折りたたみ式デバイスでは、開いた状態の大型ディスプレイと独自の折りたたみ状態により、新しいユーザー エクスペリエンスを実現できます。アプリを折りたたみ対応にするには、Jetpack WindowManager ライブラリを使用します。このライブラリには、折りたたみ式デバイスの折り目やヒンジなどのウィンドウ機能用の API サーフェスが用意されています。アプリを折りたたみ対応にすると、レイアウトを調整して、重要なコンテンツが折り目またはヒンジの領域に配置されることを回避したり、折り目またはヒンジを自然な区切り要素として使用したりすることができます。
デバイスがテーブルトップ形状やブック形状などの構成をサポートしているかどうかを把握することで、さまざまなレイアウトのサポートや特定の機能の提供に関する意思決定を導くことができます。
ウィンドウ情報
Jetpack WindowManager の WindowInfoTracker インターフェースは、ウィンドウ レイアウト情報を公開します。インターフェースの windowLayoutInfo() メソッドは、折りたたみ式デバイスの折りたたみ状態をアプリに通知する WindowLayoutInfo データのストリームを返します。WindowInfoTracker#getOrCreate() メソッドは WindowInfoTracker のインスタンスを作成します。
WindowManager は、Kotlin Flow と Java コールバックを使用した WindowLayoutInfo データの収集をサポートしています。
Kotlin Flow
WindowLayoutInfo データの収集を開始および停止するには、再実行可能なライフサイクル対応コルーチンを使用します。このコルーチンでは、ライフサイクルが STARTED 以降のときに repeatOnLifecycle コードブロックが実行され、ライフサイクルが STOPPED のときに停止されます。ライフサイクルが再び STARTED になると、自動的にコードブロックの実行が再開されます。次の例では、コードブロックが WindowLayoutInfo データを収集して使用しています。
class DisplayFeaturesActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityDisplayFeaturesBinding
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
binding = ActivityDisplayFeaturesBinding.inflate(layoutInflater)
setContentView(binding.root)
lifecycleScope.launch(Dispatchers.Main) {
lifecycle.repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(this@DisplayFeaturesActivity)
.windowLayoutInfo(this@DisplayFeaturesActivity)
.collect { newLayoutInfo ->
// Use newLayoutInfo to update the layout.
}
}
}
}
}
Java コールバック
androidx.window:window-java 依存関係に含まれるコールバック互換性レイヤを使用すると、Kotlin Flow を使用せずに WindowLayoutInfo の更新を収集できます。このアーティファクトには WindowInfoTrackerCallbackAdapter クラスが含まれています。このクラスは WindowInfoTracker を適応させて、WindowLayoutInfo の更新を受け取るコールバックの登録(および登録解除)をサポートします。次に例を示します。
public class SplitLayoutActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private WindowInfoTrackerCallbackAdapter windowInfoTracker;
private ActivitySplitLayoutBinding binding;
private final LayoutStateChangeCallback layoutStateChangeCallback =
new LayoutStateChangeCallback();
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
binding = ActivitySplitLayoutBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());
setContentView(binding.getRoot());
windowInfoTracker =
new WindowInfoTrackerCallbackAdapter(WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(this));
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
windowInfoTracker.addWindowLayoutInfoListener(
this, Runnable::run, layoutStateChangeCallback);
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
windowInfoTracker
.removeWindowLayoutInfoListener(layoutStateChangeCallback);
}
class LayoutStateChangeCallback implements Consumer<WindowLayoutInfo> {
@Override
public void accept(WindowLayoutInfo newLayoutInfo) {
SplitLayoutActivity.this.runOnUiThread( () -> {
// Use newLayoutInfo to update the layout.
});
}
}
}
RxJava のサポート
すでに RxJava(バージョン 2 または 3)を使用している場合は、Kotlin Flow を使用せずに Observable または Flowable を使用して WindowLayoutInfo の更新を収集できるアーティファクトを利用できます。
androidx.window:window-rxjava2 と androidx.window:window-rxjava3 の依存関係によって提供される互換性レイヤには、WindowInfoTracker#windowLayoutInfoFlowable() メソッドと WindowInfoTracker#windowLayoutInfoObservable() メソッドが含まれています。これらのメソッドにより、アプリは WindowLayoutInfo アップデートを受け取ることができます。次に例を示します。
class RxActivity: AppCompatActivity {
private lateinit var binding: ActivityRxBinding
private var disposable: Disposable? = null
private lateinit var observable: Observable<WindowLayoutInfo>
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
binding = ActivitySplitLayoutBinding.inflate(getLayoutInflater());
setContentView(binding.getRoot());
// Create a new observable.
observable = WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(this@RxActivity)
.windowLayoutInfoObservable(this@RxActivity)
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
// Subscribe to receive WindowLayoutInfo updates.
disposable?.dispose()
disposable = observable
.observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread())
.subscribe { newLayoutInfo ->
// Use newLayoutInfo to update the layout.
}
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
// Dispose of the WindowLayoutInfo observable.
disposable?.dispose()
}
}
折りたたみ式ディスプレイの機能
Jetpack WindowManager の WindowLayoutInfo クラスは、ディスプレイ ウィンドウの機能を DisplayFeature 要素のリストとして利用できるようにします。
FoldingFeature は DisplayFeature の一種であり、次のような折りたたみ式ディスプレイに関する情報を提供します。
state: デバイスの折りたたみ状態(FLATまたはHALF_OPENED)orientation: 折り目またはヒンジの向き(HORIZONTALまたはVERTICAL)isSeparating: 折り目またはヒンジが 2 つの論理ディスプレイ領域を生成するかどうか(true または false)
HALF_OPENED 状態の折りたたみ式デバイスは、画面が 2 つのディスプレイ領域に分割されているため、常に isSeparating を true として報告します。また、デュアル スクリーン デバイスでは、アプリが両方の画面にまたがっている場合、isSeparating は常に true になります。
FoldingFeature の bounds プロパティ(DisplayFeature から継承される)は、折り目やヒンジなどの折りたたみ機能の境界四角形を表します。この境界を使用して、折りたたみ機能からの相対位置に画面上の要素を配置できます。
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
...
lifecycleScope.launch(Dispatchers.Main) {
lifecycle.repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
// Safely collects from WindowInfoTracker when the lifecycle is
// STARTED and stops collection when the lifecycle is STOPPED.
WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(this@MainActivity)
.windowLayoutInfo(this@MainActivity)
.collect { layoutInfo ->
// New posture information.
val foldingFeature = layoutInfo.displayFeatures
.filterIsInstance<FoldingFeature>()
.firstOrNull()
// Use information from the foldingFeature object.
}
}
}
}
Java
private WindowInfoTrackerCallbackAdapter windowInfoTracker;
private final LayoutStateChangeCallback layoutStateChangeCallback =
new LayoutStateChangeCallback();
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
...
windowInfoTracker =
new WindowInfoTrackerCallbackAdapter(WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(this));
}
@Override
protected void onStart() {
super.onStart();
windowInfoTracker.addWindowLayoutInfoListener(
this, Runnable::run, layoutStateChangeCallback);
}
@Override
protected void onStop() {
super.onStop();
windowInfoTracker.removeWindowLayoutInfoListener(layoutStateChangeCallback);
}
class LayoutStateChangeCallback implements Consumer<WindowLayoutInfo> {
@Override
public void accept(WindowLayoutInfo newLayoutInfo) {
// Use newLayoutInfo to update the Layout.
List<DisplayFeature> displayFeatures = newLayoutInfo.getDisplayFeatures();
for (DisplayFeature feature : displayFeatures) {
if (feature instanceof FoldingFeature) {
// Use information from the feature object.
}
}
}
}
テーブルトップの姿勢
FoldingFeature オブジェクトに含まれる情報を使用して、アプリはテーブルトップなどの形状に対応することができます。テーブルトップとは、スマートフォンが平面に置かれ、ヒンジが水平位置で、折りたたみ式画面が半分開いた状態です。
テーブルトップ モードでは、スマートフォンを手に持たずに簡単に操作できます。テーブルトップ モードは、メディアの再生、写真の撮影、ビデオ通話に最適です。
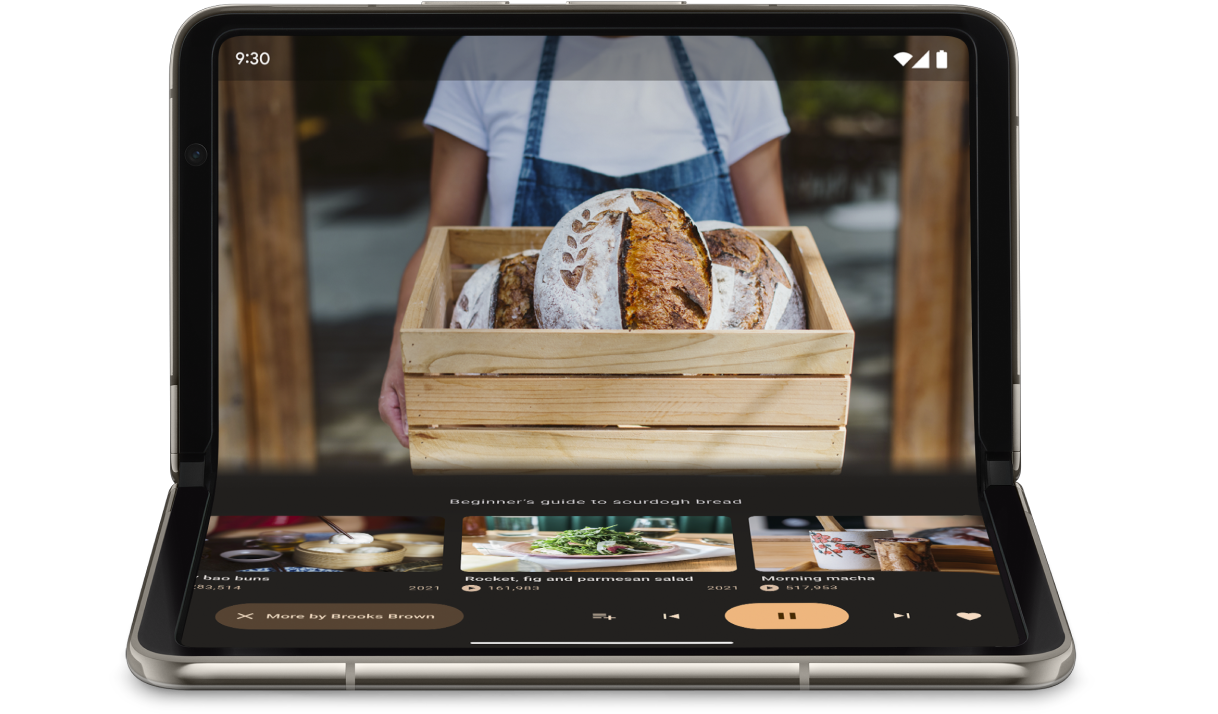
FoldingFeature.State と FoldingFeature.Orientation を使用して、デバイスがテーブルトップの形状になっているかどうかを判断します。
Kotlin
fun isTableTopPosture(foldFeature : FoldingFeature?) : Boolean {
contract { returns(true) implies (foldFeature != null) }
return foldFeature?.state == FoldingFeature.State.HALF_OPENED &&
foldFeature.orientation == FoldingFeature.Orientation.HORIZONTAL
}
Java
boolean isTableTopPosture(FoldingFeature foldFeature) {
return (foldFeature != null) &&
(foldFeature.getState() == FoldingFeature.State.HALF_OPENED) &&
(foldFeature.getOrientation() == FoldingFeature.Orientation.HORIZONTAL);
}
デバイスがテーブルトップの形状になっていることを確認したら、それに応じてアプリのレイアウトを更新します。メディアアプリの場合は、通常、ハンズフリーで視聴できるように、スクロールせずに見える範囲に再生を配置し、そのすぐ下にコントロールと補足コンテンツを配置します。
Android 15(API レベル 35)以降では、同期 API を呼び出して、デバイスの現在の状態に関係なく、デバイスがテーブルトップの向きをサポートしているかどうかを検出できます。
この API は、デバイスでサポートされているポスチャーのリストを提供します。リストにテーブルトップの向きが含まれている場合は、その向きをサポートするようにアプリ レイアウトを分割し、テーブルトップとフルスクリーンのレイアウトについてアプリ UI の A/B テストを実行できます。
Kotlin
if (WindowSdkExtensions.getInstance().extensionsVersion >= 6) {
val postures = WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(context).supportedPostures
if (postures.contains(TABLE_TOP)) {
// Device supports tabletop posture.
}
}
Java
if (WindowSdkExtensions.getInstance().getExtensionVersion() >= 6) {
List<SupportedPosture> postures = WindowInfoTracker.getOrCreate(context).getSupportedPostures();
if (postures.contains(SupportedPosture.TABLETOP)) {
// Device supports tabletop posture.
}
}
例
MediaPlayerActivityアプリ: Media3 Exoplayer と WindowManager を使用して折りたたみ対応の動画プレーヤーを作成する方法をご覧ください。Jetpack WindowManager を使用して折りたたみ式デバイスでカメラアプリを最適化する Codelab: 写真アプリにテーブルトップ形状を実装する方法を学びます。画面の上半分(スクロールせずに見える範囲)にビューファインダーを表示し、下半分(スクロールしなければ見えない範囲)にコントロールを表示します。
ブック形状
折りたたみ式独自の機能にはもう一つのブック形状があります。これは、デバイスが半分開き、ヒンジが垂直です。ブック形状は電子書籍を読むのに最適です。大きい折りたたみ式画面を製本された本のように開いて 2 ページ レイアウトにするブックモードでは、本物の本を読むようなエクスペリエンスを提供できます。
また、写真撮影に使用すれば、ハンズフリーで写真を撮る際に異なるアスペクト比でキャプチャすることもできます。
テーブルトップ形状と同じ手法でブック形状を実装します。唯一の違いは、折りたたみ機能の向きが水平ではなく垂直であることをコードで確認する必要がある点です。
Kotlin
fun isBookPosture(foldFeature : FoldingFeature?) : Boolean {
contract { returns(true) implies (foldFeature != null) }
return foldFeature?.state == FoldingFeature.State.HALF_OPENED &&
foldFeature.orientation == FoldingFeature.Orientation.VERTICAL
}
Java
boolean isBookPosture(FoldingFeature foldFeature) {
return (foldFeature != null) &&
(foldFeature.getState() == FoldingFeature.State.HALF_OPENED) &&
(foldFeature.getOrientation() == FoldingFeature.Orientation.VERTICAL);
}
ウィンドウ サイズの変更
アプリのディスプレイ領域は、デバイス設定の変更に伴って変化する可能性があります。これには、デバイスが折りたたまれたとき、広げられたとき、回転されたとき、マルチウィンドウ モードでウィンドウのサイズが変更されたときなどがあります。
Jetpack WindowManager の WindowMetricsCalculator クラスを使用すると、現在のウィンドウ指標と最大ウィンドウ指標を取得できます。API レベル 30 で導入されたプラットフォームの WindowMetrics と同様に、WindowManager の WindowMetrics はウィンドウ境界を提供しますが、API には API レベル 14 までとの下位互換性があります。
ウィンドウ サイズクラスを使用するをご覧ください。
参考情報
サンプル
- Jetpack WindowManager: Jetpack WindowManager ライブラリの使用方法の例
- Jetcaster : Compose によるテーブルトップ形状の実装
Codelab
- Jetpack WindowManager による折りたたみ式デバイスとデュアル スクリーン デバイスのサポート
- Jetpack WindowManager を使用して折りたたみ式デバイスのカメラアプリを最適化する

