กล่องโต้ตอบคือหน้าต่างเล็กๆ ที่แจ้งให้ผู้ใช้ตัดสินใจหรือป้อนข้อมูลเพิ่มเติม กล่องโต้ตอบจะไม่เต็มหน้าจอและปกติแล้วจะใช้สำหรับเหตุการณ์แบบโมดัลที่กำหนดให้ผู้ใช้ต้องดำเนินการก่อนจึงจะดำเนินการต่อได้
คลาส Dialog
เป็นคลาสพื้นฐานสําหรับกล่องโต้ตอบ แต่อย่าสร้างอินสแตนซ์ Dialog
โดยตรง แต่ให้ใช้คลาสย่อยรายการใดรายการหนึ่งต่อไปนี้แทน
AlertDialog- กล่องโต้ตอบที่แสดงชื่อ ปุ่มได้สูงสุด 3 ปุ่ม รายการที่เลือกได้ หรือเลย์เอาต์ที่กำหนดเอง
DatePickerDialogหรือTimePickerDialog- กล่องโต้ตอบที่มี UI ที่กําหนดไว้ล่วงหน้าซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้เลือกวันที่หรือเวลาได้
คลาสเหล่านี้จะกำหนดสไตล์และโครงสร้างของกล่องโต้ตอบ นอกจากนี้ คุณจะต้องมี
DialogFragment
เป็นคอนเทนเนอร์สําหรับกล่องโต้ตอบด้วย คลาส DialogFragment มีการควบคุมทั้งหมดที่จําเป็นในการสร้างกล่องโต้ตอบและจัดการลักษณะที่ปรากฏแทนการเรียกใช้เมธอดบนออบเจ็กต์ Dialog
การใช้ DialogFragment เพื่อจัดการกล่องโต้ตอบจะช่วยให้จัดการเหตุการณ์ในวงจรได้อย่างถูกต้อง เช่น เมื่อผู้ใช้แตะปุ่มย้อนกลับหรือหมุนหน้าจอ นอกจากนี้ คลาส DialogFragment ยังช่วยให้คุณนํา UI ของกล่องโต้ตอบกลับมาใช้ซ้ำได้ในฐานะคอมโพเนนต์ที่ฝังได้ใน UI ที่ใหญ่ขึ้น เช่นเดียวกับ Fragment แบบดั้งเดิม เช่น เมื่อคุณต้องการให้ UI ของกล่องโต้ตอบปรากฏแตกต่างกันในหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่และขนาดเล็ก
ส่วนต่อไปนี้ในเอกสารนี้อธิบายวิธีใช้ DialogFragment ร่วมกับออบเจ็กต์ AlertDialog หากต้องการสร้างเครื่องมือเลือกวันที่หรือเวลา โปรดอ่านหัวข้อเพิ่มเครื่องมือเลือกลงในแอป
สร้างกล่องโต้ตอบย่อย
คุณสามารถออกแบบกล่องโต้ตอบได้อย่างหลากหลาย รวมถึงเลย์เอาต์ที่กำหนดเองและที่อธิบายไว้ในกล่องโต้ตอบดีไซน์ Material โดยการขยาย DialogFragment และสร้าง AlertDialog ในเมธอด CallbackonCreateDialog()
ลองดูตัวอย่าง AlertDialog พื้นฐานที่จัดการภายใน DialogFragment ดังนี้
Kotlin
class StartGameDialogFragment : DialogFragment() { override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle?): Dialog { return activity?.let { // Use the Builder class for convenient dialog construction. val builder = AlertDialog.Builder(it) builder.setMessage("Start game") .setPositiveButton("Start") { dialog, id -> // START THE GAME! } .setNegativeButton("Cancel") { dialog, id -> // User cancelled the dialog. } // Create the AlertDialog object and return it. builder.create() } ?: throw IllegalStateException("Activity cannot be null") } } class OldXmlActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_old_xml) StartGameDialogFragment().show(supportFragmentManager, "GAME_DIALOG") } }
Java
public class StartGameDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { @Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Use the Builder class for convenient dialog construction. AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_start_game) .setPositiveButton(R.string.start, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // START THE GAME! } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User cancels the dialog. } }); // Create the AlertDialog object and return it. return builder.create(); } } // ... StartGameDialogFragment().show(supportFragmentManager, "GAME_DIALOG");
เมื่อคุณสร้างอินสแตนซ์ของคลาสนี้และเรียกใช้ show() กับออบเจ็กต์นั้น กล่องโต้ตอบจะปรากฏขึ้นดังที่แสดงในรูปภาพต่อไปนี้
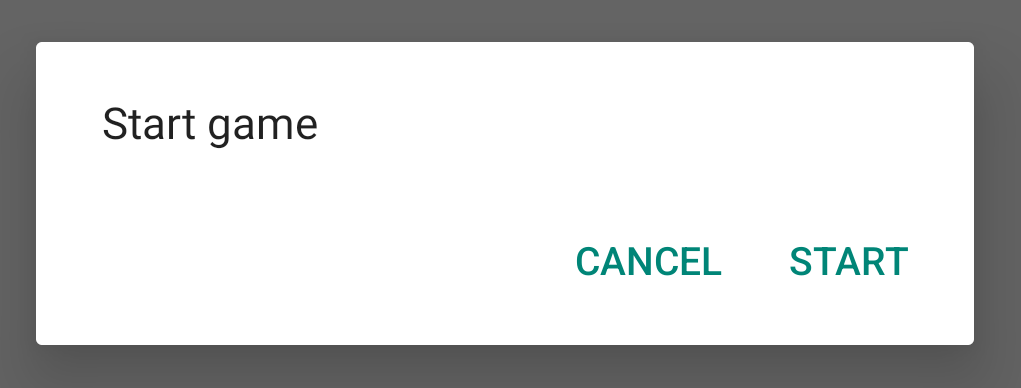
ส่วนถัดไปจะให้รายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการใช้
AlertDialog.Builder
API เพื่อสร้างกล่องโต้ตอบ
คุณสามารถใช้เมธอดการเรียกกลับอื่นๆ มากมายใน DialogFragment ซึ่งรวมถึงเมธอดวงจรชีวิตของส่วนที่ใช้งานอยู่พื้นฐานทั้งหมด ทั้งนี้ขึ้นอยู่กับความซับซ้อนของกล่องโต้ตอบ
สร้างกล่องโต้ตอบการแจ้งเตือน
คลาส AlertDialog ช่วยให้คุณสร้างดีไซน์กล่องโต้ตอบที่หลากหลาย
และมักจะเป็นคลาสกล่องโต้ตอบเพียงคลาสเดียวที่คุณต้องการ ดังที่แสดงในรูปภาพต่อไปนี้ กล่องโต้ตอบการแจ้งเตือนมี 3 ภูมิภาค ดังนี้
- ชื่อ: ไม่บังคับ และใช้เฉพาะในกรณีที่พื้นที่เนื้อหามีข้อความแบบละเอียด รายการ หรือเลย์เอาต์ที่กำหนดเอง หากต้องการระบุข้อความหรือคำถามง่ายๆ ก็ไม่ต้องใช้ชื่อ
- พื้นที่เนื้อหา: พื้นที่นี้จะแสดงข้อความ รายการ หรือเลย์เอาต์ที่กำหนดเองอื่นๆ
- ปุ่มการทำงาน: กล่องโต้ตอบมีปุ่มการทำงานได้สูงสุด 3 ปุ่ม
คลาส AlertDialog.Builder มี API ที่ช่วยให้คุณสร้าง AlertDialog ที่มีเนื้อหาประเภทเหล่านี้ รวมถึงเลย์เอาต์ที่กำหนดเอง
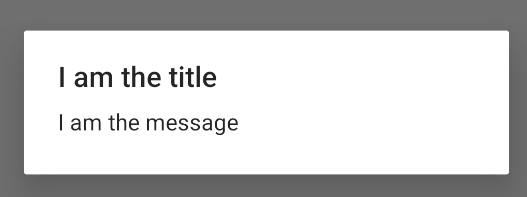
หากต้องการสร้าง AlertDialog ให้ทำดังนี้
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setMessage("I am the message") .setTitle("I am the title") val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
// 1. Instantiate an AlertDialog.Builder with its constructor. AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // 2. Chain together various setter methods to set the dialog characteristics. builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_message) .setTitle(R.string.dialog_title); // 3. Get the AlertDialog. AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
ข้อมูลโค้ดก่อนหน้าจะสร้างกล่องโต้ตอบนี้
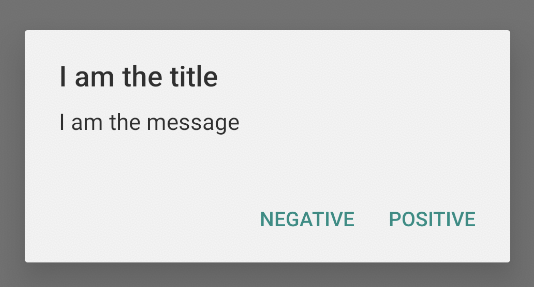
เพิ่มปุ่ม
หากต้องการเพิ่มปุ่มการทำงานดังเช่นในรูปที่ 2 ให้เรียกใช้เมธอด setPositiveButton() และ setNegativeButton() ดังนี้
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setMessage("I am the message") .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // Add the buttons. builder.setPositiveButton(R.string.ok, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User taps OK button. } }); builder.setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User cancels the dialog. } }); // Set other dialog properties. ... // Create the AlertDialog. AlertDialog dialog = builder.create();
เมธอด set...Button() ต้องมีชื่อสำหรับปุ่ม ซึ่งได้จากทรัพยากรสตริง และ DialogInterface.OnClickListener ที่กําหนดการดําเนินการที่จะทําเมื่อผู้ใช้แตะปุ่ม
คุณสามารถเพิ่มปุ่มการทำงานได้ 3 ปุ่ม ดังนี้
- บวก: ใช้เพื่อยอมรับและดําเนินการต่อ (การดําเนินการ "ตกลง")
- ลบ: ใช้เพื่อยกเลิกการดำเนินการ
- เป็นกลาง: ใช้เมื่อผู้ใช้อาจไม่ต้องการดําเนินการต่อ แต่ก็ไม่จําเป็นต้องยกเลิก โดยจะปรากฏระหว่างปุ่มเชิงบวกและเชิงลบ เช่น การดำเนินการอาจเป็น "ช่วยเตือนฉันในภายหลัง"
คุณจะเพิ่มปุ่มแต่ละประเภทได้เพียง 1 ปุ่มใน AlertDialog เช่น คุณมีปุ่ม "บวก" ได้ไม่เกิน 1 ปุ่ม
ข้อมูลโค้ดก่อนหน้านี้จะแสดงกล่องโต้ตอบการแจ้งเตือนดังตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
เพิ่มรายการ
รายการที่พร้อมใช้งานใน AlertDialog API มีอยู่ 3 ประเภทด้วยกัน ได้แก่
- รายการแบบเลือกตัวเลือกเดียวแบบดั้งเดิม
- รายการแบบเลือกตัวเลือกเดียวแบบถาวร (ปุ่มตัวเลือก)
- รายการแบบเลือกหลายรายการถาวร (ช่องทําเครื่องหมาย)
หากต้องการสร้างรายการแบบเลือกรายการเดียวดังที่แสดงในรูปที่ 5 ให้ใช้วิธีต่อไปนี้
setItems()
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } .setItems(arrayOf("Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three")) { dialog, which -> // Do something on item tapped. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
@Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); builder.setTitle(R.string.pick_color) .setItems(R.array.colors_array, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) { // The 'which' argument contains the index position of the selected item. } }); return builder.create(); }
ข้อมูลโค้ดนี้จะสร้างกล่องโต้ตอบดังต่อไปนี้
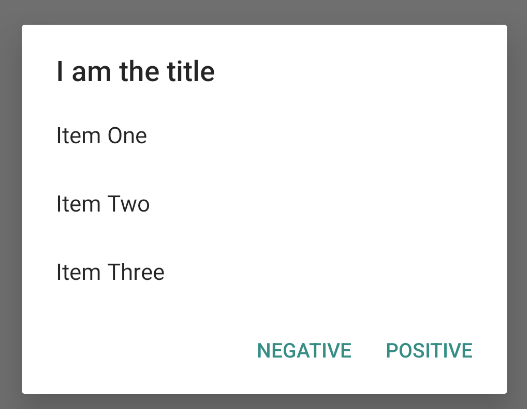
เนื่องจากรายการปรากฏในพื้นที่เนื้อหาของกล่องโต้ตอบ กล่องโต้ตอบจึงไม่สามารถแสดงทั้งข้อความและรายการ ตั้งชื่อกล่องโต้ตอบด้วย setTitle()
หากต้องการระบุรายการสำหรับรายการ ให้เรียกใช้ setItems() โดยส่งอาร์เรย์ หรือจะระบุรายการโดยใช้ setAdapter() ก็ได้
ซึ่งจะช่วยให้คุณสำรองข้อมูลรายการด้วยข้อมูลแบบไดนามิก เช่น จากฐานข้อมูล โดยใช้ ListAdapter
หากคุณสนับสนุนรายการด้วย ListAdapter ให้ใช้ Loader เสมอเพื่อให้เนื้อหาโหลดแบบไม่พร้อมกัน โปรดดูรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมในหัวข้อสร้างเลย์เอาต์ด้วยอะแดปเตอร์และโปรแกรมโหลด
เพิ่มรายการแบบหลายตัวเลือกหรือแบบตัวเลือกเดียวแบบถาวร
หากต้องการเพิ่มรายการแบบเลือกหลายรายการ (ช่องทําเครื่องหมาย) หรือรายการแบบเลือกรายการเดียว (ปุ่มตัวเลือก) ให้ใช้เมธอด setMultiChoiceItems() หรือ setSingleChoiceItems() ตามลำดับ
ตัวอย่างเช่น วิธีสร้างรายการแบบเลือกหลายรายการดังที่แสดงในรูปที่ 6 ซึ่งจะบันทึกรายการที่เลือกไว้ในArrayListมีดังนี้
Kotlin
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } .setMultiChoiceItems( arrayOf("Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three"), null) { dialog, which, isChecked -> // Do something. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
@Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { selectedItems = new ArrayList(); // Where we track the selected items AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // Set the dialog title. builder.setTitle(R.string.pick_toppings) // Specify the list array, the items to be selected by default (null for // none), and the listener through which to receive callbacks when items // are selected. .setMultiChoiceItems(R.array.toppings, null, new DialogInterface.OnMultiChoiceClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which, boolean isChecked) { if (isChecked) { // If the user checks the item, add it to the selected // items. selectedItems.add(which); } else if (selectedItems.contains(which)) { // If the item is already in the array, remove it. selectedItems.remove(which); } } }) // Set the action buttons .setPositiveButton(R.string.ok, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // User taps OK, so save the selectedItems results // somewhere or return them to the component that opens the // dialog. ... } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { ... } }); return builder.create(); }
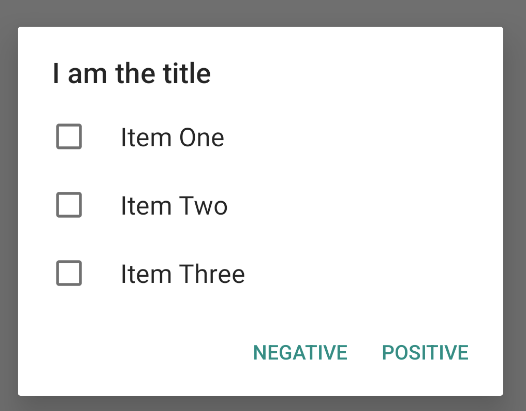
กล่องโต้ตอบการแจ้งเตือนแบบเลือกรายการเดียวจะปรากฏขึ้นดังนี้
Kotlin
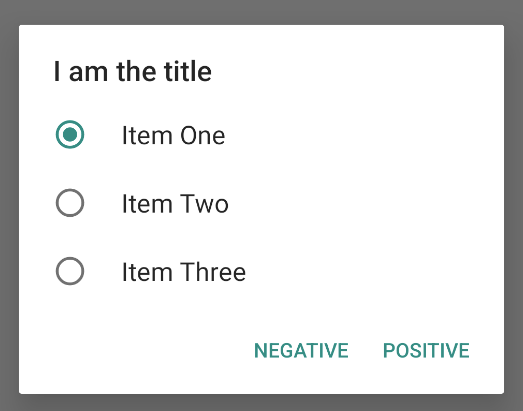
val builder: AlertDialog.Builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context) builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive") { dialog, which -> // Do something. } .setNegativeButton("Negative") { dialog, which -> // Do something else. } .setSingleChoiceItems( arrayOf("Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three"), 0 ) { dialog, which -> // Do something. } val dialog: AlertDialog = builder.create() dialog.show()
Java
String[] choices = {"Item One", "Item Two", "Item Three"}; AlertDialog.Builder builder = AlertDialog.Builder(context); builder .setTitle("I am the title") .setPositiveButton("Positive", (dialog, which) -> { }) .setNegativeButton("Negative", (dialog, which) -> { }) .setSingleChoiceItems(choices, 0, (dialog, which) -> { }); AlertDialog dialog = builder.create(); dialog.show();
ซึ่งทำให้เกิดในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
สร้างเลย์เอาต์ที่กำหนดเอง
หากต้องการเลย์เอาต์ที่กำหนดเองในกล่องโต้ตอบ ให้สร้างเลย์เอาต์และเพิ่มลงใน AlertDialog โดยเรียกใช้ setView() ในออบเจ็กต์ AlertDialog.Builder
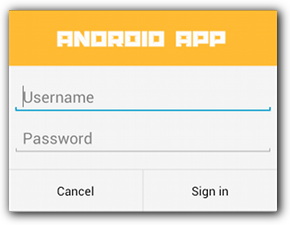
เลย์เอาต์ที่กำหนดเองจะแสดงในหน้าต่างกล่องโต้ตอบโดยค่าเริ่มต้น แต่คุณยังคงใช้เมธอด AlertDialog.Builder เพื่อเพิ่มปุ่มและชื่อได้
ตัวอย่างเช่น ไฟล์เลย์เอาต์สำหรับกล่องโต้ตอบที่กําหนดเองก่อนหน้านี้มีดังนี้
res/layout/dialog_signin.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <ImageView android:src="@drawable/header_logo" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="64dp" android:scaleType="center" android:background="#FFFFBB33" android:contentDescription="@string/app_name" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/username" android:inputType="textEmailAddress" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="16dp" android:layout_marginLeft="4dp" android:layout_marginRight="4dp" android:layout_marginBottom="4dp" android:hint="@string/username" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/password" android:inputType="textPassword" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="4dp" android:layout_marginLeft="4dp" android:layout_marginRight="4dp" android:layout_marginBottom="16dp" android:fontFamily="sans-serif" android:hint="@string/password"/> </LinearLayout>
หากต้องการขยายเลย์เอาต์ใน DialogFragment ให้รับ
LayoutInflater
ที่มี
getLayoutInflater()
แล้วเรียกใช้
inflate()
พารามิเตอร์แรกคือรหัสทรัพยากรเลย์เอาต์ และพารามิเตอร์ที่ 2 คือ View หลักของเลย์เอาต์ จากนั้นคุณจะเรียกใช้ setView() เพื่อวางเลย์เอาต์ในกล่องโต้ตอบได้ ตัวอย่างนี้จะแสดงในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle?): Dialog { return activity?.let { val builder = AlertDialog.Builder(it) // Get the layout inflater. val inflater = requireActivity().layoutInflater; // Inflate and set the layout for the dialog. // Pass null as the parent view because it's going in the dialog // layout. builder.setView(inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog_signin, null)) // Add action buttons. .setPositiveButton(R.string.signin, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> // Sign in the user. }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> getDialog().cancel() }) builder.create() } ?: throw IllegalStateException("Activity cannot be null") }
Java
@Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); // Get the layout inflater. LayoutInflater inflater = requireActivity().getLayoutInflater(); // Inflate and set the layout for the dialog. // Pass null as the parent view because it's going in the dialog layout. builder.setView(inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog_signin, null)) // Add action buttons .setPositiveButton(R.string.signin, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // Sign in the user. } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { LoginDialogFragment.this.getDialog().cancel(); } }); return builder.create(); }
หากต้องการกล่องโต้ตอบที่กําหนดเอง คุณสามารถแสดง Activity เป็นกล่องโต้ตอบแทนการใช้ Dialog API สร้างกิจกรรมและตั้งค่าธีมเป็น Theme.Holo.Dialog ในองค์ประกอบ <activity> ของไฟล์ Manifest ดังนี้
<activity android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Holo.Dialog" >
กิจกรรมจะแสดงในหน้าต่างกล่องโต้ตอบแทนแบบเต็มหน้าจอ
ส่งเหตุการณ์กลับไปยังโฮสต์ของกล่องโต้ตอบ
เมื่อผู้ใช้แตะปุ่มดำเนินการของกล่องโต้ตอบหรือเลือกรายการจากรายการ DialogFragment อาจดำเนินการที่จำเป็นด้วยตนเอง แต่บ่อยครั้งที่คุณต้องการส่งเหตุการณ์ไปยังกิจกรรมหรือส่วนที่เปิดกล่องโต้ตอบ โดยให้กําหนดอินเทอร์เฟซที่มีเมธอดสําหรับเหตุการณ์การคลิกแต่ละประเภท จากนั้นนําอินเทอร์เฟซนั้นไปใช้ในคอมโพเนนต์โฮสต์ที่รับเหตุการณ์การดําเนินการจากกล่องโต้ตอบ
ตัวอย่างเช่น DialogFragment ต่อไปนี้จะกําหนดอินเทอร์เฟซที่ใช้ส่งเหตุการณ์กลับไปยังกิจกรรมโฮสต์
Kotlin
class NoticeDialogFragment : DialogFragment() { // Use this instance of the interface to deliver action events. internal lateinit var listener: NoticeDialogListener // The activity that creates an instance of this dialog fragment must // implement this interface to receive event callbacks. Each method passes // the DialogFragment in case the host needs to query it. interface NoticeDialogListener { fun onDialogPositiveClick(dialog: DialogFragment) fun onDialogNegativeClick(dialog: DialogFragment) } // Override the Fragment.onAttach() method to instantiate the // NoticeDialogListener. override fun onAttach(context: Context) { super.onAttach(context) // Verify that the host activity implements the callback interface. try { // Instantiate the NoticeDialogListener so you can send events to // the host. listener = context as NoticeDialogListener } catch (e: ClassCastException) { // The activity doesn't implement the interface. Throw exception. throw ClassCastException((context.toString() + " must implement NoticeDialogListener")) } } }
Java
public class NoticeDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { // The activity that creates an instance of this dialog fragment must // implement this interface to receive event callbacks. Each method passes // the DialogFragment in case the host needs to query it. public interface NoticeDialogListener { public void onDialogPositiveClick(DialogFragment dialog); public void onDialogNegativeClick(DialogFragment dialog); } // Use this instance of the interface to deliver action events. NoticeDialogListener listener; // Override the Fragment.onAttach() method to instantiate the // NoticeDialogListener. @Override public void onAttach(Context context) { super.onAttach(context); // Verify that the host activity implements the callback interface. try { // Instantiate the NoticeDialogListener so you can send events to // the host. listener = (NoticeDialogListener) context; } catch (ClassCastException e) { // The activity doesn't implement the interface. Throw exception. throw new ClassCastException(activity.toString() + " must implement NoticeDialogListener"); } } ... }
กิจกรรมที่โฮสต์กล่องโต้ตอบจะสร้างอินสแตนซ์ของกล่องโต้ตอบด้วยคอนสตรัคเตอร์ของข้อมูลโค้ดที่เป็นส่วนย่อยของกล่องโต้ตอบ และรับเหตุการณ์ของกล่องโต้ตอบผ่านการใช้งานอินเทอร์เฟซ NoticeDialogListener ดังนี้
Kotlin
class MainActivity : FragmentActivity(), NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener { fun showNoticeDialog() { // Create an instance of the dialog fragment and show it. val dialog = NoticeDialogFragment() dialog.show(supportFragmentManager, "NoticeDialogFragment") } // The dialog fragment receives a reference to this Activity through the // Fragment.onAttach() callback, which it uses to call the following // methods defined by the NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener // interface. override fun onDialogPositiveClick(dialog: DialogFragment) { // User taps the dialog's positive button. } override fun onDialogNegativeClick(dialog: DialogFragment) { // User taps the dialog's negative button. } }
Java
public class MainActivity extends FragmentActivity implements NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener{ ... public void showNoticeDialog() { // Create an instance of the dialog fragment and show it. DialogFragment dialog = new NoticeDialogFragment(); dialog.show(getSupportFragmentManager(), "NoticeDialogFragment"); } // The dialog fragment receives a reference to this Activity through the // Fragment.onAttach() callback, which it uses to call the following // methods defined by the NoticeDialogFragment.NoticeDialogListener // interface. @Override public void onDialogPositiveClick(DialogFragment dialog) { // User taps the dialog's positive button. ... } @Override public void onDialogNegativeClick(DialogFragment dialog) { // User taps the dialog's negative button. ... } }
เนื่องจากกิจกรรมโฮสต์ใช้ NoticeDialogListener ซึ่งบังคับใช้โดยเมธอด Callback ของ onAttach() ที่แสดงในตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ เศษส่วนของกล่องโต้ตอบจึงใช้เมธอด Callback ของอินเทอร์เฟซเพื่อส่งเหตุการณ์การคลิกไปยังกิจกรรมได้ ดังนี้
Kotlin
override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle): Dialog { return activity?.let { // Build the dialog and set up the button click handlers. val builder = AlertDialog.Builder(it) builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_start_game) .setPositiveButton(R.string.start, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> // Send the positive button event back to the // host activity. listener.onDialogPositiveClick(this) }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, DialogInterface.OnClickListener { dialog, id -> // Send the negative button event back to the // host activity. listener.onDialogNegativeClick(this) }) builder.create() } ?: throw IllegalStateException("Activity cannot be null") }
Java
public class NoticeDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { ... @Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Build the dialog and set up the button click handlers. AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(getActivity()); builder.setMessage(R.string.dialog_start_game) .setPositiveButton(R.string.start, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // Send the positive button event back to the host activity. listener.onDialogPositiveClick(NoticeDialogFragment.this); } }) .setNegativeButton(R.string.cancel, new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int id) { // Send the negative button event back to the host activity. listener.onDialogNegativeClick(NoticeDialogFragment.this); } }); return builder.create(); } }
แสดงกล่องโต้ตอบ
เมื่อต้องการแสดงกล่องโต้ตอบ ให้สร้างอินสแตนซ์ของ DialogFragment และการเรียกใช้ show() โดยส่ง FragmentManager และชื่อแท็กสำหรับส่วนย่อยของกล่องโต้ตอบ
คุณสามารถรับ FragmentManager ได้โดยโทรไปที่
getSupportFragmentManager()
จาก
FragmentActivity
หรือโทร
getParentFragmentManager()
จาก Fragment โปรดดูตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
fun confirmStartGame() { val newFragment = StartGameDialogFragment() newFragment.show(supportFragmentManager, "game") }
Java
public void confirmStartGame() { DialogFragment newFragment = new StartGameDialogFragment(); newFragment.show(getSupportFragmentManager(), "game"); }
อาร์กิวเมนต์ที่ 2 "game" เป็นชื่อแท็กที่ไม่ซ้ำกันซึ่งระบบจะใช้ในการบันทึกและกู้คืนสถานะส่วนย่อย เมื่อจําเป็น แท็กยังช่วยให้คุณมีแฮนเดิลส่วนย่อยโดยการเรียกใช้ findFragmentByTag() ด้วย
แสดงกล่องโต้ตอบแบบเต็มหน้าจอหรือเป็นข้อมูลโค้ดที่ฝัง
คุณอาจต้องการให้การออกแบบ UI บางส่วนปรากฏเป็นกล่องโต้ตอบในบางสถานการณ์ และปรากฏเป็นหน้าจอแบบเต็มหรือส่วนที่ฝังในบางสถานการณ์ นอกจากนี้ คุณอาจต้องการให้ไอคอนปรากฏแตกต่างกันไปตามขนาดหน้าจอของอุปกรณ์ คลาส DialogFragment มีความยืดหยุ่นในการบรรลุเป้าหมายนี้ เนื่องจากสามารถทํางานเป็น Fragment แบบฝังได้
แต่ไม่สามารถใช้ออบเจ็กต์ AlertDialog.Builder หรือ Dialog อื่นๆ เพื่อสร้างกล่องโต้ตอบได้ในกรณีนี้ หากต้องการให้ DialogFragment เป็นแบบฝังได้ ให้กำหนด UI ของกล่องโต้ตอบในเลย์เอาต์ จากนั้นโหลดเลย์เอาต์ใน Callback onCreateView()
ต่อไปนี้คือตัวอย่าง DialogFragment ที่อาจปรากฏเป็นกล่องโต้ตอบหรือเศษข้อมูลที่ฝังได้โดยใช้เลย์เอาต์ชื่อ purchase_items.xml
Kotlin
class CustomDialogFragment : DialogFragment() { // The system calls this to get the DialogFragment's layout, regardless of // whether it's being displayed as a dialog or an embedded fragment. override fun onCreateView( inflater: LayoutInflater, container: ViewGroup?, savedInstanceState: Bundle? ): View { // Inflate the layout to use as a dialog or embedded fragment. return inflater.inflate(R.layout.purchase_items, container, false) } // The system calls this only when creating the layout in a dialog. override fun onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState: Bundle): Dialog { // The only reason you might override this method when using // onCreateView() is to modify the dialog characteristics. For example, // the dialog includes a title by default, but your custom layout might // not need it. Here, you can remove the dialog title, but you must // call the superclass to get the Dialog. val dialog = super.onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState) dialog.requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE) return dialog } }
Java
public class CustomDialogFragment extends DialogFragment { // The system calls this to get the DialogFragment's layout, regardless of // whether it's being displayed as a dialog or an embedded fragment. @Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { // Inflate the layout to use as a dialog or embedded fragment. return inflater.inflate(R.layout.purchase_items, container, false); } // The system calls this only when creating the layout in a dialog. @Override public Dialog onCreateDialog(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // The only reason you might override this method when using // onCreateView() is to modify the dialog characteristics. For example, // the dialog includes a title by default, but your custom layout might // not need it. Here, you can remove the dialog title, but you must // call the superclass to get the Dialog. Dialog dialog = super.onCreateDialog(savedInstanceState); dialog.requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE); return dialog; } }
ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้จะกำหนดว่าจะแสดงข้อมูลโค้ดเป็นกล่องโต้ตอบหรือ UI แบบเต็มหน้าจอโดยอิงตามขนาดหน้าจอ
Kotlin
fun showDialog() { val fragmentManager = supportFragmentManager val newFragment = CustomDialogFragment() if (isLargeLayout) { // The device is using a large layout, so show the fragment as a // dialog. newFragment.show(fragmentManager, "dialog") } else { // The device is smaller, so show the fragment fullscreen. val transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction() // For a polished look, specify a transition animation. transaction.setTransition(FragmentTransaction.TRANSIT_FRAGMENT_OPEN) // To make it fullscreen, use the 'content' root view as the container // for the fragment, which is always the root view for the activity. transaction .add(android.R.id.content, newFragment) .addToBackStack(null) .commit() } }
Java
public void showDialog() { FragmentManager fragmentManager = getSupportFragmentManager(); CustomDialogFragment newFragment = new CustomDialogFragment(); if (isLargeLayout) { // The device is using a large layout, so show the fragment as a // dialog. newFragment.show(fragmentManager, "dialog"); } else { // The device is smaller, so show the fragment fullscreen. FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction(); // For a polished look, specify a transition animation. transaction.setTransition(FragmentTransaction.TRANSIT_FRAGMENT_OPEN); // To make it fullscreen, use the 'content' root view as the container // for the fragment, which is always the root view for the activity. transaction.add(android.R.id.content, newFragment) .addToBackStack(null).commit(); } }
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการทำธุรกรรมกับข้อมูลโค้ดได้ที่ข้อมูลโค้ด
ในตัวอย่างนี้ บูลีน mIsLargeLayout จะระบุว่าอุปกรณ์ปัจจุบันต้องใช้การออกแบบเลย์เอาต์ขนาดใหญ่ของแอปหรือไม่ และแสดงข้อมูลโค้ดนี้ในกล่องโต้ตอบแทนการแสดงแบบเต็มหน้าจอ วิธีที่ดีที่สุดในการตั้งค่าบูลีนประเภทนี้คือประกาศค่าทรัพยากรบูลีนที่มีค่าทรัพยากรทางเลือกสําหรับหน้าจอขนาดต่างๆ ต่อไปนี้เป็นตัวอย่างทรัพยากรบูลีน 2 เวอร์ชันสำหรับหน้าจอขนาดต่างๆ
res/values/bools.xml
<!-- Default boolean values --> <resources> <bool name="large_layout">false</bool> </resources>
res/values-large/bools.xml
<!-- Large screen boolean values --> <resources> <bool name="large_layout">true</bool> </resources>
จากนั้นคุณสามารถเริ่มต้นค่า mIsLargeLayout ในระหว่างวิธี onCreate() ของกิจกรรมได้ ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้
Kotlin
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) setContentView(R.layout.activity_main) isLargeLayout = resources.getBoolean(R.bool.large_layout) }
Java
boolean isLargeLayout; @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); isLargeLayout = getResources().getBoolean(R.bool.large_layout); }
แสดงกิจกรรมเป็นกล่องโต้ตอบบนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
แทนที่จะแสดงกล่องโต้ตอบเป็น UI แบบเต็มหน้าจอในหน้าจอขนาดเล็ก คุณก็รับผลลัพธ์แบบเดียวกันได้โดยการแสดง Activity เป็นกล่องโต้ตอบบนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ แนวทางที่คุณเลือกขึ้นอยู่กับการออกแบบแอป แต่การแสดงกิจกรรมเป็นกล่องโต้ตอบมักมีประโยชน์เมื่อแอปออกแบบมาสำหรับหน้าจอขนาดเล็กและคุณต้องการปรับปรุงประสบการณ์การใช้งานบนแท็บเล็ตด้วยการแสดงกิจกรรมที่มีระยะเวลาสั้นๆ เป็นกล่องโต้ตอบ
หากต้องการแสดงกิจกรรมเป็นกล่องโต้ตอบในหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่เท่านั้น ให้ใช้ธีม Theme.Holo.DialogWhenLarge กับองค์ประกอบไฟล์ Manifest <activity> ดังนี้
<activity android:theme="@android:style/Theme.Holo.DialogWhenLarge" >
ดูข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมเกี่ยวกับการจัดสไตล์กิจกรรมด้วยธีมได้ที่สไตล์และธีม
ปิดกล่องโต้ตอบ
เมื่อผู้ใช้แตะปุ่มดำเนินการที่สร้างด้วย AlertDialog.Builder ระบบจะปิดกล่องโต้ตอบให้คุณ
นอกจากนี้ ระบบจะปิดกล่องโต้ตอบเมื่อผู้ใช้แตะรายการในรายการของกล่องโต้ตอบด้วย ยกเว้นในกรณีที่รายการใช้ปุ่มตัวเลือกหรือช่องทําเครื่องหมาย หรือจะปิดกล่องโต้ตอบด้วยตนเองโดยเรียกใช้ dismiss() ใน DialogFragment ก็ได้
หากต้องการดำเนินการบางอย่างเมื่อกล่องโต้ตอบหายไป ให้ใช้เมธอด onDismiss() ใน DialogFragment
นอกจากนี้ คุณยังยกเลิกกล่องโต้ตอบได้ด้วย เหตุการณ์นี้เป็นเหตุการณ์พิเศษที่บ่งบอกว่าผู้ใช้ออกจากกล่องโต้ตอบโดยไม่ทํางานให้เสร็จ กรณีนี้เกิดขึ้นเมื่อผู้ใช้แตะปุ่มย้อนกลับหรือแตะหน้าจอนอกบริเวณกล่องโต้ตอบ หรือหากคุณเรียกใช้ cancel() อย่างชัดเจนใน Dialog เช่น ตอบสนองต่อปุ่ม "ยกเลิก" ในกล่องโต้ตอบ
ดังที่แสดงในตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้ คุณจะตอบกลับเหตุการณ์การยกเลิกได้โดยนำ onCancel() มาใช้ในชั้นเรียน DialogFragment

