本課程將說明如何建立可鏡像反映較新 API 但支援舊版裝置的實作項目。
決定替代解決方案
如要以回溯相容的方式使用新版 UI 功能,最棘手的工作,就是決定並針對舊版平台版本決定及實作舊版 (備用) 解決方案。在許多情況下,您可以使用舊版 UI 架構功能來實現新版 UI 元件的目的。例如:
-
您可以使用含有圖片按鈕的水平
LinearLayout實作動作列,做為自訂標題列或活動版面配置的檢視畫面。溢位動作可以在裝置的「選單」按鈕下方顯示。 -
如要實作動作列分頁,可使用包含按鈕的水平
LinearLayout或使用TabWidgetUI 元素。 -
NumberPicker和Switch小工具可分別使用Spinner和ToggleButton小工具實作。 -
您可以使用
PopupWindow小工具實作ListPopupWindow和PopupMenu小工具。
一般來說,將較新的 UI 元件向後移植到舊裝置時,不會有一體適用的解決方案。注意使用者體驗:在舊版裝置上,使用者可能不熟悉較新的設計模式和 UI 元件。請思考一下,如何運用熟悉的元素提供相同功能。在多數情況下,這樣就不太值得關注:如果新的 UI 元件在應用程式生態系統 (例如動作列) 很顯眼,或是互動模型相當簡單且符合直覺 (例如使用 ViewPager 滑動檢視畫面),
使用較舊的 API 實作分頁
如要建立舊版的動作列分頁實作方式,可以使用 TabWidget 和 TabHost (不過您也可以改用水平配置的 Button 小工具)。由於此實作所使用的 API 晚於 Android 2.0 (Eclair),因此在名為 TabHelperEclair 和 CompatTabEclair 的類別中實作此做法。
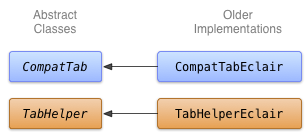
圖 1. 用於 Eclair 分頁的類別圖。
CompatTabEclair 實作會將分頁屬性 (例如分頁文字和圖示) 儲存在執行個體變數中,因為沒有可用的 ActionBar.Tab 物件來處理此儲存空間:
Kotlin
class CompatTabEclair internal constructor(val activity: FragmentActivity, tag: String) : CompatTab(tag) { // Store these properties in the instance, // as there is no ActionBar.Tab object. private var text: CharSequence? = null ... override fun setText(resId: Int): CompatTab { // Our older implementation simply stores this // information in the object instance. text = activity.resources.getText(resId) return this } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
Java
public class CompatTabEclair extends CompatTab { // Store these properties in the instance, // as there is no ActionBar.Tab object. private CharSequence text; ... public CompatTab setText(int resId) { // Our older implementation simply stores this // information in the object instance. text = activity.getResources().getText(resId); return this; } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
TabHelperEclair 實作會使用
用於建立 TabHost.TabSpec 的 TabHost 小工具
物件和分頁指標:
Kotlin
class TabHelperEclair internal constructor(activity: FragmentActivity) : TabHelper(activity) { private var tabHost: TabHost? = null ... override fun setUp() { // Our activity layout for pre-Honeycomb devices // must contain a TabHost. tabHost = tabHost ?: mActivity.findViewById<TabHost>(android.R.id.tabhost).apply { setup() } } override fun addTab(tab: CompatTab) { ... tabHost?.newTabSpec(tab.tag)?.run { setIndicator(tab.getText()) // And optional icon ... tabHost?.addTab(this) } } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
Java
public class TabHelperEclair extends TabHelper { private TabHost tabHost; ... protected void setUp() { if (tabHost == null) { // Our activity layout for pre-Honeycomb devices // must contain a TabHost. tabHost = (TabHost) mActivity.findViewById( android.R.id.tabhost); tabHost.setup(); } } public void addTab(CompatTab tab) { ... TabSpec spec = tabHost .newTabSpec(tag) .setIndicator(tab.getText()); // And optional icon ... tabHost.addTab(spec); } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
您現在有兩種實作的 CompatTab 和 TabHelper:一種適用於搭載 Android 3.0 以上版本的裝置並使用新 API,另一種則適用於搭載 Android 2.0 以上版本的裝置並使用舊版 API。下一堂課會探討如何在應用程式中使用這些實作。
