Wear OS 手表可能会采用不同的硬件按钮配置。本指南将介绍每种按钮类型最适合的使用情形。
按钮类型
以下是 Wear OS 设备上最常见的按钮类型。
操作系统按钮

多功能按钮

按下状态
您可以通过以下方式与 Wear OS 按钮互动。
按一下

图 1. 用户按下按钮,然后迅速松开。
按住

图 2. 用户按下按钮并保持 500 毫秒或更长时间。
多功能按钮映射
您的应用可以将多功能按钮分配给相应操作,只要这样做适合应用的用例。不过,我们并不要求应用为多功能按钮分配操作。
如果存在以下任一情况,请在应用中使用多功能按钮:
- 应用存在明显的二元操作(例如播放/暂停)。
- 用户主要在不看显示屏的情况下使用应用。

图 3. 这款健身应用为一个多功能按钮分配了暂停/恢复操作,让用户可以在不看屏幕的情况下执行操作。
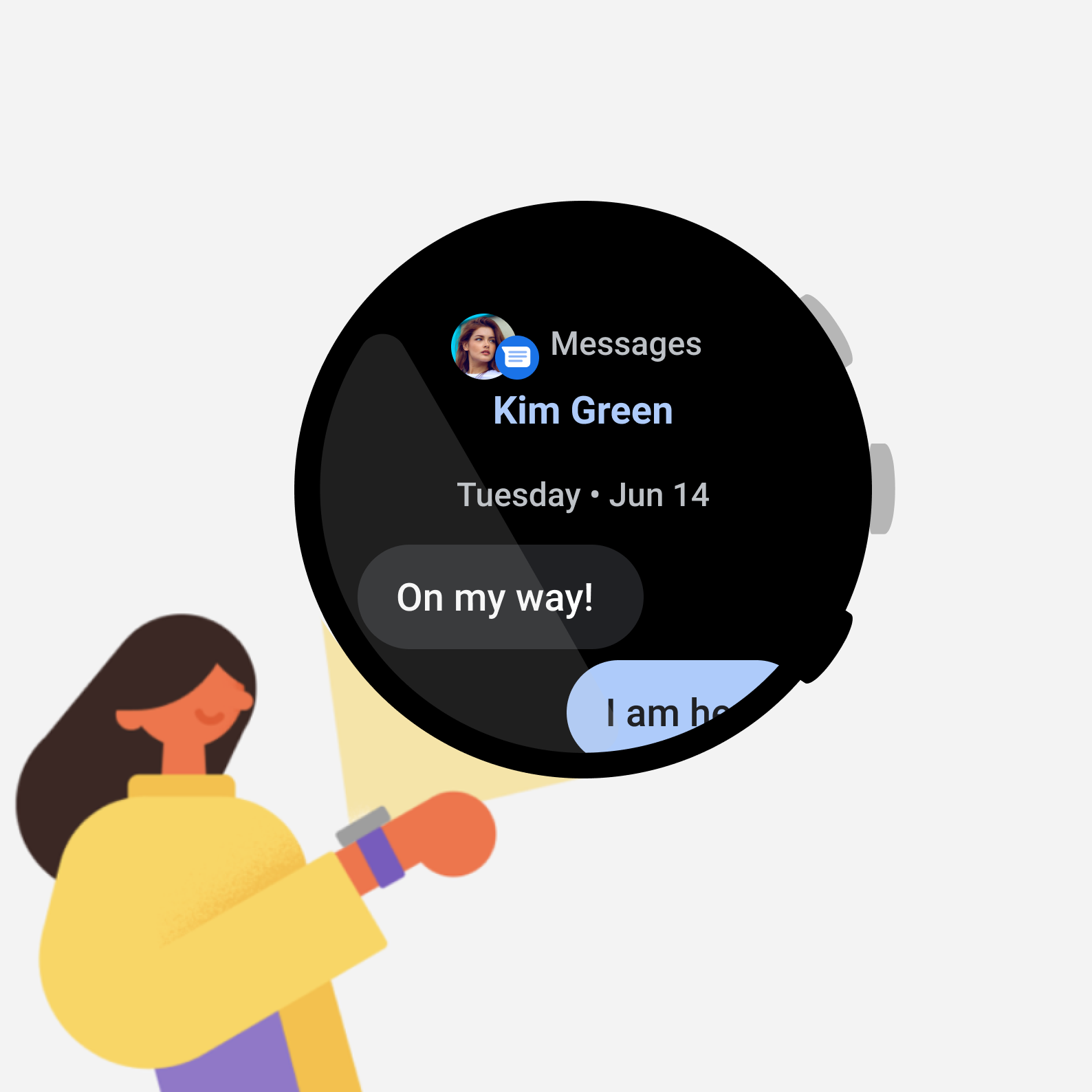
图 4. 这款即时通讯应用包括回复操作,此操作需要执行多个步骤,只按一下按钮无法完成。
二元操作
二元操作有助于用户了解每次按下按钮时会发生什么。例如,秒表上的“启动”和“停止”就构成了一项二元操作,这是很适合使用多功能按钮的一种情形。
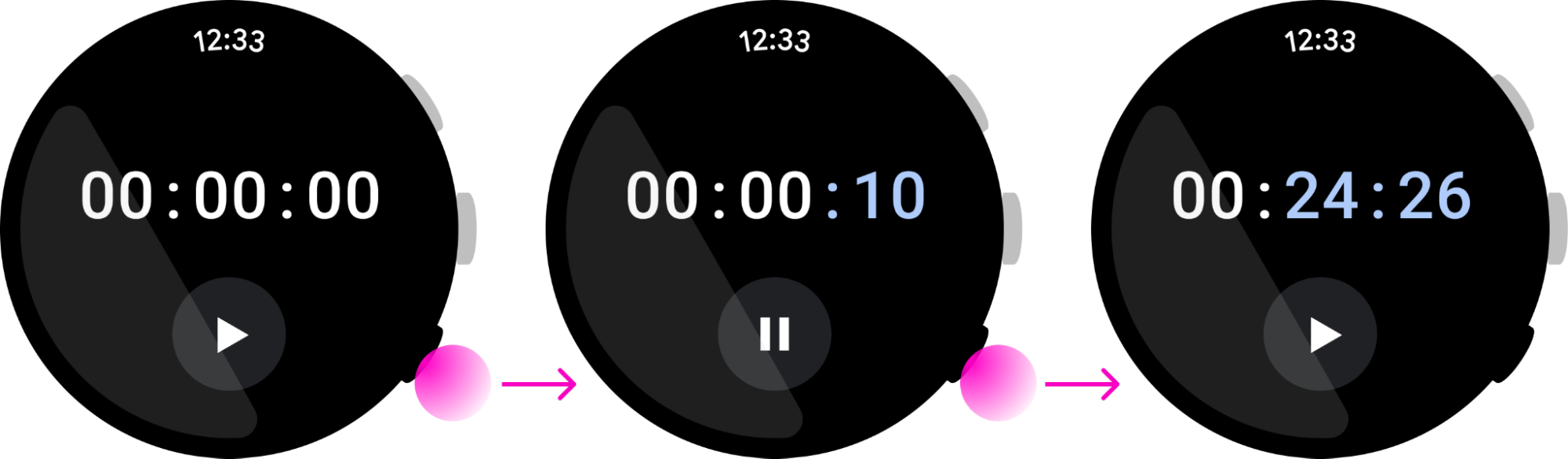
多功能按钮用作替代方案
由于某些手表没有多功能按钮,因此要让多功能按钮操作可以通过屏幕上的界面元素来使用。不过,您也可以使用多功能按钮来替代屏幕上的按钮。
如果某项操作无法使用屏幕上的界面元素来执行,请不要将多功能按钮用于该操作。
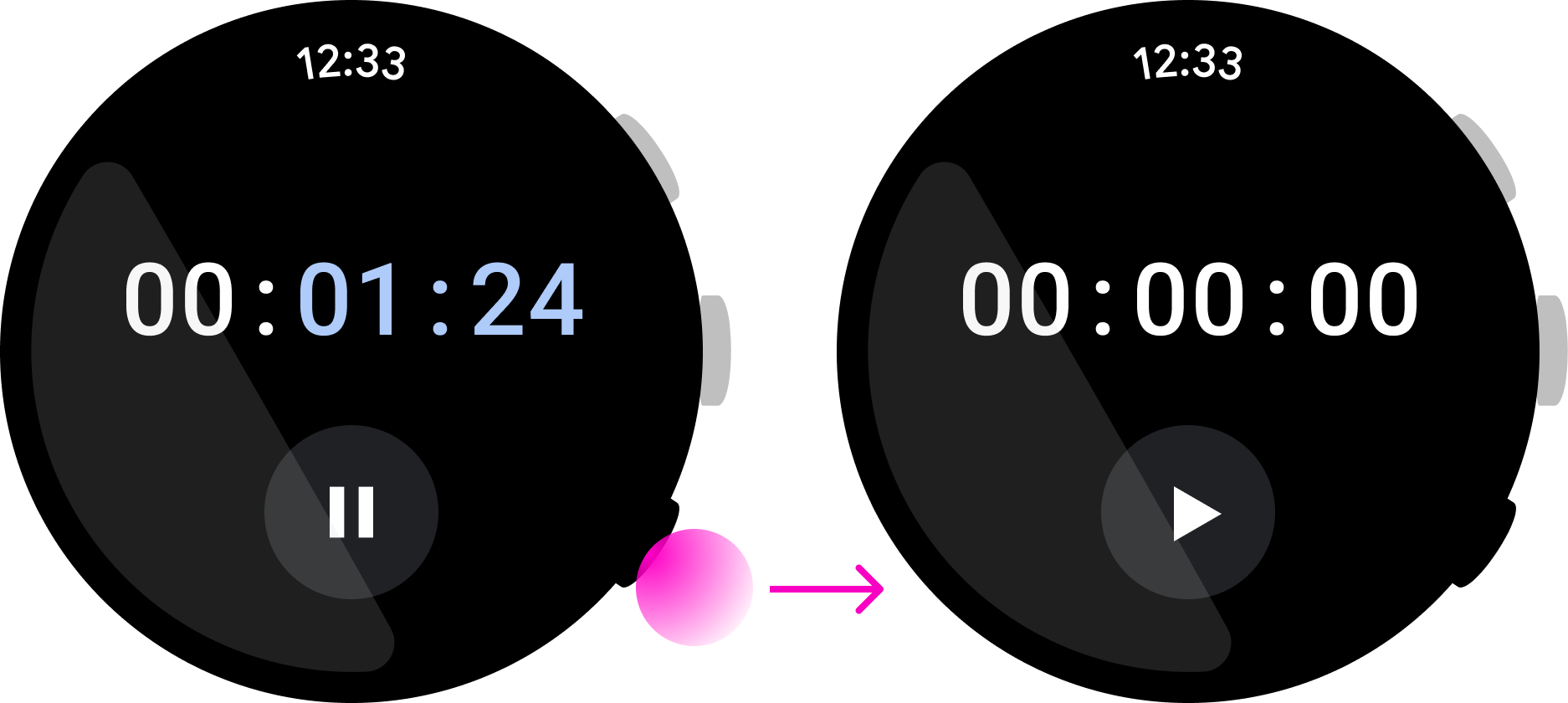
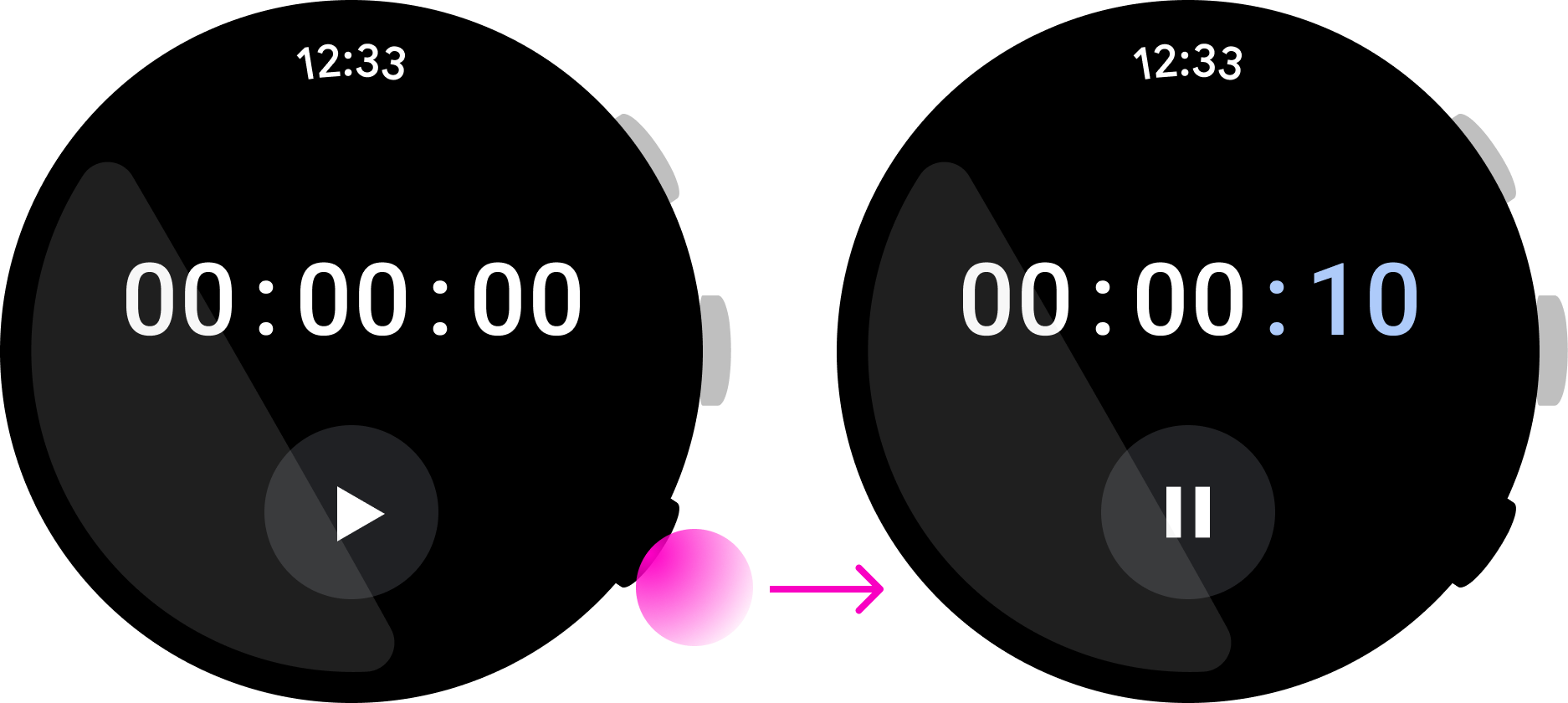
注重简洁性和即时性
按下多功能按钮应立即执行分配给它的操作。为了让用户无需查看屏幕,请使用多功能按钮执行只需按一下按钮即可完成的操作。
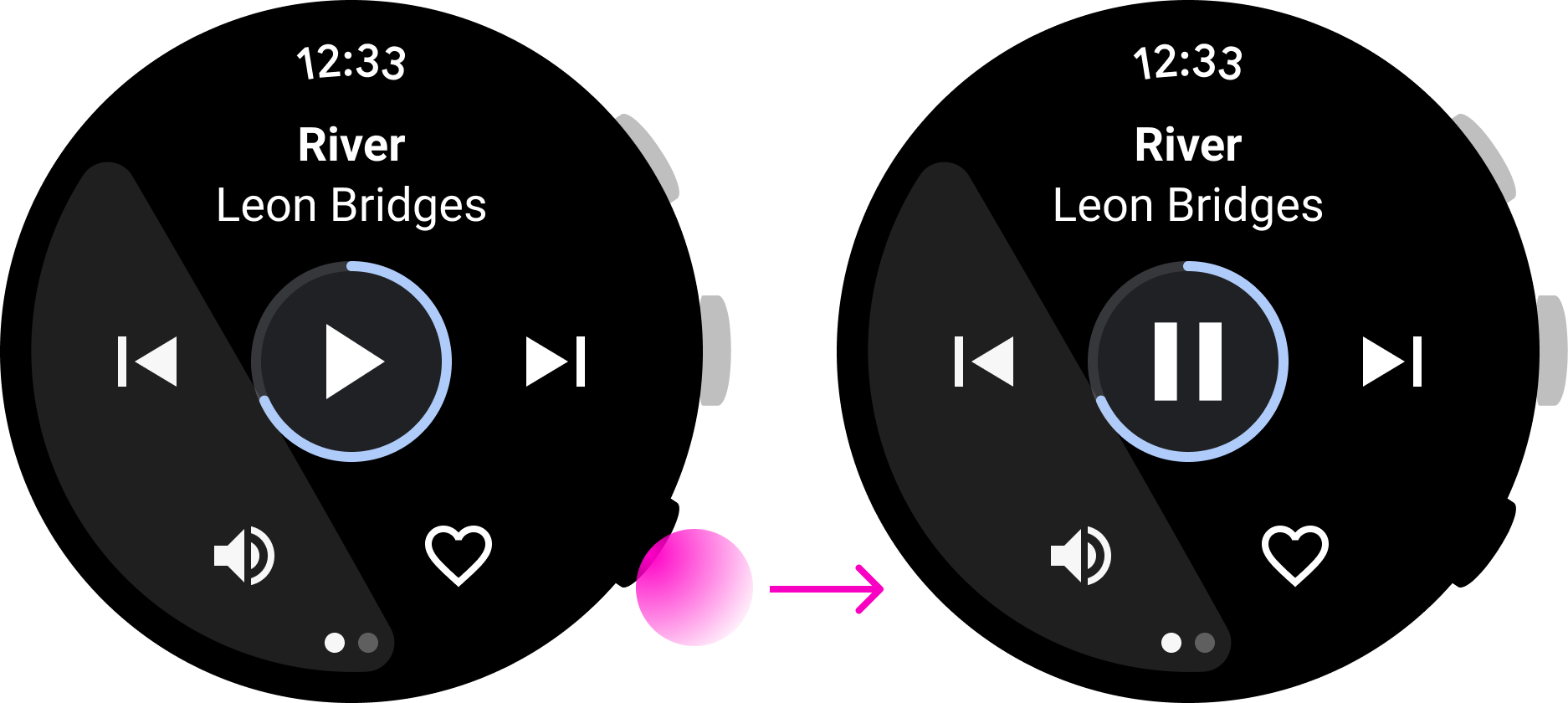
正确做法
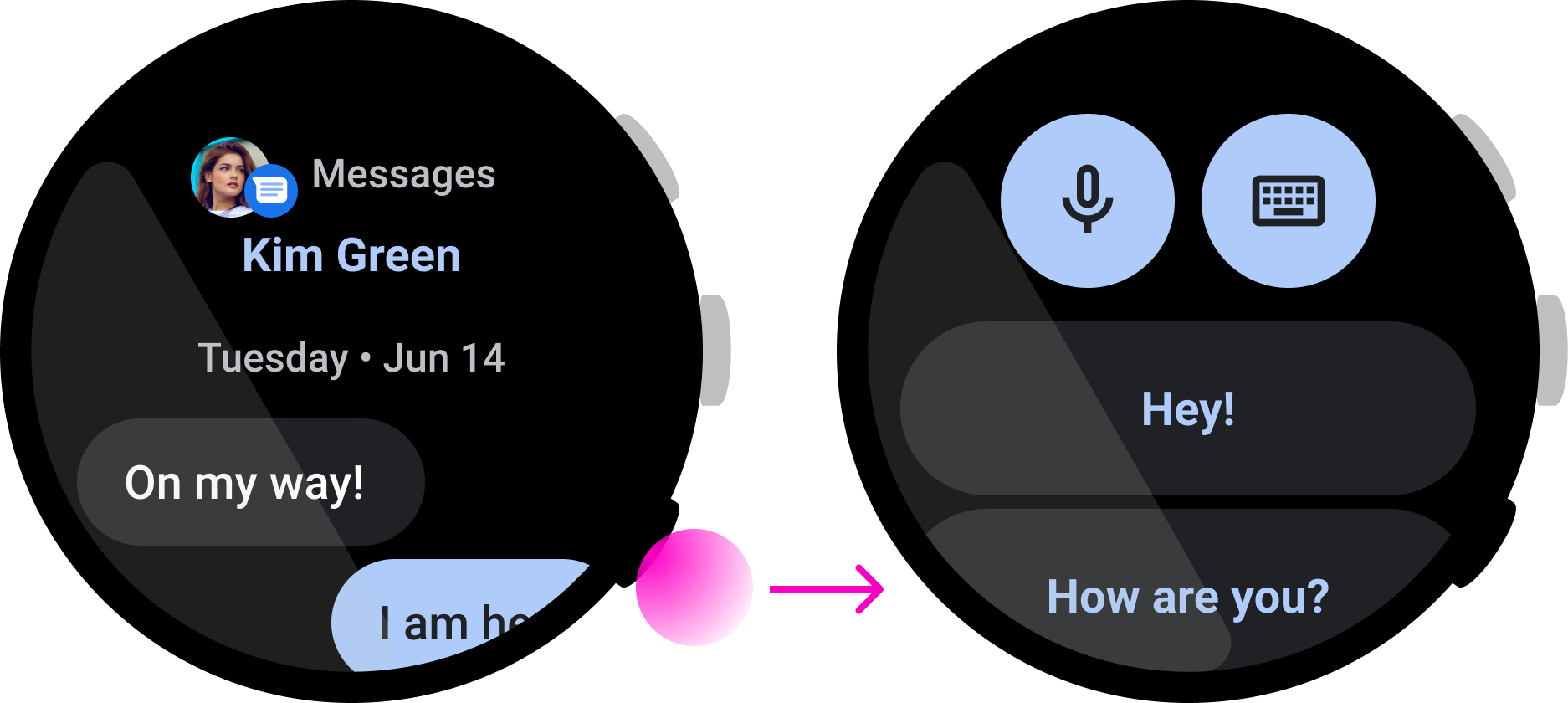
错误做法
在上面这款音乐应用中,用户可以迅速暂停播放歌曲,这是很适合使用多功能按钮的一个例子。然而,在上面这款即时通讯应用中,按下按钮就会开始回复操作,但用户在完成回复操作前可能需要先查看消息。这意味着,这种互动并不适合使用多功能按钮来完成。
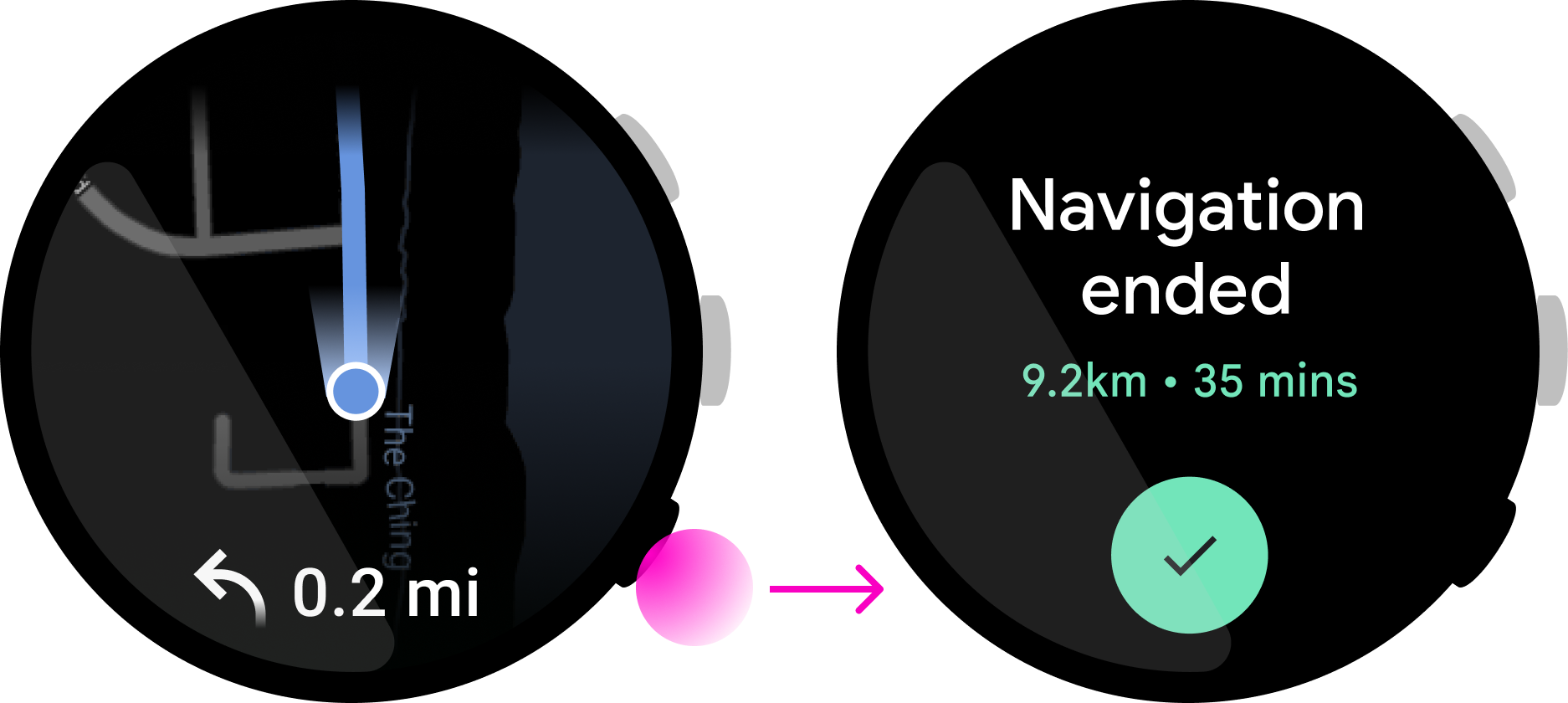
可撤消
按钮操作应当可撤消。不要使用多功能按钮触发破坏性操作,例如删除数据或停止持续性活动。以这款地图应用为例,按下多功能按钮会执行一项操作来“停止导航”,这可能导致用户在关键时刻失去方向。