בשיעור הזה תלמדו איך ליצור כיתות משנה של הכיתות המופשטות CompatTab ו-TabHelper ולהשתמש בממשקי API חדשים. האפליקציה יכולה להשתמש בהטמעה הזו במכשירים עם גרסת פלטפורמה שתומכת בהם.
הטמעת כרטיסיות באמצעות ממשקי API חדשים
המחלקות הממשיות של CompatTab ו-TabHelper שמשתמשות בממשקי API חדשים יותר הן הטמעה של שרת proxy. המחלקות המופשטות שהוגדרו בשיעור הקודם משקפים את ממשקי ה-API החדשים (מבנה המחלקה, חתימות השיטה וכו'), ולכן המחלקות הקורנטיות שמשתמשות בממשקי ה-API החדשים האלה פשוט קריאות לשיטות שרת proxy והתוצאות שלהן.
בגלל טעינה מדורגת של כיתות, אפשר להשתמש ישירות בממשקי API חדשים יותר במחלקות הבטון האלו, ולא לקרוס במכשירים קודמים. הכיתות נטענות ומופעלות בגישה הראשונה — להפעיל את הכיתה או לגשת לאחד מהשדות הסטטיים או מהשיטות שלה בפעם הראשונה. לכן, כל עוד לא יוצרים מופע של הטמעות ספציפיות ל-Honeycomb במכשירים לפני Honeycomb, ל-VM של Dalvik לא יוצגו חריגות מסוג VerifyError.
דרך טובה לתת שמות להטמעה הזו היא להוסיף את רמת ה-API או את שם הקוד של גרסת הפלטפורמה שתואמים לממשקי ה-API שנדרשים על ידי המחלקות הבטון. לדוגמה, את ההטמעה של כרטיסיית הנייטיב אפשר לספק במחלקות CompatTabHoneycomb ו-TabHelperHoneycomb, כי הן מסתמכים על ממשקי API שזמינים ב-Android 3.0 (רמת API 11) ואילך.
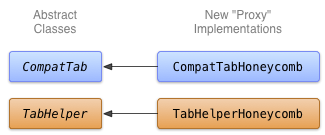
איור 1. תרשים מחלקה להטמעת Honeycomb של כרטיסיות.
הטמעת CompatTabHoneycomb
CompatTabHoneycomb הוא היישום של המחלקה המופשטת CompatTab שבה TabHelperHoneycomb משתמש כדי להפנות לכרטיסיות נפרדות. CompatTabHoneycomb פשוט מעביר את כל קריאות ה-method לאובייקט ActionBar.Tab שמוכל באמצעות שרת proxy.
התחלת ההטמעה של CompatTabHoneycomb באמצעות ממשקי ה-API החדשים של ActionBar.Tab:
Kotlin
class CompatTabHoneycomb internal constructor(val activity: Activity, tag: String) : CompatTab(tag) { ... // The native tab object that this CompatTab acts as a proxy for. private var mTab: ActionBar.Tab = // Proxy to new ActionBar.newTab API activity.actionBar.newTab() override fun setText(@StringRes textId: Int): CompatTab { // Proxy to new ActionBar.Tab.setText API mTab.setText(textId) return this } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
Java
public class CompatTabHoneycomb extends CompatTab { // The native tab object that this CompatTab acts as a proxy for. ActionBar.Tab mTab; ... protected CompatTabHoneycomb(FragmentActivity activity, String tag) { ... // Proxy to new ActionBar.newTab API mTab = activity.getActionBar().newTab(); } public CompatTab setText(int resId) { // Proxy to new ActionBar.Tab.setText API mTab.setText(resId); return this; } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
הטמעת TabHelperHoneycomb
TabHelperHoneycomb הוא היישום של המחלקה המופשטת TabHelper ש-methods מקריאה ל-method ActionBar בפועל, שמתקבלת מה-Activity הכלול בה.
הטמעת TabHelperHoneycomb, קריאות לשיטות שרת proxy ל-API של ActionBar:
Kotlin
class TabHelperHoneycomb internal constructor(activity: FragmentActivity) : TabHelper(activity) { private var mActionBar: ActionBar? = null override fun setUp() { mActionBar = mActionBar ?: mActivity.actionBar.apply { navigationMode = ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS } } override fun addTab(tab: CompatTab) { // Tab is a CompatTabHoneycomb instance, so its // native tab object is an ActionBar.Tab. mActionBar?.addTab(tab.getTab() as ActionBar.Tab) } }
Java
public class TabHelperHoneycomb extends TabHelper { ActionBar actionBar; ... protected void setUp() { if (actionBar == null) { actionBar = activity.getActionBar(); actionBar.setNavigationMode( ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS); } } public void addTab(CompatTab tab) { ... // Tab is a CompatTabHoneycomb instance, so its // native tab object is an ActionBar.Tab. actionBar.addTab((ActionBar.Tab) tab.getTab()); } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
