رابط کاربری و ناوبری پاسخگو
برای ارائه بهترین تجربه ناوبری ممکن به کاربران خود، باید یک رابط کاربری ناوبری ارائه دهید که متناسب با عرض، ارتفاع و کمترین عرض دستگاه کاربر باشد. ممکن است بخواهید از یک نوار برنامه پایین ، یک کشوی پیمایش همیشه حاضر یا جمع شونده، یک ریل یا شاید چیزی کاملاً جدید بر اساس فضای صفحه موجود و سبک منحصر به فرد برنامه خود استفاده کنید.
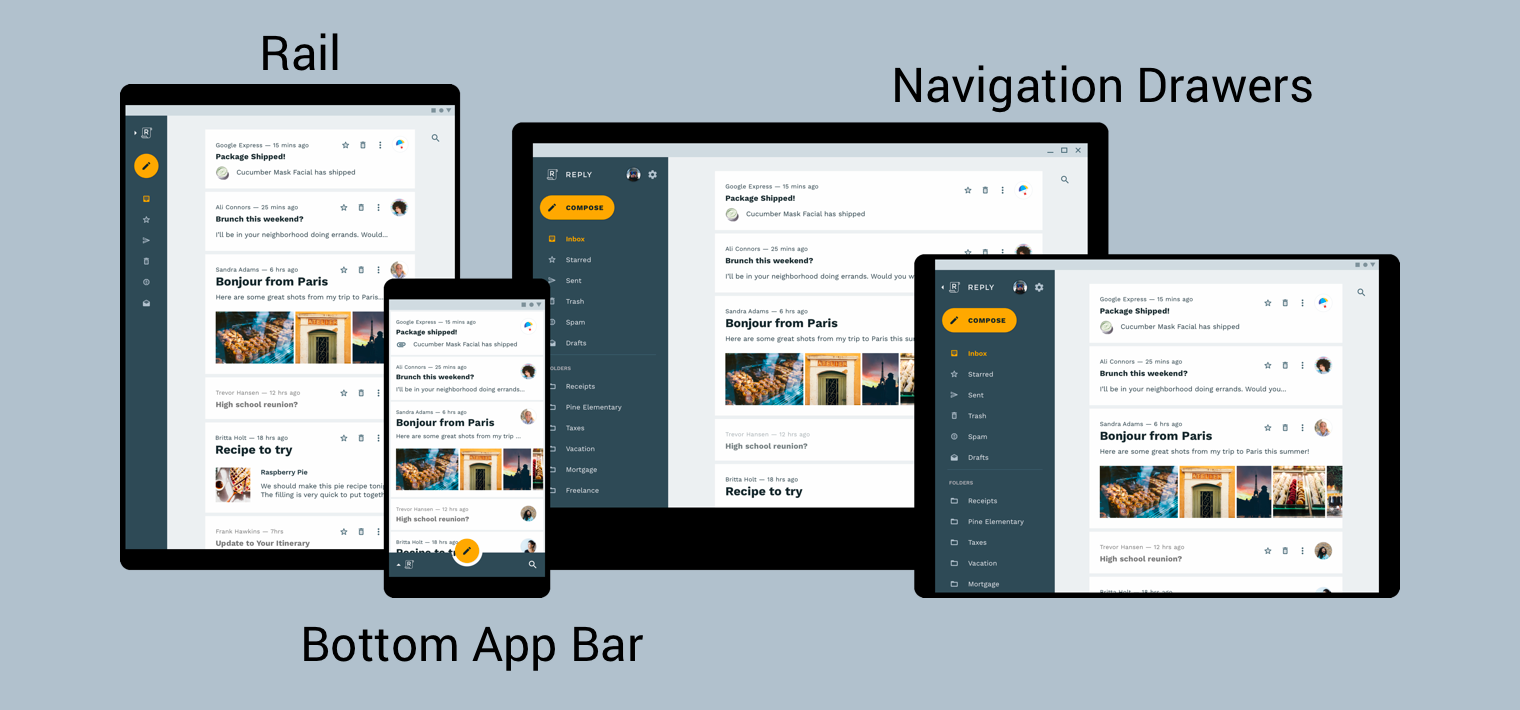
راهنمای طراحی متریال برای معماری محصول، زمینه و ملاحظات بیشتری را برای ایجاد یک رابط کاربری پاسخگو ارائه میکند - یعنی رابط کاربری که به صورت پویا با تغییرات محیطی سازگار است. چند نمونه از تغییرات محیطی شامل تنظیمات عرض، ارتفاع، جهت و ترجیح زبان کاربر است. این ویژگی های محیطی در مجموع به عنوان پیکربندی دستگاه نامیده می شود.
هنگامی که یک یا چند مورد از این ویژگی ها در زمان اجرا تغییر می کند، سیستم عامل Android با تخریب و سپس ایجاد مجدد فعالیت ها و قطعات برنامه شما پاسخ می دهد. بنابراین، بهترین کاری که میتوانید برای پشتیبانی از یک رابط کاربری واکنشگرا در Android انجام دهید این است که اطمینان حاصل کنید که در صورت لزوم از واجد شرایط پیکربندی منبع استفاده میکنید و از استفاده از اندازههای طرحبندی سختکد شده خودداری میکنید .
پیاده سازی ناوبری جهانی در یک رابط کاربری پاسخگو
اجرای ناوبری سراسری به عنوان بخشی از یک رابط کاربری پاسخگو با فعالیتی که گراف پیمایش شما را میزبانی می کند شروع می شود. برای مثال عملی، نوار کد ناوبری را بررسی کنید. همانطور که در شکل 2 نشان داده شده است، از یک NavigationView برای نمایش منوی پیمایش استفاده می کند. وقتی روی دستگاهی اجرا می شود که با عرض حداقل 960dp رندر می شود، این NavigationView همیشه روی صفحه است.
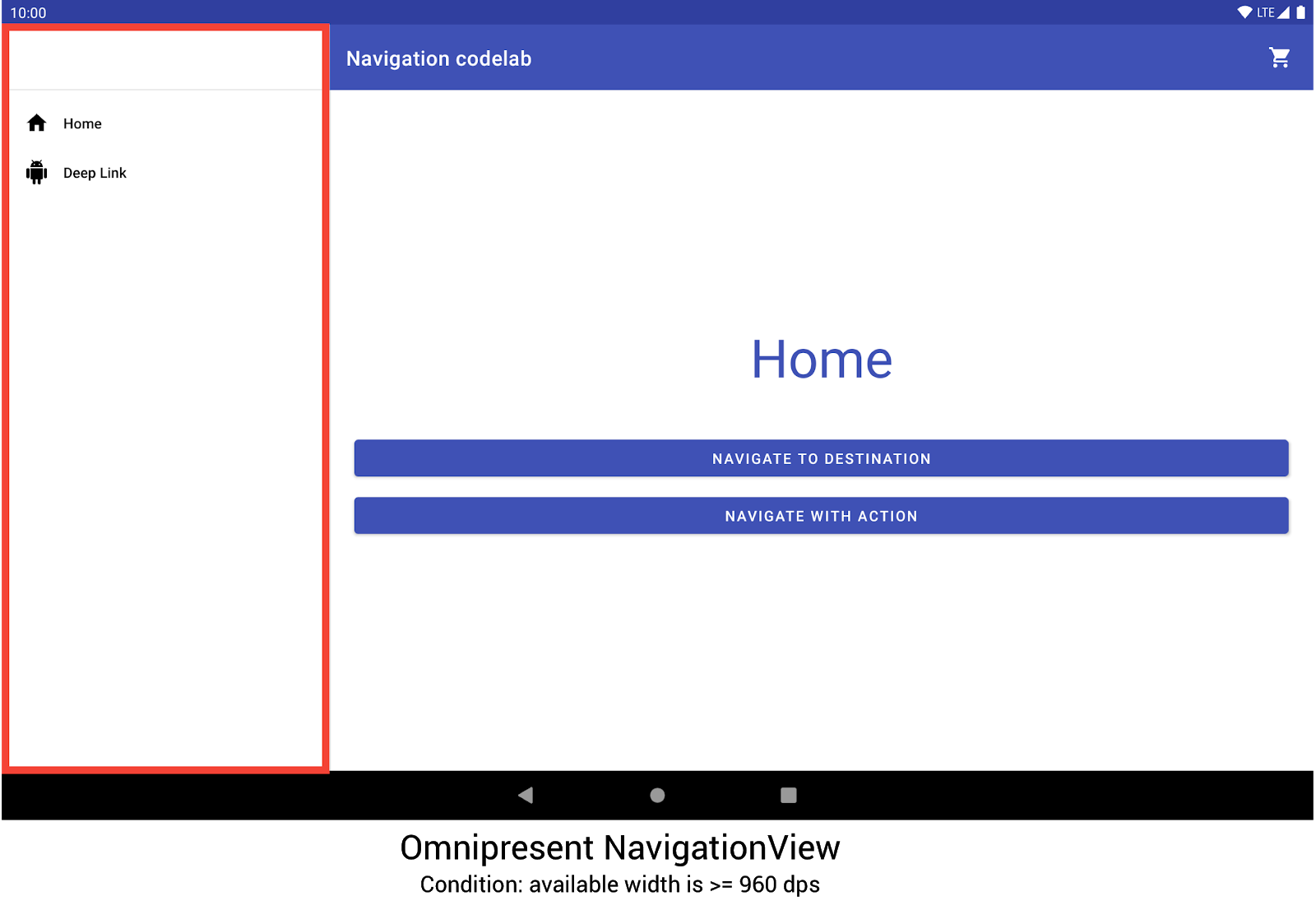
NavigationView برای نمایش منوی پیمایش استفاده می کند. اندازهها و جهتگیریهای دیگر دستگاه به صورت پویا بین DrawerLayout یا BottomNavigationView در صورت نیاز جابهجا میشوند.
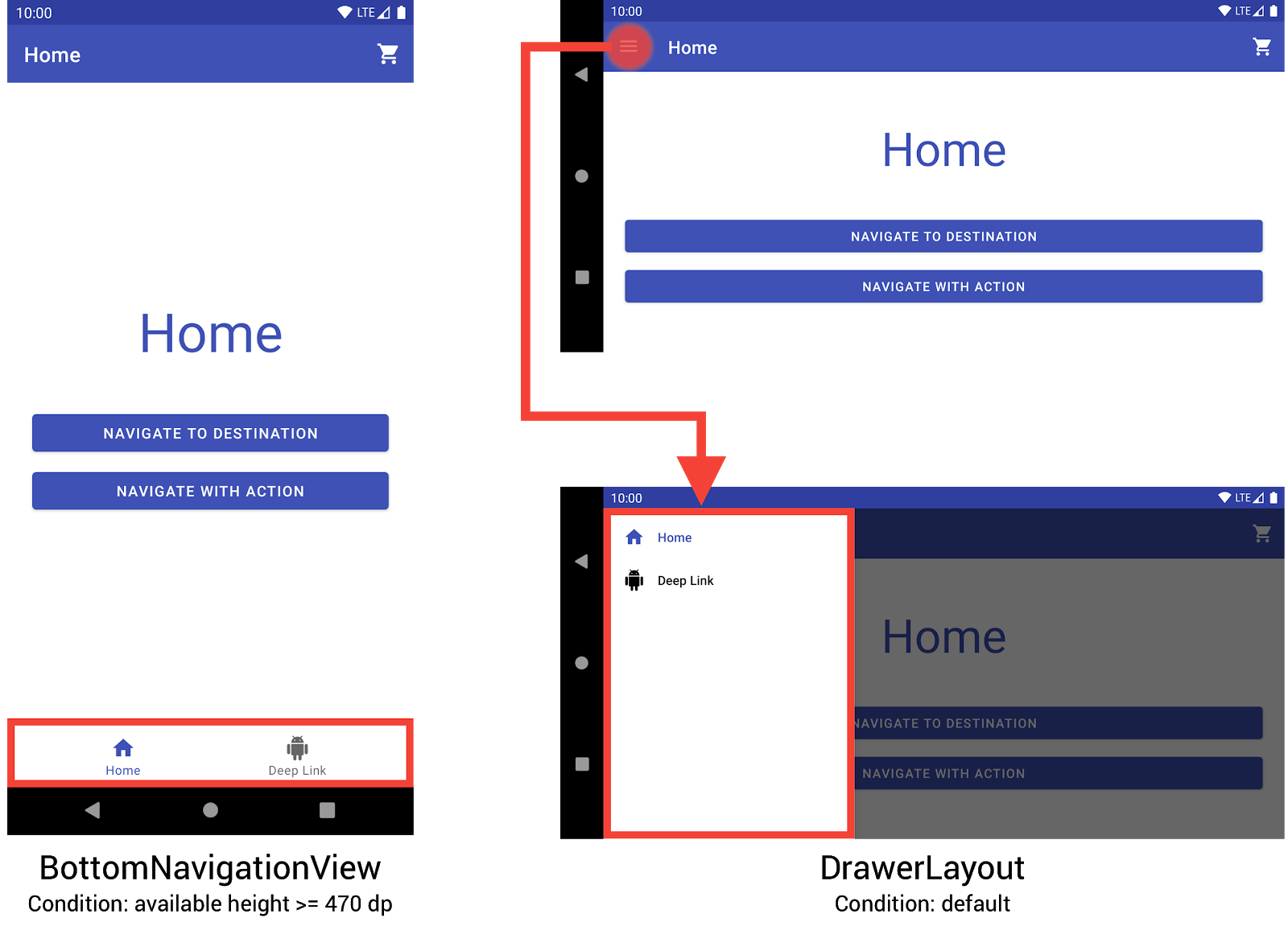
BottomNavigationView و DrawerLayout برای نمایش منوی پیمایش در دستگاه های کوچکتر استفاده می کند.شما می توانید این رفتار را با ایجاد سه طرح بندی مختلف، که در آن هر طرح بندی عناصر ناوبری مورد نظر و سلسله مراتب مشاهده را بر اساس پیکربندی دستگاه فعلی تعریف می کند، پیاده سازی کنید.
پیکربندی که هر طرح بندی برای آن اعمال می شود توسط ساختار دایرکتوری که فایل طرح بندی در آن قرار می گیرد تعیین می شود. به عنوان مثال، فایل طرح بندی NavigationView در پوشه res/layout-w960dp یافت می شود.
<!-- res/layout-w960dp/navigation_activity.xml -->
<RelativeLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.android.codelabs.navigation.MainActivity">
<com.google.android.material.navigation.NavigationView
android:id="@+id/nav_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_alignParentStart="true"
app:elevation="0dp"
app:headerLayout="@layout/nav_view_header"
app:menu="@menu/nav_drawer_menu" />
<View
android:layout_width="1dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_toEndOf="@id/nav_view"
android:background="?android:attr/listDivider" />
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_toEndOf="@id/nav_view"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
android:theme="@style/ThemeOverlay.MaterialComponents.Dark.ActionBar" />
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/my_nav_host_fragment"
android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_below="@id/toolbar"
android:layout_toEndOf="@id/nav_view"
app:defaultNavHost="true"
app:navGraph="@navigation/mobile_navigation" />
</RelativeLayout>
نمای ناوبری پایین در فهرست res/layout-h470dp یافت می شود:
<!-- res/layout-h470dp/navigation_activity.xml -->
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context="com.example.android.codelabs.navigation.MainActivity">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
android:theme="@style/ThemeOverlay.MaterialComponents.Dark.ActionBar" />
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/my_nav_host_fragment"
android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
app:defaultNavHost="true"
app:navGraph="@navigation/mobile_navigation" />
<com.google.android.material.bottomnavigation.BottomNavigationView
android:id="@+id/bottom_nav_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:menu="@menu/bottom_nav_menu" />
</LinearLayout>
طرح کشو در دایرکتوری res/layout یافت می شود. از این دایرکتوری برای طرحبندیهای پیشفرض بدون واجد شرایط پیکربندی استفاده کنید:
<!-- res/layout/navigation_activity.xml -->
<androidx.drawerlayout.widget.DrawerLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/drawer_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.android.codelabs.navigation.MainActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<androidx.appcompat.widget.Toolbar
android:id="@+id/toolbar"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@color/colorPrimary"
android:theme="@style/ThemeOverlay.MaterialComponents.Dark.ActionBar" />
<androidx.fragment.app.FragmentContainerView
android:id="@+id/my_nav_host_fragment"
android:name="androidx.navigation.fragment.NavHostFragment"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
app:defaultNavHost="true"
app:navGraph="@navigation/mobile_navigation" />
</LinearLayout>
<com.google.android.material.navigation.NavigationView
android:id="@+id/nav_view"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="start"
app:menu="@menu/nav_drawer_menu" />
</androidx.drawerlayout.widget.DrawerLayout>
اندروید هنگام تعیین منابعی که باید اعمال شود از ترتیب اولویت پیروی می کند. مخصوص این مثال، -w960dp (یا عرض موجود >= 960dp) بر -h470dp (یا ارتفاع موجود >= 470) اولویت دارد. اگر پیکربندی دستگاه با هیچ یک از این شرایط مطابقت نداشته باشد، از منبع طرحبندی پیشفرض ( res/layout/navigation_activity.xml ) استفاده میشود.
همانطور که در مثال زیر نشان داده شده است، در مدیریت رویدادهای ناوبری، فقط باید رویدادهایی را که مربوط به ویجتهایی هستند که در حال حاضر وجود دارند، سیمکشی کنید.
کاتلین
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() { private lateinit var appBarConfiguration : AppBarConfiguration override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.navigation_activity) val drawerLayout : DrawerLayout? = findViewById(R.id.drawer_layout) appBarConfiguration = AppBarConfiguration( setOf(R.id.home_dest, R.id.deeplink_dest), drawerLayout) ... // Initialize the app bar with the navigation drawer if present. // If the drawerLayout is not null here, a Navigation button will be added // to the app bar whenever the user is on a top-level destination. setupActionBarWithNavController(navController, appBarConfig) // Initialize the NavigationView if it is present, // so that clicking an item takes // the user to the appropriate destination. val sideNavView = findViewById<NavigationView>(R.id.nav_view) sideNavView?.setupWithNavController(navController) // Initialize the BottomNavigationView if it is present, // so that clicking an item takes // the user to the appropriate destination. val bottomNav = findViewById<BottomNavigationView>(R.id.bottom_nav_view) bottomNav?.setupWithNavController(navController) ... } ... }
جاوا
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private AppBarConfiguration appBarConfiguration; @Override protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.navigation_activity); NavHostFragment host = (NavHostFragment) getSupportFragmentManager() .findFragmentById(R.id.my_nav_host_fragment); NavController navController = host.getNavController(); DrawerLayout drawerLayout = findViewById(R.id.drawer_layout); appBarConfiguration = new AppBarConfiguration.Builder( R.id.home_dest, R.id.deeplink_dest) .setDrawerLayout(drawerLayout) .build(); // Initialize the app bar with the navigation drawer if present. // If the drawerLayout is not null here, a Navigation button will be added to // the app bar whenever the user is on a top-level destination. NavigationUI.setupActionBarWithNavController( this, navController, appBarConfiguration); // Initialize the NavigationView if it is present, // so that clicking an item takes // the user to the appropriate destination. NavigationView sideNavView = findViewById(R.id.nav_view); if(sideNavView != null) { NavigationUI.setupWithNavController(sideNavView, navController); } // Initialize the BottomNavigationView if it is present, // so that clicking an item takes // the user to the appropriate destination. BottomNavigationView bottomNav = findViewById(R.id.bottom_nav_view); if(bottomNav != null) { NavigationUI.setupWithNavController(bottomNav, navController); } } }
اگر پیکربندی دستگاه تغییر کند، مگر اینکه به طور صریح پیکربندی شده باشد ، Android فعالیت پیکربندی قبلی را به همراه نماهای مرتبط با آن از بین میبرد. سپس فعالیت را با منابع طراحی شده برای پیکربندی جدید بازسازی می کند. این اکتیویتی که از بین می رود و دوباره ایجاد می شود، سپس به طور خودکار عناصر ناوبری جهانی مناسب را در onCreate() متصل می کند.
جایگزین هایی برای طرح بندی های تقسیم شده در نظر بگیرید
طرحبندیهای با نمای تقسیم، یا چیدمانهای اصلی/جزئیات ، زمانی روشی بسیار محبوب و توصیهشده برای طراحی تبلتها و دیگر دستگاههای صفحهنمایش بزرگ بودند.
از زمان معرفی تبلت های اندرویدی، اکوسیستم دستگاه ها به سرعت رشد کرده است. یکی از عواملی که به طور قابل توجهی بر فضای طراحی دستگاههای صفحهنمایش بزرگ تأثیر گذاشته است، معرفی حالتهای چند پنجرهای، بهویژه پنجرههای آزاد که کاملاً قابل تغییر اندازه هستند، مانند موارد موجود در دستگاههای ChromeOS است. این امر به جای تغییر ساختار ناوبری بر اساس اندازه صفحه، تاکید بیشتری بر پاسخگو بودن هر صفحه از برنامه شما دارد.
در حالی که امکان پیادهسازی یک رابط طرحبندی تقسیمبندی با استفاده از کتابخانه پیمایش وجود دارد، باید گزینههای دیگری را در نظر بگیرید .
نام مقصد
اگر نام مقصد را در نمودار خود با استفاده از ویژگی android:label ارائه میکنید، مطمئن شوید که همیشه از مقادیر منابع استفاده میکنید تا محتوای شما همچنان بومیسازی شود.
<navigation ...>
<fragment
android:id="@+id/my_dest"
android:name="com.example.MyFragment"
android:label="@string/my_dest_label"
tools:layout="@layout/my_fragment" />
...
با مقادیر منابع، هر زمان که پیکربندی شما تغییر کند، مقاصد شما به طور خودکار مناسبترین منابع را دارند.

