หน้านี้จะกล่าวถึงข้อมูลเบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับ AGSL และวิธีอื่นๆ ในการใช้ AGSL บน Android แอป
เครื่องมือเฉดสี AGSL อย่างง่าย
จะมีการเรียกโค้ดตัวปรับแสงเงาสำหรับพิกเซลที่วาดแต่ละพิกเซล และจะแสดงสีที่พิกเซลนั้น
ที่ควรใช้ เครื่องมือเฉดสีที่เรียบง่ายที่สุดจะให้ผลลัพธ์
สีเดียว ตัวอย่างนี้ใช้สีแดง กำหนดเฉดสีภายใน String
Kotlin
private const val COLOR_SHADER_SRC = """half4 main(float2 fragCoord) { return half4(1,0,0,1); }"""
Java
private static final String COLOR_SHADER_SRC = "half4 main(float2 fragCoord) {\n" + "return half4(1,0,0,1);\n" + "}";
ขั้นตอนถัดไปคือการสร้างRuntimeShader
เริ่มต้นด้วยสตริงตัวปรับแสงเงาของคุณ ซึ่งจะรวมตัวปรับแสงเงาด้วย
Kotlin
val fixedColorShader = RuntimeShader(COLOR_SHADER_SRC)
Java
RuntimeShader fixedColorShader = new RuntimeShader(COLOR_SHADER_SRC);
RuntimeShader ของคุณสามารถใช้ได้ทุกที่ที่เครื่องมือเฉดสีของ Android มาตรฐานสามารถทำได้ ในฐานะ
ตัวอย่างเช่น คุณสามารถใช้แท็กนี้เพื่อวาดลงใน View ที่กำหนดเองโดยใช้
Canvas
Kotlin
val paint = Paint() paint.shader = fixedColorShader override fun onDrawForeground(canvas: Canvas?) { canvas?.let { canvas.drawPaint(paint) // fill the Canvas with the shader } }
Java
Paint paint = new Paint(); paint.setShader(fixedColorShader); public void onDrawForeground(@Nullable Canvas canvas) { if (canvas != null) { canvas.drawPaint(paint); // fill the Canvas with the shader } }
การดำเนินการนี้จะวาด View สีแดง คุณสามารถใช้ uniform เพื่อส่งผ่านพารามิเตอร์สีไปยัง
ตัวปรับแสงเงาที่จะวาด ก่อนอื่น ให้เพิ่มสี uniform ลงในเฉดสี ดังนี้
Kotlin
private const val COLOR_SHADER_SRC = """layout(color) uniform half4 iColor; half4 main(float2 fragCoord) { return iColor; }"""
Java
private static final String COLOR_SHADER_SRC = "layout(color) uniform half4 iColor;\n"+ "half4 main(float2 fragCoord) {\n" + "return iColor;\n" + "}";
จากนั้น เรียก setColorUniform จาก View ที่คุณกำหนดเองเพื่อส่งสีที่ต้องการ
ลงในตัวปรับแสงเงา AGSL
Kotlin
fixedColorShader.setColorUniform("iColor", Color.GREEN )
Java
fixedColorShader.setColorUniform("iColor", Color.GREEN );
ตอนนี้คุณจะได้รับ View สีเขียว สีของ View ถูกควบคุมโดยใช้
จากโค้ดใน View ที่กำหนดเองแทนที่จะฝังลงใน
ตัวปรับแสงเงา
สร้างเอฟเฟกต์การไล่ระดับสีแทนได้ ก่อนอื่นคุณจะต้องเปลี่ยน
ตัวปรับแสงเงาเพื่อยอมรับความละเอียด View เป็นอินพุต
Kotlin
private const val COLOR_SHADER_SRC = """uniform float2 iResolution; half4 main(float2 fragCoord) { float2 scaled = fragCoord/iResolution.xy; return half4(scaled, 0, 1); }"""
Java
private static final String COLOR_SHADER_SRC = "uniform float2 iResolution;\n" + "half4 main(float2 fragCoord) {\n" + "float2 scaled = fragCoord/iResolution.xy;\n" + "return half4(scaled, 0, 1);\n" + "}";
การวาดการไล่ระดับสี
เฉดสีนี้ทำอะไรที่หรูหราเล็กน้อย สำหรับแต่ละพิกเซล ระบบจะสร้างfloat2
เวกเตอร์ที่มีพิกัด x และ y หารด้วยความละเอียด ซึ่ง
จะสร้างค่าระหว่าง 0 ถึง 1 จากนั้นจะใช้เวกเตอร์ที่ปรับขนาดเพื่อ
สร้างส่วนประกอบสีแดงและเขียวของสีแสดงผล
คุณได้ส่งความละเอียดของ View ไปยังเครื่องมือให้เฉดสี AGSL uniform โดยการเรียกใช้
setFloatUniform
Kotlin
val paint = Paint() paint.shader = fixedColorShader override fun onDrawForeground(canvas: Canvas?) { canvas?.let { fixedColorShader.setFloatUniform("iResolution", width.toFloat(), height.toFloat()) canvas.drawPaint(paint) } }
Java
Paint paint = new Paint(); paint.setShader(fixedColorShader); public void onDrawForeground(@Nullable Canvas canvas) { if (canvas != null) { fixedColorShader.setFloatUniform("iResolution", (float)getWidth(), (float()getHeight())); canvas.drawPaint(paint); } }
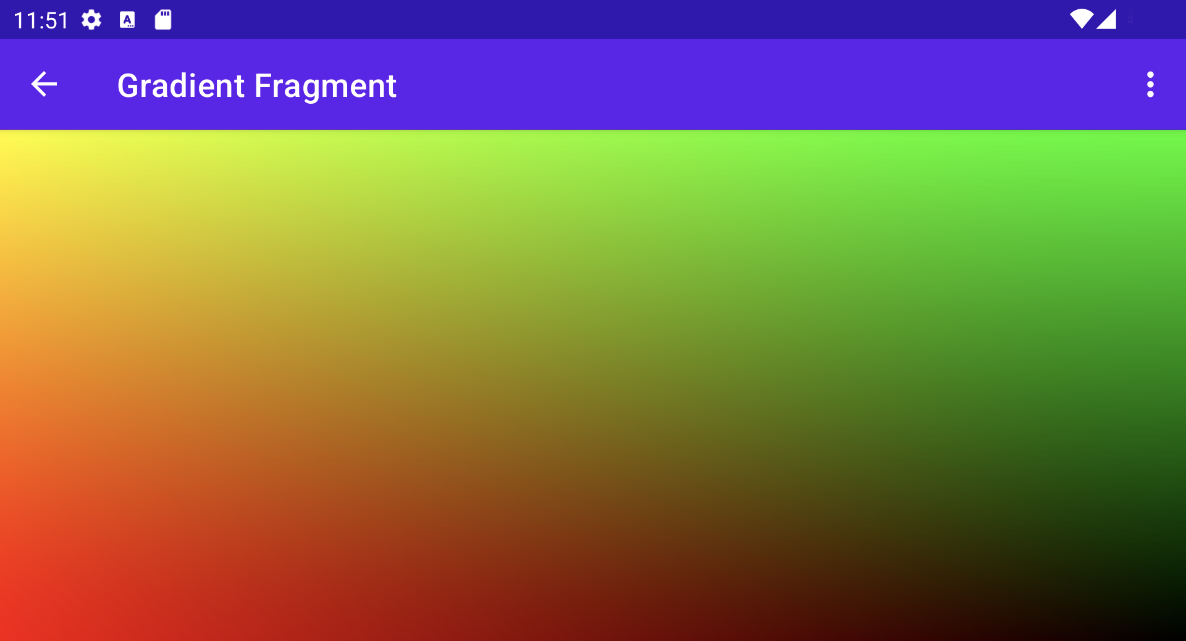

การสร้างภาพเคลื่อนไหวของตัวปรับแสงเงา
คุณสามารถใช้เทคนิคที่คล้ายกันเพื่อสร้างภาพเคลื่อนไหวของตัวให้เฉดสีได้โดยแก้ไขให้รับเครื่องแบบ iTime และ iDuration ตัวปรับแสงเงาจะใช้ค่าเหล่านี้เพื่อสร้าง
คลื่นสามเหลี่ยมสำหรับสี ทำให้สีวนกลับไปกลับมาตามค่าการไล่ระดับสี
Kotlin
private const val DURATION = 4000f private const val COLOR_SHADER_SRC = """ uniform float2 iResolution; uniform float iTime; uniform float iDuration; half4 main(in float2 fragCoord) { float2 scaled = abs(1.0-mod(fragCoord/iResolution.xy+iTime/(iDuration/2.0),2.0)); return half4(scaled, 0, 1.0); } """
Java
private static final float DURATION = 4000f; private static final String COLOR_SHADER_SRC = "uniform float2 iResolution;\n"+ "uniform float iTime;\n"+ "uniform float iDuration;\n"+ "half4 main(in float2 fragCoord) {\n"+ "float2 scaled = abs(1.0-mod(fragCoord/iResolution.xy+iTime/(iDuration/2.0),2.0));\n"+ "return half4(scaled, 0, 1.0);\n"+ "}";
จากซอร์สโค้ดของมุมมองที่กำหนดเอง
ValueAnimator อัปเดต
เครื่องแบบ iTime
Kotlin
// declare the ValueAnimator private val shaderAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0f, DURATION) // use it to animate the time uniform shaderAnimator.duration = DURATION.toLong() shaderAnimator.repeatCount = ValueAnimator.INFINITE shaderAnimator.repeatMode = ValueAnimator.RESTART shaderAnimator.interpolator = LinearInterpolator() animatedShader.setFloatUniform("iDuration", DURATION ) shaderAnimator.addUpdateListener { animation -> animatedShader.setFloatUniform("iTime", animation.animatedValue as Float ) } shaderAnimator.start()
Java
// declare the ValueAnimator private final ValueAnimator shaderAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0f, DURATION); // use it to animate the time uniform shaderAnimator.setDuration((long)DURATION); shaderAnimator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE); shaderAnimator.setRepeatMode(ValueAnimator.RESTART); shaderAnimator.setInterpolator(new LinearInterpolator()); animatedShader.setFloatUniform("iDuration", DURATION ); shaderAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() { public final void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) { animatedShader.setFloatUniform("iTime", (float)animation.getAnimatedValue()); } });

การวาดภาพวัตถุที่ซับซ้อน
คุณไม่ต้องวาดแถบเฉดสีเพื่อเติมพื้นหลัง อาจเป็นไปได้
ใช้ในที่ใดก็ตามที่ยอมรับ
Paint ของออบเจ็กต์ เช่น
drawText
Kotlin
canvas.drawText(ANIMATED_TEXT, TEXT_MARGIN_DP, TEXT_MARGIN_DP + bounds.height(), paint)
Java
canvas.drawText(ANIMATED_TEXT, TEXT_MARGIN_DP, TEXT_MARGIN_DP + bounds.height(), paint);

การลงเฉดสีและการเปลี่ยนรูปแบบ Canvas
คุณสามารถใช้การเปลี่ยนรูปแบบเพิ่มเติม Canvas รายการในข้อความที่แรเงาได้ เช่น
การหมุน ใน ValueAnimator คุณสามารถอัปเดตเมทริกซ์สำหรับการหมุน 3 มิติ
โดยใช้
android.graphics.Camera ชั้นเรียน
Kotlin
// in the ValueAnimator camera.rotate(0.0f, animation.animatedValue as Float / DURATION * 360f, 0.0f)
Java
// in the ValueAnimator camera.rotate(0.0f, (Float)animation.getAnimatedValue() / DURATION * 360f, 0.0f);
เนื่องจากคุณต้องการหมุนข้อความจากแกนกึ่งกลางแทนที่จะหมุนจากมุม
รับขอบเขตของข้อความ แล้วใช้ preTranslate และ postTranslate เพื่อปรับเปลี่ยน
เมทริกซ์เพื่อแปลข้อความเพื่อให้ 0,0 เป็นศูนย์กลางของการหมุนโดยไม่มี
เปลี่ยนตำแหน่งที่จะวาดข้อความบนหน้าจอ
Kotlin
linearColorPaint.getTextBounds(ANIMATED_TEXT, 0, ANIMATED_TEXT.length, bounds) camera.getMatrix(rotationMatrix) val centerX = (bounds.width().toFloat())/2 val centerY = (bounds.height().toFloat())/2 rotationMatrix.preTranslate(-centerX, -centerY) rotationMatrix.postTranslate(centerX, centerY) canvas.save() canvas.concat(rotationMatrix) canvas.drawText(ANIMATED_TEXT, 0f, 0f + bounds.height(), paint) canvas.restore()
Java
linearColorPaint.getTextBounds(ANIMATED_TEXT, 0, ANIMATED_TEXT.length(), bounds); camera.getMatrix(rotationMatrix); float centerX = (float)bounds.width()/2.0f; float centerY = (float)bounds.height()/2.0f; rotationMatrix.preTranslate(-centerX, -centerY); rotationMatrix.postTranslate(centerX, centerY); canvas.save(); canvas.concat(rotationMatrix); canvas.drawText(ANIMATED_TEXT, 0f, 0f + bounds.height(), paint); canvas.restore();

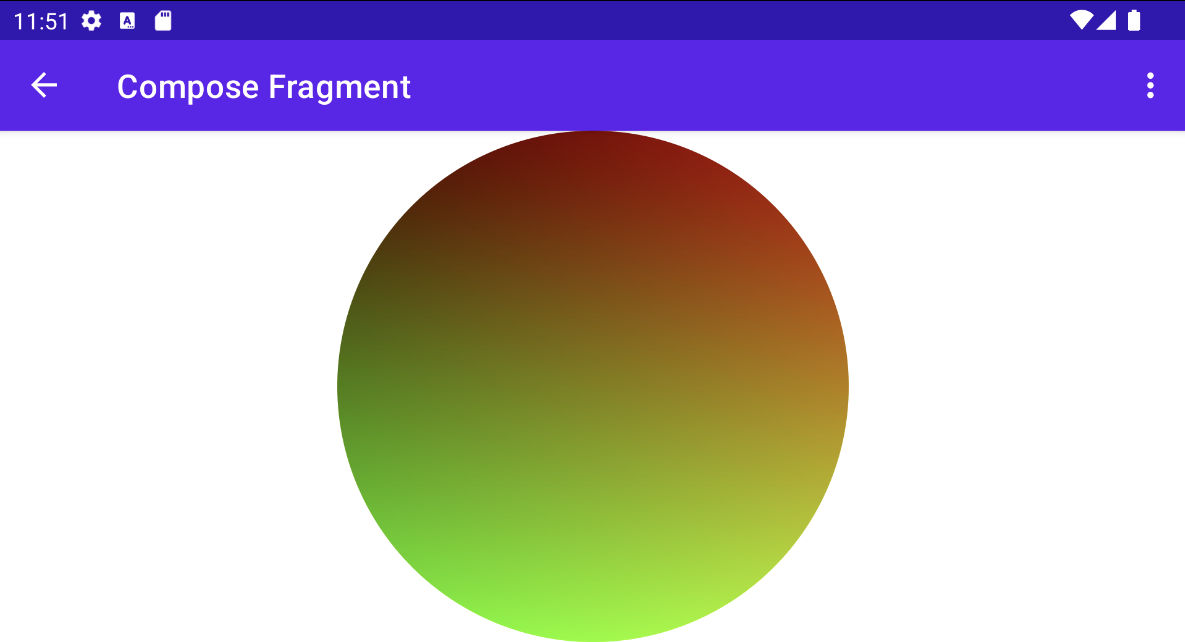
การใช้ RuntimeShader กับ Jetpack Compose
การใช้ RuntimeShader จะง่ายขึ้นไปอีกหากคุณแสดงผล UI โดยใช้
Jetpack Compose เริ่มต้นด้วยตัวไล่ระดับสีเดียวกันจาก
ก่อน:
private const val COLOR_SHADER_SRC =
"""uniform float2 iResolution;
half4 main(float2 fragCoord) {
float2 scaled = fragCoord/iResolution.xy;
return half4(scaled, 0, 1);
}"""
คุณสามารถใช้ตัวปรับแสงเงานั้นกับ
ShaderBrush คุณ
แล้วใช้ ShaderBrush เป็นพารามิเตอร์กับคำสั่งวาดภายใน
ขอบเขตการวาดของ Canvas
// created as top level constants
val colorShader = RuntimeShader(COLOR_SHADER_SRC)
val shaderBrush = ShaderBrush(colorShader)
Canvas(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize()
) {
colorShader.setFloatUniform("iResolution",
size.width, size.height)
drawCircle(brush = shaderBrush)
}
การใช้ RuntimeShader กับ RenderEffect
คุณสามารถใช้
RenderEffect เพื่อใช้
RuntimeShader ไปยัง View ระดับบน
และการดูของเด็กทั้งหมด ราคานี้แพงกว่าการวาด View แบบกำหนดเอง แต่
ทำให้คุณสามารถสร้างผลลัพธ์
ที่รวมสิ่งที่ต้องมี
เดิมวาดโดยใช้
createRuntimeShaderEffect
Kotlin
view.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createRuntimeShaderEffect(myShader, "background"))
Java
view.setRenderEffect(RenderEffect.createRuntimeShaderEffect(myShader, "background"));
พารามิเตอร์ที่ 2 คือชื่อของชุดเครื่องมือให้เฉดสีที่คุณสามารถevalโดยใช้
พารามิเตอร์พิกัด (เช่น ค่าที่ส่งใน fragCoord) เพื่อให้ได้สีเดิม
ของ
RenderNode (ข้อมูลพร็อพเพอร์ตี้และองค์ประกอบย่อย
) ซึ่งทำให้คุณสร้างเอฟเฟกต์ได้ทุกประเภท
uniform shader background; // Root node of View tree to be altered
return mix(returnColor, background.eval(fragCoord), 0.5);
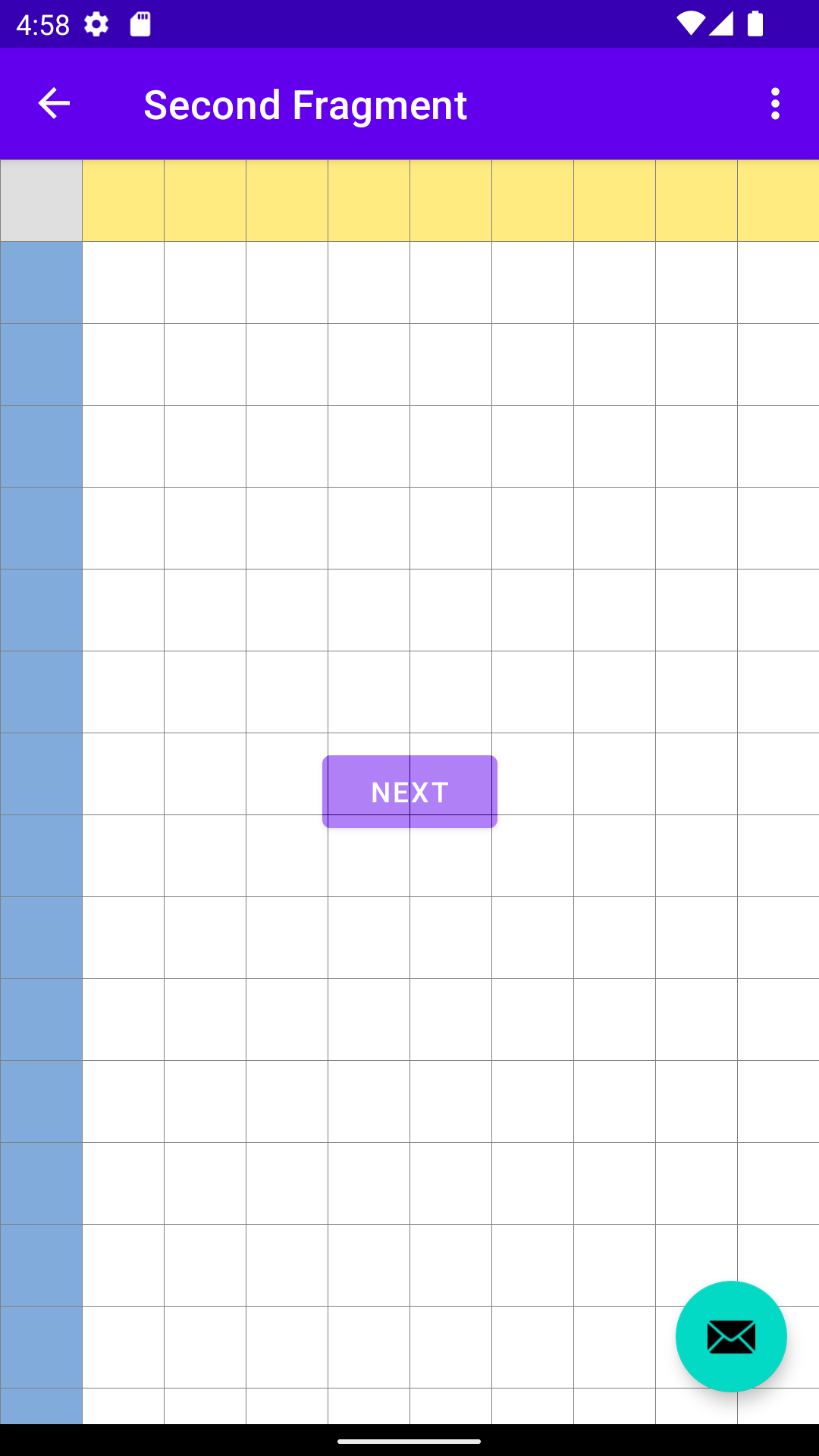
เอฟเฟกต์ตารางกริดผสมปนกับปุ่ม แต่อยู่ใต้ปุ่มการทำงานแบบลอย
(เนื่องจากอยู่ในลำดับชั้น View ที่ต่างกัน)
