บทเรียนนี้แสดงวิธีจัดระดับย่อยของคลาสนามธรรม CompatTab และ TabHelper และใช้ API ใหม่ แอปพลิเคชันของคุณสามารถใช้การติดตั้งนี้บนอุปกรณ์ที่ใช้เวอร์ชันแพลตฟอร์มที่รองรับการใช้งาน
ใช้งานแท็บโดยใช้ API ใหม่
คลาสคอนกรีตสำหรับ CompatTab และ TabHelper ที่ใช้ API รุ่นใหม่คือการนำพร็อกซีมาใช้ เนื่องจากคลาสนามธรรมที่กำหนดไว้ในบทเรียนก่อนหน้าจะมิเรอร์ API ใหม่ (โครงสร้างคลาส ลายเซ็นเมธอด ฯลฯ) คลาสที่เป็นรูปธรรมที่ใช้ API รุ่นใหม่เหล่านี้เพียงแค่เรียกใช้เมธอดพร็อกซีและผลลัพธ์
คุณสามารถใช้ API รุ่นใหม่กว่าในชั้นเรียนที่เป็นรูปธรรมเหล่านี้ได้โดยตรงและไม่เกิดข้อขัดข้องในอุปกรณ์รุ่นเก่า เนื่องจากการโหลดคลาสแบบ Lazy Loading ระบบจะโหลดและเริ่มต้นชั้นเรียนเมื่อเข้าถึงครั้งแรก ซึ่งเป็นการยืนยันคลาสหรือการเข้าถึงช่องหรือเมธอดแบบคงที่เป็นครั้งแรก ดังนั้น ตราบใดที่คุณไม่ได้สร้างการติดตั้งใช้งานเฉพาะสำหรับ Honeycomb ในอุปกรณ์ Pre-Honeycomb อุปกรณ์ Dalvik VM ก็จะไม่ส่งข้อยกเว้น VerifyError
รูปแบบการตั้งชื่อที่ดีสำหรับการติดตั้งใช้งานนี้คือการเพิ่มระดับ API หรือชื่อโค้ดเวอร์ชันของแพลตฟอร์มที่สอดคล้องกับ API ที่จำเป็นสำหรับคลาสที่เป็นรูปธรรม เช่น คลาส CompatTabHoneycomb และ TabHelperHoneycomb สามารถติดตั้งใช้งานแท็บเนทีฟได้ เนื่องจากคลาสเหล่านี้ต้องใช้ API ที่มีอยู่ใน Android 3.0 (API ระดับ 11) ขึ้นไป
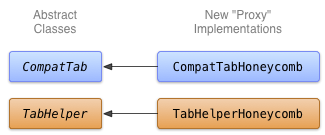
รูปที่ 1 แผนภาพชั้นเรียนสำหรับการใช้งานแท็บ Honeycomb
ใช้ CompatTabHoneycomb
CompatTabHoneycomb คือการใช้งานคลาสนามธรรม CompatTab ที่ TabHelperHoneycomb ใช้เพื่ออ้างอิงแต่ละแท็บ CompatTabHoneycomb เพียงพร็อกซีการเรียกเมธอดทั้งหมดไปยังออบเจ็กต์ ActionBar.Tab ที่มีอยู่
เริ่มใช้ CompatTabHoneycomb โดยใช้ ActionBar.Tab API ใหม่:
Kotlin
class CompatTabHoneycomb internal constructor(val activity: Activity, tag: String) : CompatTab(tag) { ... // The native tab object that this CompatTab acts as a proxy for. private var mTab: ActionBar.Tab = // Proxy to new ActionBar.newTab API activity.actionBar.newTab() override fun setText(@StringRes textId: Int): CompatTab { // Proxy to new ActionBar.Tab.setText API mTab.setText(textId) return this } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
Java
public class CompatTabHoneycomb extends CompatTab { // The native tab object that this CompatTab acts as a proxy for. ActionBar.Tab mTab; ... protected CompatTabHoneycomb(FragmentActivity activity, String tag) { ... // Proxy to new ActionBar.newTab API mTab = activity.getActionBar().newTab(); } public CompatTab setText(int resId) { // Proxy to new ActionBar.Tab.setText API mTab.setText(resId); return this; } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
ติดตั้งใช้งาน TabHelperHoneycomb
TabHelperHoneycomb คือการใช้งานคลาส Abstract TabHelper ที่เรียกใช้เมธอดพร็อกซีไปยัง ActionBar จริง ซึ่งได้มาจาก Activity ที่มีอยู่
ใช้ TabHelperHoneycomb การเรียกเมธอดพร็อกซีไปยัง ActionBar API:
Kotlin
class TabHelperHoneycomb internal constructor(activity: FragmentActivity) : TabHelper(activity) { private var mActionBar: ActionBar? = null override fun setUp() { mActionBar = mActionBar ?: mActivity.actionBar.apply { navigationMode = ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS } } override fun addTab(tab: CompatTab) { // Tab is a CompatTabHoneycomb instance, so its // native tab object is an ActionBar.Tab. mActionBar?.addTab(tab.getTab() as ActionBar.Tab) } }
Java
public class TabHelperHoneycomb extends TabHelper { ActionBar actionBar; ... protected void setUp() { if (actionBar == null) { actionBar = activity.getActionBar(); actionBar.setNavigationMode( ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS); } } public void addTab(CompatTab tab) { ... // Tab is a CompatTabHoneycomb instance, so its // native tab object is an ActionBar.Tab. actionBar.addTab((ActionBar.Tab) tab.getTab()); } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
