يوضِّح لك هذا الدرس كيفية وضع فئات فرعية للفئة المجرّدة CompatTab وTabHelper واستخدام واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة. يمكن لتطبيقك استخدام طريقة التنفيذ هذه على الأجهزة التي تعمل بإصدار نظام أساسي يتوافق مع هذه الإجراءات.
تنفيذ علامات التبويب باستخدام واجهات برمجة تطبيقات جديدة
الفئة الملموسة لكل من CompatTab وTabHelper التي تستخدم واجهات برمجة تطبيقات أحدث هي خادم وكيل. نظرًا لأن الفئات المجردة في الدرس السابق تعكس واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة (بنية الفئة، وتوقيعات الطرق، وما إلى ذلك)، فإن الفئات الملموسة التي تستخدم واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الحديثة هذه هي ببساطة استدعاءات طريقة الخادم الوكيل ونتائجها.
ويمكنك استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الجديدة مباشرةً في هذه الفئات، وعدم تعطُّلها على الأجهزة السابقة بسبب التحميل الكسول للفئة. يتم تحميل الفئات وإعدادها عند الوصول لأول مرة - مع إضافة الفئة أو الوصول إلى أحد حقولها أو الطرق الثابتة لأول مرة. ولهذا السبب، لن تنشئ Dalvik VM أي استثناءات VerifyError طالما أنّك لا تنشئ مثيلاً لعمليات التنفيذ الخاصة بـ Honeycomb على الأجهزة السابقة لـ Honeycomb.
هناك اصطلاح جيد لتسمية هذا التطبيق، وهو إلحاق اسم الرمز البرمجي لإصدار النظام الأساسي أو مستوى واجهة برمجة التطبيقات المقابل لواجهات برمجة التطبيقات التي تتطلّبها الفئات الملموسة. على سبيل المثال، يمكن أن توفّر الصفوف CompatTabHoneycomb وTabHelperHoneycomb علامة التبويب المدمجة مع المحتوى لأنّها تعتمد على واجهات برمجة التطبيقات المتوفّرة في الإصدار Android 3.0 (المستوى 11 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) أو الإصدارات الأحدث.
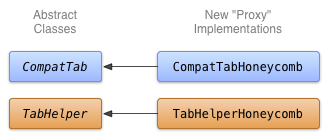
الشكل 1. مخطط لفئة تنفيذ Honeycomb لعلامات التبويب.
تنفيذ CompatTabHoneycomb
CompatTabHoneycomb هي تطبيق لفئة CompatTab المجرّدة التي يستخدمها TabHelperHoneycomb للإشارة إلى علامات تبويب فردية. يعمل CompatTabHoneycomb ببساطة على إنشاء وكيل لجميع استدعاءات الطرق إلى كائن ActionBar.Tab الموجود.
بدء تنفيذ CompatTabHoneycomb باستخدام واجهات برمجة تطبيقات ActionBar.Tab الجديدة:
Kotlin
class CompatTabHoneycomb internal constructor(val activity: Activity, tag: String) : CompatTab(tag) { ... // The native tab object that this CompatTab acts as a proxy for. private var mTab: ActionBar.Tab = // Proxy to new ActionBar.newTab API activity.actionBar.newTab() override fun setText(@StringRes textId: Int): CompatTab { // Proxy to new ActionBar.Tab.setText API mTab.setText(textId) return this } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
Java
public class CompatTabHoneycomb extends CompatTab { // The native tab object that this CompatTab acts as a proxy for. ActionBar.Tab mTab; ... protected CompatTabHoneycomb(FragmentActivity activity, String tag) { ... // Proxy to new ActionBar.newTab API mTab = activity.getActionBar().newTab(); } public CompatTab setText(int resId) { // Proxy to new ActionBar.Tab.setText API mTab.setText(resId); return this; } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
تنفيذ TabHelperHoneycomb
الدالة TabHelperHoneycomb هي تنفيذ لفئة TabHelper مجرّدة تعمل على إرسال استدعاءات طريقة وكيلة إلى ActionBar فعلية، ويتم الحصول عليها من Activity المضمّنة.
تنفيذ TabHelperHoneycomb، تنفيذ طلبات طريقة استدعاء واجهة برمجة التطبيقات ActionBar كخادم وكيل:
Kotlin
class TabHelperHoneycomb internal constructor(activity: FragmentActivity) : TabHelper(activity) { private var mActionBar: ActionBar? = null override fun setUp() { mActionBar = mActionBar ?: mActivity.actionBar.apply { navigationMode = ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS } } override fun addTab(tab: CompatTab) { // Tab is a CompatTabHoneycomb instance, so its // native tab object is an ActionBar.Tab. mActionBar?.addTab(tab.getTab() as ActionBar.Tab) } }
Java
public class TabHelperHoneycomb extends TabHelper { ActionBar actionBar; ... protected void setUp() { if (actionBar == null) { actionBar = activity.getActionBar(); actionBar.setNavigationMode( ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS); } } public void addTab(CompatTab tab) { ... // Tab is a CompatTabHoneycomb instance, so its // native tab object is an ActionBar.Tab. actionBar.addTab((ActionBar.Tab) tab.getTab()); } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
