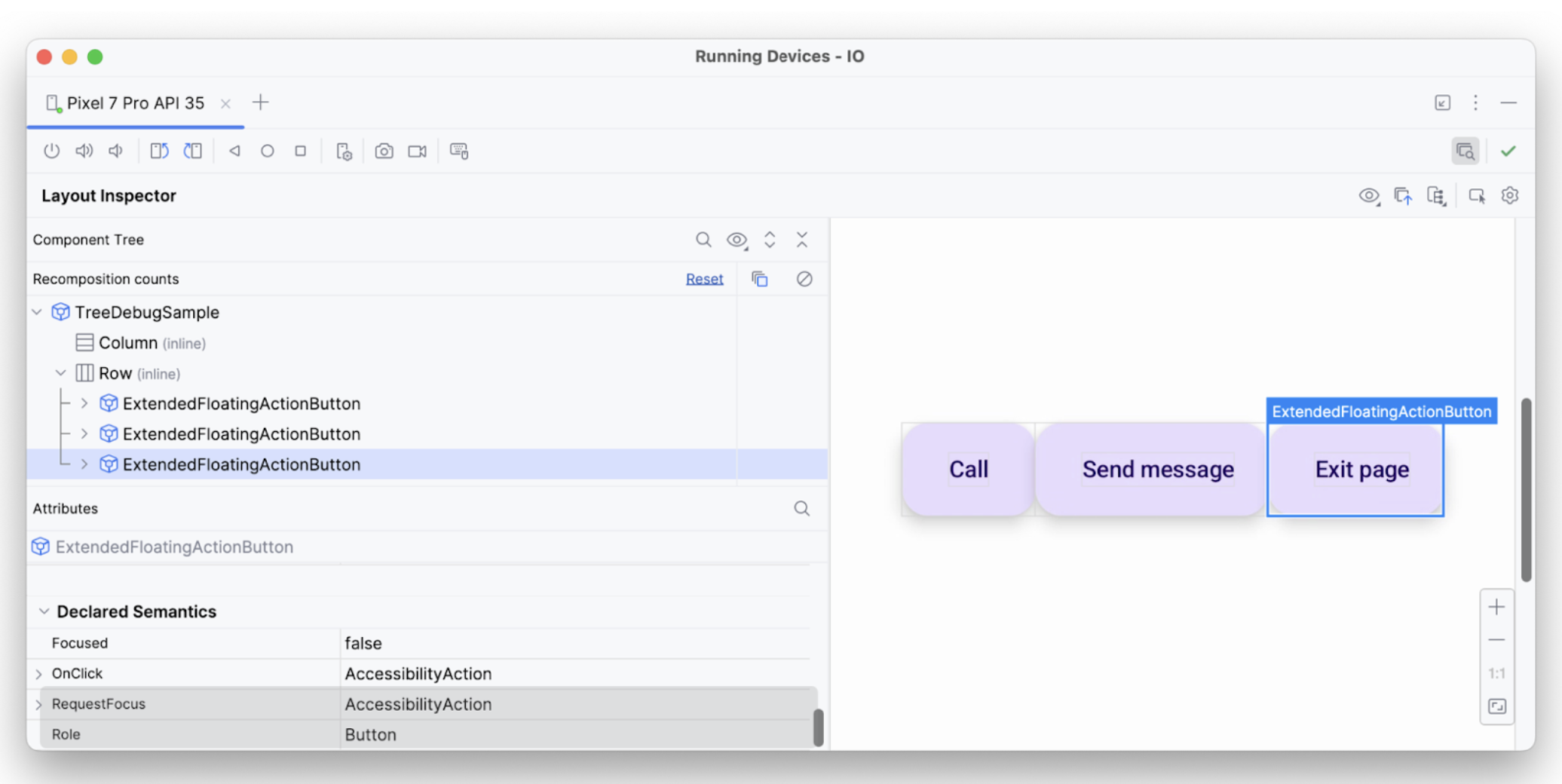
כך תוכלו להשתמש בכלי לניפוי באגים כדי לבדוק למה שירותי הנגישות לא מבצעים הודעות או בחירות מסוימות.
מומלץ עבורך
- הערה: טקסט הקישור מוצג כש-JavaScript מושבת
- נגישות ב-Compose
- [Material Design 2 ב-Compose][19]
- בדיקת הפריסה של 'כתיבה'
