Cải thiện trải nghiệm người dùng bằng cách đảm bảo mọi người có thể dùng ứng dụng của bạn khi kết nối mạng không ổn định hoặc khi người dùng không kết nối mạng. Có một cách để thực hiện việc này là cùng lúc phân trang từ mạng và từ cơ sở dữ liệu cục bộ. Bằng cách này, ứng dụng của bạn sẽ điều khiển giao diện người dùng từ bộ nhớ đệm của cơ sở dữ liệu cục bộ và chỉ yêu cầu kết nối mạng khi không còn dữ liệu trong cơ sở dữ liệu.
Hướng dẫn này giả định rằng bạn đã quen thuộc với thư viện lưu trữ của Phòng và cách sử dụng cơ bản của thư viện Phân trang.
Tải dữ liệu toạ độ
Thư viện Phân trang cung cấp thành phần
RemoteMediator
cho trường hợp sử dụng này. RemoteMediator đóng vai trò là tín hiệu từ thư viện Phân trang
khi ứng dụng dùng hết dữ liệu được lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm. Bạn có thể sử dụng tín hiệu này để tải dữ liệu bổ sung từ mạng, rồi lưu trữ dữ liệu đó trong cơ sở dữ liệu cục bộ, từ đó PagingSource có thể tải và cung cấp dữ liệu cho giao diện người dùng để hiển thị.
Khi cần thêm dữ liệu, thư viện Phân trang gọi phương thức
load() từ
quá trình triển khai RemoteMediator. Đây là một hàm tạm ngưng nên
có thể an tâm thực hiện công việc chạy trong thời gian dài. Hàm này thường tìm nạp dữ liệu mới từ
một nguồn mạng và lưu dữ liệu đó vào bộ nhớ cục bộ.
Quá trình này áp dụng cho cả dữ liệu mới, nhưng theo thời gian, dữ liệu được lưu trữ trong cơ sở dữ liệu
yêu cầu phải vô hiệu hoá, chẳng hạn như khi người dùng kích hoạt quá trình làm mới theo cách thủ công. Điều này
thể hiện qua thuộc tính LoadType
được chuyển đến phương thức load(). Thuộc tính LoadType sẽ thông báo cho
RemoteMediator xem cần làm mới dữ liệu hiện có hay tìm nạp
dữ liệu bổ sung để thêm vào đầu hoặc thêm vào cuối danh sách hiện tại.
Bằng cách này, RemoteMediator đảm bảo ứng dụng của bạn tải dữ liệu mà
người dùng muốn xem theo thứ tự phù hợp.
Vòng đời của hoạt động phân trang
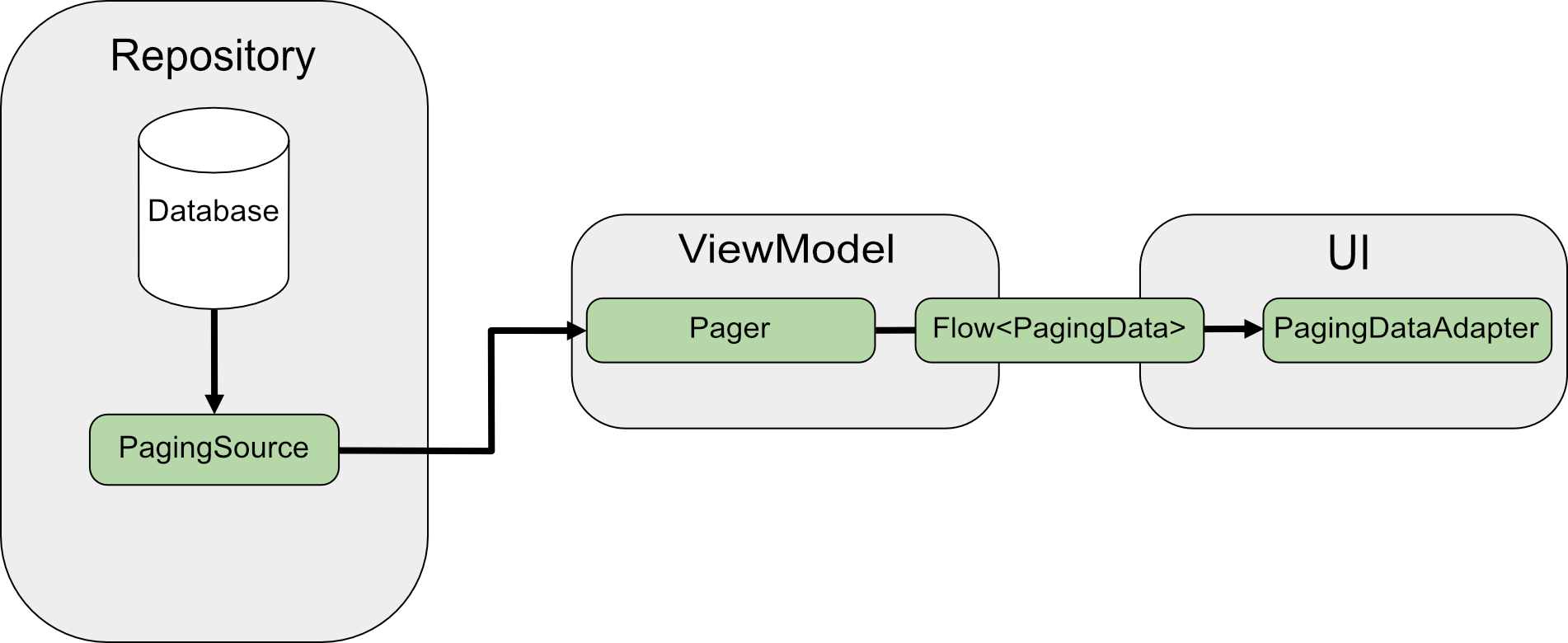
Khi phân trang trực tiếp từ mạng, PagingSource sẽ tải dữ liệu và
trả về một đối tượng
LoadResult. Quá trình triển khai PagingSource được chuyển đến
Pager thông qua tham số
pagingSourceFactory.
Vì giao diện người dùng yêu cầu dữ liệu mới, Pager gọi phương thức
load() từ
PagingSource và trả về luồng của đối tượng
PagingData
đóng gói dữ liệu mới. Mỗi đối tượng PagingData thường được lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm trong
ViewModel trước khi được gửi đến giao diện người dùng để hiển thị.
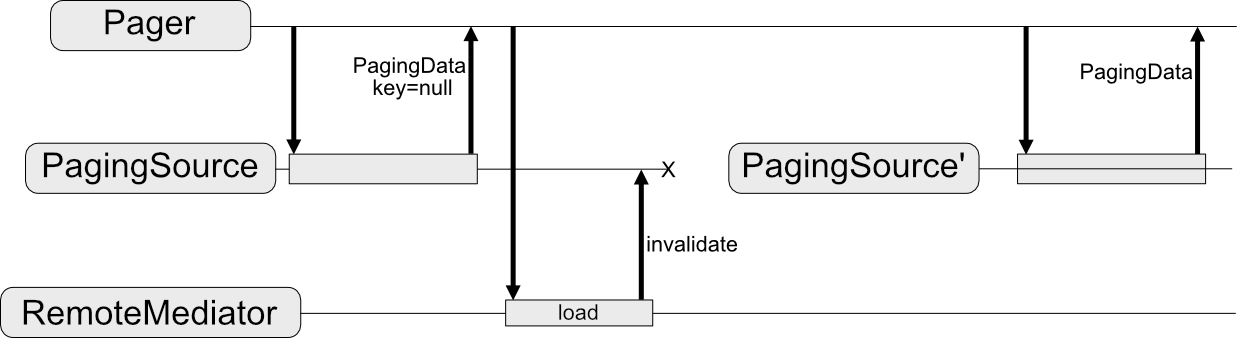
RemoteMediator sẽ thay đổi luồng dữ liệu này. PagingSource vẫn tải dữ liệu;
nhưng khi hết dữ liệu được phân trang, thư viện Phân trang kích hoạt
RemoteMediator để tải dữ liệu mới từ nguồn mạng. RemoteMediator
lưu trữ dữ liệu mới trong cơ sở dữ liệu cục bộ nên bạn không cần sử dụng bộ nhớ đệm của bộ nhớ trong
ViewModel. Cuối cùng, PagingSource sẽ tự vô hiệu hoá và
Pager tạo bản sao mới để tải dữ liệu mới từ cơ sở dữ liệu.
Cách sử dụng cơ bản
Giả sử bạn muốn ứng dụng của mình tải các trang chứa mục User từ một nguồn dữ liệu
của mạng có khoá mục vào bộ nhớ đệm cục bộ được lưu trữ trong cơ sở dữ liệu của Phòng.

Quá trình triển khai RemoteMediator giúp tải dữ liệu phân trang từ mạng vào
cơ sở dữ liệu, nhưng không trực tiếp tải dữ liệu vào giao diện người dùng. Thay vào đó, ứng dụng sử dụng
cơ sở dữ liệu làm nguồn
tin cậy. Nói cách khác, ứng dụng chỉ
hiển thị dữ liệu đã được lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm trong cơ sở dữ liệu. Quá trình triển khai PagingSource
(ví dụ: hoạt động do Phòng tạo ra) sẽ xử lý việc tải dữ liệu được lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm
từ cơ sở dữ liệu vào giao diện người dùng.
Tạo thực thể của Phòng
Trước tiên, hãy sử dụng thư viện lưu trữ của
Phòng để xác định cơ sở dữ liệu lưu giữ
bộ nhớ đệm cục bộ của dữ liệu phân trang từ nguồn dữ liệu của mạng. Bắt đầu bằng cách
triển khai RoomDatabase
như mô tả trong phần Lưu dữ liệu trong cơ sở dữ liệu cục bộ bằng
Phòng.
Tiếp theo, hãy xác định một thực thể của Phòng để đại diện bảng mục trong danh sách như mô tả trong phần
Xác định dữ liệu bằng thực thể của Phòng.
Cung cấp thực thể cho trường id để làm khoá chính cũng như các trường cho mọi
thông tin khác mà mục trong danh sách của bạn có chứa.
Kotlin
@Entity(tableName = "users") data class User(val id: String, val label: String)
Java
@Entity(tableName = "users") public class User { public String id; public String label; }
Java
@Entity(tableName = "users") public class User { public String id; public String label; }
Bạn cũng phải xác định đối tượng truy cập dữ liệu (DAO) cho thực thể này của Phòng như mô tả trong phần Truy cập dữ liệu bằng các DAO của Phòng. DAO cho các thực thể mục trong danh sách phải bao gồm những phương thức sau:
- Phương thức
insertAll()chèn danh sách mục vào bảng. - Phương thức này sẽ lấy chuỗi truy vấn làm tham số và trả về đối tượng
PagingSourcecho danh sách kết quả. Bằng cách này, đối tượngPagercó thể dùng bảng này làm nguồn của dữ liệu phân trang. - Phương thức
clearAll()xoá tất cả dữ liệu của bảng.
Kotlin
@Dao interface UserDao { @Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE) suspend fun insertAll(users: List<User>) @Query("SELECT * FROM users WHERE label LIKE :query") fun pagingSource(query: String): PagingSource<Int, User> @Query("DELETE FROM users") suspend fun clearAll() }
Java
@Dao interface UserDao { @Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE) void insertAll(List<User> users); @Query("SELECT * FROM users WHERE mLabel LIKE :query") PagingSource<Integer, User> pagingSource(String query); @Query("DELETE FROM users") int clearAll(); }
Java
@Dao interface UserDao { @Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE) void insertAll(List<User> users); @Query("SELECT * FROM users WHERE mLabel LIKE :query") PagingSource<Integer, User> pagingSource(String query); @Query("DELETE FROM users") int clearAll(); }
Triển khai RemoteMediator
Vai trò chính của RemoteMediator là tải thêm dữ liệu từ mạng khi
Pager hết dữ liệu hoặc dữ liệu hiện có không hợp lệ. Hoạt động này
bao gồm phương thức load() mà bạn phải ghi đè để xác định hành vi
tải.
Quá trình triển khai RemoteMediator thông thường bao gồm các tham số sau:
query: Chuỗi truy vấn xác định dữ liệu cần truy xuất từ dịch vụ phụ trợ.database: Cơ sở dữ liệu của Phòng đóng vai trò là bộ nhớ đệm cục bộ.networkService: Phiên bản API của dịch vụ phụ trợ.
Tạo quá trình triển khai RemoteMediator<Key, Value>. Loại Key và
Value phải giống như khi bạn xác định
PagingSource cho cùng một nguồn dữ liệu mạng. Để biết thêm thông tin về
cách chọn tham số cho loại, hãy xem phần Chọn kiểu khoá và
giá trị.
Kotlin
@OptIn(ExperimentalPagingApi::class) class ExampleRemoteMediator( private val query: String, private val database: RoomDb, private val networkService: ExampleBackendService ) : RemoteMediator<Int, User>() { val userDao = database.userDao() override suspend fun load( loadType: LoadType, state: PagingState<Int, User> ): MediatorResult { // ... } }
Java
@UseExperimental(markerClass = ExperimentalPagingApi.class) class ExampleRemoteMediator extends RxRemoteMediator<Integer, User> { private String query; private ExampleBackendService networkService; private RoomDb database; private UserDao userDao; ExampleRemoteMediator( String query, ExampleBackendService networkService, RoomDb database ) { query = query; networkService = networkService; database = database; userDao = database.userDao(); } @NotNull @Override public Single<MediatorResult> loadSingle( @NotNull LoadType loadType, @NotNull PagingState<Integer, User> state ) { ... } }
Java
class ExampleRemoteMediator extends ListenableFutureRemoteMediator<Integer, User> { private String query; private ExampleBackendService networkService; private RoomDb database; private UserDao userDao; private Executor bgExecutor; ExampleRemoteMediator( String query, ExampleBackendService networkService, RoomDb database, Executor bgExecutor ) { this.query = query; this.networkService = networkService; this.database = database; this.userDao = database.userDao(); this.bgExecutor = bgExecutor; } @NotNull @Override public ListenableFuture<MediatorResult> loadFuture( @NotNull LoadType loadType, @NotNull PagingState<Integer, User> state ) { ... } }
Phương thức load() chịu trách nhiệm cập nhật tập dữ liệu sao lưu và
vô hiệu hoá PagingSource. Một số thư viện hỗ trợ phân trang (như Phòng)
sẽ tự động xử lý việc vô hiệu hoá các đối tượng PagingSource do
triển khai hoạt động này.
Phương thức load() có 2 tham số:
PagingStatechứa thông tin về trang đã tải cho đến nay, chỉ mục đã truy cập gần đây nhất và đối tượngPagingConfigmà bạn dùng để khởi động luồng phân trang.LoadTypecho biết loại tải:REFRESH,APPENDhoặcPREPEND.
Giá trị trả về của phương thức load() là đối tượng
MediatorResult. MediatorResult có thể là
MediatorResult.Error
(bao gồm nội dung mô tả lỗi) hoặc
MediatorResult.Success
(bao gồm tín hiệu cho biết liệu có cần tải thêm dữ liệu hay không).
Phương thức load() phải thực hiện các bước sau:
- Xác định trang sẽ tải từ mạng tuỳ thuộc vào loại tải và dữ liệu đã tải tính đến thời điểm này.
- Kích hoạt yêu cầu về mạng.
- Thực hiện các hành động tuỳ thuộc vào kết quả của hoạt động tải:
- Nếu tải thành công và danh sách mục nhận được không để trống,
hãy lưu trữ các mục trong danh sách vào cơ sở dữ liệu và trả về
MediatorResult.Success(endOfPaginationReached = false). Sau khi lưu trữ dữ liệu, hãy vô hiệu hoá nguồn dữ liệu để thông báo cho thư viện Phân trang về dữ liệu mới. - Nếu tải thành công và danh sách các mục nhận đang để trống
hoặc là chỉ mục của trang cuối cùng, hãy trả về
MediatorResult.Success(endOfPaginationReached = true). Sau khi lưu trữ dữ liệu, hãy vô hiệu hoá nguồn dữ liệu để thông báo cho thư viện Phân trang về dữ liệu mới. - Nếu yêu cầu gây ra lỗi, hãy trả về
MediatorResult.Error.
- Nếu tải thành công và danh sách mục nhận được không để trống,
hãy lưu trữ các mục trong danh sách vào cơ sở dữ liệu và trả về
Kotlin
override suspend fun load( loadType: LoadType, state: PagingState<Int, User> ): MediatorResult { return try { // The network load method takes an optional after=<user.id> // parameter. For every page after the first, pass the last user // ID to let it continue from where it left off. For REFRESH, // pass null to load the first page. val loadKey = when (loadType) { LoadType.REFRESH -> null // In this example, you never need to prepend, since REFRESH // will always load the first page in the list. Immediately // return, reporting end of pagination. LoadType.PREPEND -> return MediatorResult.Success(endOfPaginationReached = true) LoadType.APPEND -> { val lastItem = state.lastItemOrNull() // You must explicitly check if the last item is null when // appending, since passing null to networkService is only // valid for initial load. If lastItem is null it means no // items were loaded after the initial REFRESH and there are // no more items to load. if (lastItem == null) { return MediatorResult.Success( endOfPaginationReached = true ) } lastItem.id } } // Suspending network load via Retrofit. This doesn't need to be // wrapped in a withContext(Dispatcher.IO) { ... } block since // Retrofit's Coroutine CallAdapter dispatches on a worker // thread. val response = networkService.searchUsers( query = query, after = loadKey ) database.withTransaction { if (loadType == LoadType.REFRESH) { userDao.deleteByQuery(query) } // Insert new users into database, which invalidates the // current PagingData, allowing Paging to present the updates // in the DB. userDao.insertAll(response.users) } MediatorResult.Success( endOfPaginationReached = response.nextKey == null ) } catch (e: IOException) { MediatorResult.Error(e) } catch (e: HttpException) { MediatorResult.Error(e) } }
Java
@NotNull @Override public Single<MediatorResult> loadSingle( @NotNull LoadType loadType, @NotNull PagingState<Integer, User> state ) { // The network load method takes an optional after=<user.id> parameter. For // every page after the first, pass the last user ID to let it continue from // where it left off. For REFRESH, pass null to load the first page. String loadKey = null; switch (loadType) { case REFRESH: break; case PREPEND: // In this example, you never need to prepend, since REFRESH will always // load the first page in the list. Immediately return, reporting end of // pagination. return Single.just(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); case APPEND: User lastItem = state.lastItemOrNull(); // You must explicitly check if the last item is null when appending, // since passing null to networkService is only valid for initial load. // If lastItem is null it means no items were loaded after the initial // REFRESH and there are no more items to load. if (lastItem == null) { return Single.just(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); } loadKey = lastItem.getId(); break; } return networkService.searchUsers(query, loadKey) .subscribeOn(Schedulers.io()) .map((Function<SearchUserResponse, MediatorResult>) response -> { database.runInTransaction(() -> { if (loadType == LoadType.REFRESH) { userDao.deleteByQuery(query); } // Insert new users into database, which invalidates the current // PagingData, allowing Paging to present the updates in the DB. userDao.insertAll(response.getUsers()); }); return new MediatorResult.Success(response.getNextKey() == null); }) .onErrorResumeNext(e -> { if (e instanceof IOException || e instanceof HttpException) { return Single.just(new MediatorResult.Error(e)); } return Single.error(e); }); }
Java
@NotNull @Override public ListenableFuture<MediatorResult> loadFuture( @NotNull LoadType loadType, @NotNull PagingState<Integer, User> state ) { // The network load method takes an optional after=<user.id> parameter. For // every page after the first, pass the last user ID to let it continue from // where it left off. For REFRESH, pass null to load the first page. String loadKey = null; switch (loadType) { case REFRESH: break; case PREPEND: // In this example, you never need to prepend, since REFRESH will always // load the first page in the list. Immediately return, reporting end of // pagination. return Futures.immediateFuture(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); case APPEND: User lastItem = state.lastItemOrNull(); // You must explicitly check if the last item is null when appending, // since passing null to networkService is only valid for initial load. // If lastItem is null it means no items were loaded after the initial // REFRESH and there are no more items to load. if (lastItem == null) { return Futures.immediateFuture(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); } loadKey = lastItem.getId(); break; } ListenableFuture<MediatorResult> networkResult = Futures.transform( networkService.searchUsers(query, loadKey), response -> { database.runInTransaction(() -> { if (loadType == LoadType.REFRESH) { userDao.deleteByQuery(query); } // Insert new users into database, which invalidates the current // PagingData, allowing Paging to present the updates in the DB. userDao.insertAll(response.getUsers()); }); return new MediatorResult.Success(response.getNextKey() == null); }, bgExecutor); ListenableFuture<MediatorResult> ioCatchingNetworkResult = Futures.catching( networkResult, IOException.class, MediatorResult.Error::new, bgExecutor ); return Futures.catching( ioCatchingNetworkResult, HttpException.class, MediatorResult.Error::new, bgExecutor ); }
Xác định phương thức khởi tạo
Quá trình triển khai RemoteMediator cũng có thể ghi đè phương thức
initialize()
để kiểm tra xem dữ liệu được lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm đã được cập nhật hay chưa và quyết định có kích hoạt
tính năng làm mới từ xa hay không. Phương thức này chạy trước khi thực hiện bất kỳ thao tác tải nào nên bạn có thể
sửa đổi cơ sở dữ liệu (ví dụ: để xoá dữ liệu cũ) trước khi kích hoạt bất kỳ
lần tải cục bộ hoặc tải từ xa nào.
Do initialize() là hàm không đồng bộ, bạn có thể tải để
xác định mức độ liên quan của dữ liệu hiện có trong cơ sở dữ liệu. Trường hợp phổ biến nhất
là dữ liệu được lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm chỉ có hiệu lực trong một khoảng thời gian nhất định.
RemoteMediator có thể kiểm tra xem liệu thời gian hết hạn này đã qua chưa. Trong
trường hợp đó, thư viện Phân trang cần làm mới dữ liệu hoàn toàn. Quá trình triển khai
initialize() sẽ trả về InitializeAction như sau:
- Trong trường hợp cần làm mới hoàn toàn dữ liệu cục bộ,
initialize()sẽ trả vềInitializeAction.LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH. Trường hợp này khiếnRemoteMediatorthực hiện thao tác làm mới từ xa để tải lại toàn bộ dữ liệu. Mọi lần tảiAPPENDhoặcPREPENDtừ xa đều phải đợi thao tác tảiREFRESHthành công thì mới có thể tiến hành. - Trong trường hợp không cần làm mới dữ liệu cục bộ,
initialize()sẽ trả vềInitializeAction.SKIP_INITIAL_REFRESH. Trường hợp này khiếnRemoteMediatorbỏ qua thao tác làm mới từ xa và tải dữ liệu được lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm.
Kotlin
override suspend fun initialize(): InitializeAction { val cacheTimeout = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(1, TimeUnit.HOURS) return if (System.currentTimeMillis() - db.lastUpdated() <= cacheTimeout) { // Cached data is up-to-date, so there is no need to re-fetch // from the network. InitializeAction.SKIP_INITIAL_REFRESH } else { // Need to refresh cached data from network; returning // LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH here will also block RemoteMediator's // APPEND and PREPEND from running until REFRESH succeeds. InitializeAction.LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH } }
Java
@NotNull @Override public Single<InitializeAction> initializeSingle() { long cacheTimeout = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(1, TimeUnit.HOURS); return mUserDao.lastUpdatedSingle() .map(lastUpdatedMillis -> { if (System.currentTimeMillis() - lastUpdatedMillis <= cacheTimeout) { // Cached data is up-to-date, so there is no need to re-fetch // from the network. return InitializeAction.SKIP_INITIAL_REFRESH; } else { // Need to refresh cached data from network; returning // LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH here will also block RemoteMediator's // APPEND and PREPEND from running until REFRESH succeeds. return InitializeAction.LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH; } }); }
Java
@NotNull @Override public ListenableFuture<InitializeAction> initializeFuture() { long cacheTimeout = TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS.convert(1, TimeUnit.HOURS); return Futures.transform( mUserDao.lastUpdated(), lastUpdatedMillis -> { if (System.currentTimeMillis() - lastUpdatedMillis <= cacheTimeout) { // Cached data is up-to-date, so there is no need to re-fetch // from the network. return InitializeAction.SKIP_INITIAL_REFRESH; } else { // Need to refresh cached data from network; returning // LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH here will also block RemoteMediator's // APPEND and PREPEND from running until REFRESH succeeds. return InitializeAction.LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH; } }, mBgExecutor); }
Tạo trình chuyển trang
Cuối cùng, bạn phải tạo một phiên bản Pager để thiết lập luồng dữ liệu phân trang.
Thao tác này tương tự như việc tạo Pager từ một nguồn dữ liệu mạng đơn giản, nhưng
bạn phải thực hiện hai công việc khác nhau:
- Thay vì chuyển trực tiếp hàm dựng
PagingSource, bạn phải cung cấp phương thức truy vấn trả về đối tượngPagingSourcetừ DAO. - Bạn phải cung cấp một bản sao của quá trình triển khai
RemoteMediatordưới dạng tham số củaremoteMediator.
Kotlin
val userDao = database.userDao() val pager = Pager( config = PagingConfig(pageSize = 50) remoteMediator = ExampleRemoteMediator(query, database, networkService) ) { userDao.pagingSource(query) }
Java
UserDao userDao = database.userDao(); Pager<Integer, User> pager = Pager( new PagingConfig(/* pageSize = */ 20), null, // initialKey, new ExampleRemoteMediator(query, database, networkService) () -> userDao.pagingSource(query));
Java
UserDao userDao = database.userDao(); Pager<Integer, User> pager = Pager( new PagingConfig(/* pageSize = */ 20), null, // initialKey new ExampleRemoteMediator(query, database, networkService, bgExecutor), () -> userDao.pagingSource(query));
Xử lý tình trạng tranh đua
Một tình huống mà ứng dụng của bạn cần phải xử lý khi tải dữ liệu từ nhiều nguồn là trường hợp dữ liệu được lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm cục bộ không đồng bộ với nguồn dữ liệu từ xa.
Khi phương thức initialize() từ quá trình triển khai RemoteMediator trả về
LAUNCH_INITIAL_REFRESH, dữ liệu đã hết hạn và phải được thay thế bằng dữ liệu
mới. Mọi yêu cầu tải PREPEND hoặc APPEND phải chờ yêu cầu tải
REFRESH từ xa thành công trước. Do các yêu cầu PREPEND hoặc APPEND đã
được đưa vào hàng đợi trước yêu cầu REFRESH, nên có thể PagingState
được chuyển tới các lệnh gọi tải đó sẽ hết hạn vào thời điểm chạy.
Tuỳ thuộc vào cách lưu trữ dữ liệu cục bộ, ứng dụng của bạn có thể bỏ qua những yêu cầu thừa
nếu các thay đổi đối với dữ liệu được lưu vào bộ nhớ đệm gây ra tình trạng vô hiệu hoá và phải tìm nạp dữ liệu mới.
Ví dụ: Phòng sẽ vô hiệu hoá các truy vấn về mọi hoạt động chèn dữ liệu. Điều đó đồng nghĩa các đối tượng
PagingSource mới có dữ liệu đã làm mới sẽ được cung cấp cho các yêu cầu tải đang chờ xử lý
khi dữ liệu mới được chèn vào cơ sở dữ liệu.
Nhằm đảm bảo người dùng xem được dữ liệu đã cập nhật và phù hợp nhất, việc giải quyết vấn đề đồng bộ hoá dữ liệu này là rất cần thiết. Giải pháp tốt nhất phụ thuộc chủ yếu vào cách nguồn dữ liệu mạng phân trang dữ liệu. Trong mọi trường hợp, khoá từ xa đều cho phép bạn lưu thông tin về trang gần đây nhất được yêu cầu từ máy chủ. Ứng dụng của bạn có thể dùng thông tin này để xác định và yêu cầu đúng trang dữ liệu cần tải tiếp theo.
Quản lý khoá từ xa
Khoá từ xa là các khoá mà quá trình triển khai RemoteMediator sử dụng để cho
dịch vụ phụ trợ biết dữ liệu cần tải tiếp theo. Trong trường hợp đơn giản nhất, mỗi mục của
dữ liệu phân trang bao gồm một khoá từ xa mà bạn có thể dễ dàng tham chiếu. Tuy nhiên, nếu
khoá từ xa không tương ứng với từng mục, bạn cần lưu trữ riêng các khoá này
và quản lý bằng phương thức load() của mình.
Phần này mô tả cách thu thập, lưu trữ và cập nhật khoá từ xa không được lưu trữ trong các mục riêng lẻ.
Khoá mục
Phần này mô tả cách thao tác với khoá từ xa tương ứng với
các mục riêng lẻ. Thông thường, khi khoá API bị gỡ khỏi các mục riêng lẻ, mã mục
sẽ được chuyển đi dưới dạng tham số truy vấn. Tên tham số cho biết
máy chủ có cần phản hồi các mục trước hoặc sau khi nhận được mã nhận dạng hay không. Trong ví dụ
về lớp mô hình User, trường id từ máy chủ được dùng làm khoá
từ xa khi yêu cầu thêm dữ liệu.
Khi phương thức load() cần quản lý khoá từ xa của một số mục, các khoá này
thường là mã nhận dạng của dữ liệu được nạp từ máy chủ. Làm mới các thao tác
không cần khoá tải, do những thao tác này chỉ truy xuất dữ liệu gần đây nhất.
Tương tự, các thao tác thêm vào đầu không cần tìm nạp bất kỳ dữ liệu bổ sung nào vì
hoạt động làm mới luôn lấy dữ liệu mới nhất từ máy chủ.
Tuy nhiên, thao tác thêm vào cuối cần có mã nhận dạng. Hoạt động này yêu cầu bạn phải tải
mục mới nhất từ cơ sở dữ liệu và sử dụng mã nhận dạng để tải trang dữ liệu tiếp theo. Nếu
không có mục nào trong cơ sở dữ liệu, endOfPaginationReached được đặt thành đúng,
cho biết cần làm mới dữ liệu.
Kotlin
@OptIn(ExperimentalPagingApi::class) class ExampleRemoteMediator( private val query: String, private val database: RoomDb, private val networkService: ExampleBackendService ) : RemoteMediator<Int, User>() { val userDao = database.userDao() override suspend fun load( loadType: LoadType, state: PagingState<Int, User> ): MediatorResult { return try { // The network load method takes an optional String // parameter. For every page after the first, pass the String // token returned from the previous page to let it continue // from where it left off. For REFRESH, pass null to load the // first page. val loadKey = when (loadType) { LoadType.REFRESH -> null // In this example, you never need to prepend, since REFRESH // will always load the first page in the list. Immediately // return, reporting end of pagination. LoadType.PREPEND -> return MediatorResult.Success( endOfPaginationReached = true ) // Get the last User object id for the next RemoteKey. LoadType.APPEND -> { val lastItem = state.lastItemOrNull() // You must explicitly check if the last item is null when // appending, since passing null to networkService is only // valid for initial load. If lastItem is null it means no // items were loaded after the initial REFRESH and there are // no more items to load. if (lastItem == null) { return MediatorResult.Success( endOfPaginationReached = true ) } lastItem.id } } // Suspending network load via Retrofit. This doesn't need to // be wrapped in a withContext(Dispatcher.IO) { ... } block // since Retrofit's Coroutine CallAdapter dispatches on a // worker thread. val response = networkService.searchUsers(query, loadKey) // Store loaded data, and next key in transaction, so that // they're always consistent. database.withTransaction { if (loadType == LoadType.REFRESH) { userDao.deleteByQuery(query) } // Insert new users into database, which invalidates the // current PagingData, allowing Paging to present the updates // in the DB. userDao.insertAll(response.users) } // End of pagination has been reached if no users are returned from the // service MediatorResult.Success( endOfPaginationReached = response.users.isEmpty() ) } catch (e: IOException) { MediatorResult.Error(e) } catch (e: HttpException) { MediatorResult.Error(e) } } }
Java
@NotNull @Override public Single>MediatorResult< loadSingle( @NotNull LoadType loadType, @NotNull PagingState>Integer, User< state ) { // The network load method takes an optional String parameter. For every page // after the first, pass the String token returned from the previous page to // let it continue from where it left off. For REFRESH, pass null to load the // first page. Single>String< remoteKeySingle = null; switch (loadType) { case REFRESH: // Initial load should use null as the page key, so you can return null // directly. remoteKeySingle = Single.just(null); break; case PREPEND: // In this example, you never need to prepend, since REFRESH will always // load the first page in the list. Immediately return, reporting end of // pagination. return Single.just(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); case APPEND: User lastItem = state.lastItemOrNull(); // You must explicitly check if the last item is null when // appending, since passing null to networkService is only // valid for initial load. If lastItem is null it means no // items were loaded after the initial REFRESH and there are // no more items to load. if (lastItem == null) { return Single.just(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); } remoteKeySingle = Single.just(lastItem.getId()); break; } return remoteKeySingle .subscribeOn(Schedulers.io()) .flatMap((Function<String, Single<MediatorResult>>) remoteKey -> { return networkService.searchUsers(query, remoteKey) .map(response -> { database.runInTransaction(() -> { if (loadType == LoadType.REFRESH) { userDao.deleteByQuery(query); } // Insert new users into database, which invalidates the current // PagingData, allowing Paging to present the updates in the DB. userDao.insertAll(response.getUsers()); }); return new MediatorResult.Success(response.getUsers().isEmpty()); }); }) .onErrorResumeNext(e -> { if (e instanceof IOException || e instanceof HttpException) { return Single.just(new MediatorResult.Error(e)); } return Single.error(e); }); }
Java
@NotNull @Override public ListenableFuture<MediatorResult> loadFuture( @NotNull LoadType loadType, @NotNull PagingState<Integer, User> state ) { // The network load method takes an optional after=<user.id> parameter. // For every page after the first, pass the last user ID to let it continue // from where it left off. For REFRESH, pass null to load the first page. ResolvableFuture<String> remoteKeyFuture = ResolvableFuture.create(); switch (loadType) { case REFRESH: remoteKeyFuture.set(null); break; case PREPEND: // In this example, you never need to prepend, since REFRESH will always // load the first page in the list. Immediately return, reporting end of // pagination. return Futures.immediateFuture(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); case APPEND: User lastItem = state.lastItemOrNull(); // You must explicitly check if the last item is null when appending, // since passing null to networkService is only valid for initial load. // If lastItem is null it means no items were loaded after the initial // REFRESH and there are no more items to load. if (lastItem == null) { return Futures.immediateFuture(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); } remoteKeyFuture.set(lastItem.getId()); break; } return Futures.transformAsync(remoteKeyFuture, remoteKey -> { ListenableFuture<MediatorResult> networkResult = Futures.transform( networkService.searchUsers(query, remoteKey), response -> { database.runInTransaction(() -> { if (loadType == LoadType.REFRESH) { userDao.deleteByQuery(query); } // Insert new users into database, which invalidates the current // PagingData, allowing Paging to present the updates in the DB. userDao.insertAll(response.getUsers()); }); return new MediatorResult.Success(response.getUsers().isEmpty()); }, bgExecutor); ListenableFuture<MediatorResult> ioCatchingNetworkResult = Futures.catching( networkResult, IOException.class, MediatorResult.Error::new, bgExecutor ); return Futures.catching( ioCatchingNetworkResult, HttpException.class, MediatorResult.Error::new, bgExecutor ); }, bgExecutor); }
Khoá trang
Phần này mô tả cách thao tác với khoá từ xa không tương ứng với các mục riêng lẻ.
Thêm bảng khoá từ xa
Khi các khoá từ xa không được liên kết trực tiếp với các mục trong danh sách, bạn nên lưu trữ các khoá đó vào một bảng riêng trong cơ sở dữ liệu cục bộ. Xác định thực thể của Phòng thể hiện bảng khoá từ xa:
Kotlin
@Entity(tableName = "remote_keys") data class RemoteKey(val label: String, val nextKey: String?)
Java
@Entity(tableName = "remote_keys") public class RemoteKey { public String label; public String nextKey; }
Java
@Entity(tableName = "remote_keys") public class RemoteKey { public String label; public String nextKey; }
Bạn cũng phải xác định DAO cho thực thể RemoteKey:
Kotlin
@Dao interface RemoteKeyDao { @Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE) suspend fun insertOrReplace(remoteKey: RemoteKey) @Query("SELECT * FROM remote_keys WHERE label = :query") suspend fun remoteKeyByQuery(query: String): RemoteKey @Query("DELETE FROM remote_keys WHERE label = :query") suspend fun deleteByQuery(query: String) }
Java
@Dao interface RemoteKeyDao { @Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE) void insertOrReplace(RemoteKey remoteKey); @Query("SELECT * FROM remote_keys WHERE label = :query") Single<RemoteKey> remoteKeyByQuerySingle(String query); @Query("DELETE FROM remote_keys WHERE label = :query") void deleteByQuery(String query); }
Java
@Dao interface RemoteKeyDao { @Insert(onConflict = OnConflictStrategy.REPLACE) void insertOrReplace(RemoteKey remoteKey); @Query("SELECT * FROM remote_keys WHERE label = :query") ListenableFuture<RemoteKey> remoteKeyByQueryFuture(String query); @Query("DELETE FROM remote_keys WHERE label = :query") void deleteByQuery(String query); }
Tải bằng khoá từ xa
Khi phương thức load() cần quản lý các khoá trang từ xa, bạn phải thay đổi quy trình xác định
các khoá này bằng những cách sau để so với cách sử dụng thông thường của
RemoteMediator:
- Thêm một thuộc tính bổ sung chứa tệp tham chiếu đến DAO cho bảng khoá từ xa của bạn.
- Xác định khoá cần tải tiếp theo bằng cách truy vấn bảng khoá từ xa thay vì
sử dụng
PagingState. - Ngoài dữ liệu phân trang, hãy chèn thêm hoặc lưu trữ khoá từ xa được trả về từ nguồn dữ liệu mạng.
Kotlin
@OptIn(ExperimentalPagingApi::class) class ExampleRemoteMediator( private val query: String, private val database: RoomDb, private val networkService: ExampleBackendService ) : RemoteMediator<Int, User>() { val userDao = database.userDao() val remoteKeyDao = database.remoteKeyDao() override suspend fun load( loadType: LoadType, state: PagingState<Int, User> ): MediatorResult { return try { // The network load method takes an optional String // parameter. For every page after the first, pass the String // token returned from the previous page to let it continue // from where it left off. For REFRESH, pass null to load the // first page. val loadKey = when (loadType) { LoadType.REFRESH -> null // In this example, you never need to prepend, since REFRESH // will always load the first page in the list. Immediately // return, reporting end of pagination. LoadType.PREPEND -> return MediatorResult.Success( endOfPaginationReached = true ) // Query remoteKeyDao for the next RemoteKey. LoadType.APPEND -> { val remoteKey = database.withTransaction { remoteKeyDao.remoteKeyByQuery(query) } // You must explicitly check if the page key is null when // appending, since null is only valid for initial load. // If you receive null for APPEND, that means you have // reached the end of pagination and there are no more // items to load. if (remoteKey.nextKey == null) { return MediatorResult.Success( endOfPaginationReached = true ) } remoteKey.nextKey } } // Suspending network load via Retrofit. This doesn't need to // be wrapped in a withContext(Dispatcher.IO) { ... } block // since Retrofit's Coroutine CallAdapter dispatches on a // worker thread. val response = networkService.searchUsers(query, loadKey) // Store loaded data, and next key in transaction, so that // they're always consistent. database.withTransaction { if (loadType == LoadType.REFRESH) { remoteKeyDao.deleteByQuery(query) userDao.deleteByQuery(query) } // Update RemoteKey for this query. remoteKeyDao.insertOrReplace( RemoteKey(query, response.nextKey) ) // Insert new users into database, which invalidates the // current PagingData, allowing Paging to present the updates // in the DB. userDao.insertAll(response.users) } MediatorResult.Success( endOfPaginationReached = response.nextKey == null ) } catch (e: IOException) { MediatorResult.Error(e) } catch (e: HttpException) { MediatorResult.Error(e) } } }
Java
@NotNull @Override public Single<MediatorResult> loadSingle( @NotNull LoadType loadType, @NotNull PagingState<Integer, User> state ) { // The network load method takes an optional String parameter. For every page // after the first, pass the String token returned from the previous page to // let it continue from where it left off. For REFRESH, pass null to load the // first page. Single<RemoteKey> remoteKeySingle = null; switch (loadType) { case REFRESH: // Initial load should use null as the page key, so you can return null // directly. remoteKeySingle = Single.just(new RemoteKey(mQuery, null)); break; case PREPEND: // In this example, you never need to prepend, since REFRESH will always // load the first page in the list. Immediately return, reporting end of // pagination. return Single.just(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); case APPEND: // Query remoteKeyDao for the next RemoteKey. remoteKeySingle = mRemoteKeyDao.remoteKeyByQuerySingle(mQuery); break; } return remoteKeySingle .subscribeOn(Schedulers.io()) .flatMap((Function<RemoteKey, Single<MediatorResult>>) remoteKey -> { // You must explicitly check if the page key is null when appending, // since null is only valid for initial load. If you receive null // for APPEND, that means you have reached the end of pagination and // there are no more items to load. if (loadType != REFRESH && remoteKey.getNextKey() == null) { return Single.just(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); } return networkService.searchUsers(query, remoteKey.getNextKey()) .map(response -> { database.runInTransaction(() -> { if (loadType == LoadType.REFRESH) { userDao.deleteByQuery(query); remoteKeyDao.deleteByQuery(query); } // Update RemoteKey for this query. remoteKeyDao.insertOrReplace(new RemoteKey(query, response.getNextKey())); // Insert new users into database, which invalidates the current // PagingData, allowing Paging to present the updates in the DB. userDao.insertAll(response.getUsers()); }); return new MediatorResult.Success(response.getNextKey() == null); }); }) .onErrorResumeNext(e -> { if (e instanceof IOException || e instanceof HttpException) { return Single.just(new MediatorResult.Error(e)); } return Single.error(e); }); }
Java
@NotNull @Override public ListenableFuture<MediatorResult> loadFuture( @NotNull LoadType loadType, @NotNull PagingState<Integer, User> state ) { // The network load method takes an optional after=<user.id> parameter. For // every page after the first, pass the last user ID to let it continue from // where it left off. For REFRESH, pass null to load the first page. ResolvableFuture<RemoteKey> remoteKeyFuture = ResolvableFuture.create(); switch (loadType) { case REFRESH: remoteKeyFuture.set(new RemoteKey(query, null)); break; case PREPEND: // In this example, you never need to prepend, since REFRESH will always // load the first page in the list. Immediately return, reporting end of // pagination. return Futures.immediateFuture(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); case APPEND: User lastItem = state.lastItemOrNull(); // You must explicitly check if the last item is null when appending, // since passing null to networkService is only valid for initial load. // If lastItem is null it means no items were loaded after the initial // REFRESH and there are no more items to load. if (lastItem == null) { return Futures.immediateFuture(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); } // Query remoteKeyDao for the next RemoteKey. remoteKeyFuture.setFuture( remoteKeyDao.remoteKeyByQueryFuture(query)); break; } return Futures.transformAsync(remoteKeyFuture, remoteKey -> { // You must explicitly check if the page key is null when appending, // since null is only valid for initial load. If you receive null // for APPEND, that means you have reached the end of pagination and // there are no more items to load. if (loadType != LoadType.REFRESH && remoteKey.getNextKey() == null) { return Futures.immediateFuture(new MediatorResult.Success(true)); } ListenableFuture<MediatorResult> networkResult = Futures.transform( networkService.searchUsers(query, remoteKey.getNextKey()), response -> { database.runInTransaction(() -> { if (loadType == LoadType.REFRESH) { userDao.deleteByQuery(query); remoteKeyDao.deleteByQuery(query); } // Update RemoteKey for this query. remoteKeyDao.insertOrReplace(new RemoteKey(query, response.getNextKey())); // Insert new users into database, which invalidates the current // PagingData, allowing Paging to present the updates in the DB. userDao.insertAll(response.getUsers()); }); return new MediatorResult.Success(response.getNextKey() == null); }, bgExecutor); ListenableFuture<MediatorResult> ioCatchingNetworkResult = Futures.catching( networkResult, IOException.class, MediatorResult.Error::new, bgExecutor ); return Futures.catching( ioCatchingNetworkResult, HttpException.class, MediatorResult.Error::new, bgExecutor ); }, bgExecutor); }
Làm mới tại chỗ
Nếu ứng dụng của bạn chỉ cần hỗ trợ làm mới mạng từ đầu danh sách như
trong các ví dụ trước đó, RemoteMediator của bạn không cần xác định
hoạt động tải thêm vào trước.
Tuy nhiên, nếu ứng dụng của bạn cần hỗ trợ tải dần lên từ mạng
vào cơ sở dữ liệu cục bộ thì bạn phải tiếp tục hỗ trợ quá trình phân trang
bắt đầu từ điểm neo, vị trí cuộn của người dùng. Quá trình triển khai PagingSource
của Phòng sẽ giúp bạn xử lý vấn đề này, nhưng nếu không sử dụng Phòng, bạn có thể thực hiện
bằng cách ghi đè
PagingSource.getRefreshKey().
Để tìm hiểu ví dụ về quá trình triển khai getRefreshKey(), hãy xem phần Xác định
PagingSource.
Hình 4 minh hoạ quá trình tải dữ liệu ban đầu từ cơ sở dữ liệu cục bộ, sau đó là quá trình tải dữ liệu từ mạng khi cơ sở dữ liệu đã hết dữ liệu.

Tài nguyên khác
Để tìm hiểu thêm về thư viện Paging, hãy xem các tài nguyên khác sau đây:
Lớp học lập trình
Mẫu
Đề xuất cho bạn
- Lưu ý: văn bản có đường liên kết sẽ hiện khi JavaScript tắt
- Tải và hiện dữ liệu được phân trang
- Kiểm thử việc triển khai Phân trang (Paging)
- Di chuyển sang Paging 3
