يتوقع كل حقل نصي نوعًا معيّنًا من إدخال النص، مثل عنوان بريد إلكتروني أو رقم هاتف أو نص عادي. يجب تحديد نوع الإدخال لكل حقل نص في تطبيقك حتى يعرض النظام طريقة الإدخال المناسبة، مثل لوحة مفاتيح على الشاشة.
بالإضافة إلى نوع الأزرار المتاحة مع أسلوب الإدخال، يمكنك تحديد سلوكيات، مثل ما إذا كان أسلوب الإدخال يقدّم اقتراحات إملائية ويكتب الجمل الجديدة بأحرف كبيرة ويحلّ محل زر "مفتاح المسافة" بزر إجراء مثل تم أو التالي. توضّح هذه الصفحة كيفية تحديد هذه الخصائص.
تحديد نوع لوحة المفاتيح
حدِّد دائمًا طريقة الإدخال لحقول النص من خلال إضافة سمة
android:inputType
إلى العنصر
<EditText>.
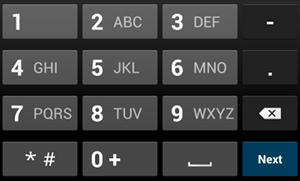
phoneعلى سبيل المثال، إذا كنت تريد طريقة إدخال لإدخال رقم هاتف، استخدِم القيمة
"phone":
<EditText android:id="@+id/phone" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/phone_hint" android:inputType="phone" />
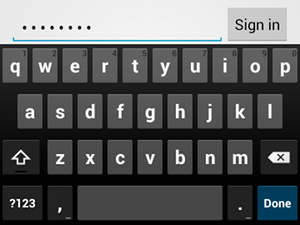
textPasswordإذا كان حقل النص مخصّصًا لكلمة مرور، استخدِم القيمة "textPassword" لكي يخفي حقل النص إدخال المستخدم:
<EditText android:id="@+id/password" android:hint="@string/password_hint" android:inputType="textPassword" ... />
هناك عدة قيم محتملة تم توثيقها باستخدام السمة android:inputType،
ويمكنك دمج بعض القيم لتحديد مظهر طريقة الإدخال وأحد السلوكيات
الإضافية.
تفعيل الاقتراحات الإملائية والسلوكيات الأخرى
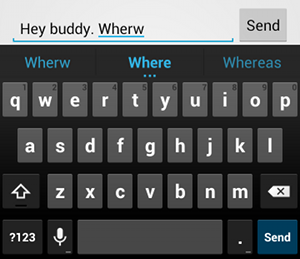
textAutoCorrect إلى توفير التصحيح التلقائي لكلماته
التي تحتوي على أخطاء إملائية.تتيح لك السمة android:inputType تحديد سلوكيات مختلفة لطريقة
الإدخال. والأهم من ذلك، إذا كان حقل النص مخصّصًا لإدخال نص أساسي، مثل
رسالة نصية، يمكنك تفعيل ميزة التصحيح الإملائي التلقائي باستخدام القيمة "textAutoCorrect".
يمكنك الجمع بين السلوكيات المختلفة وأنماط طرق الإدخال باستخدام سمة
android:inputType. على سبيل المثال، إليك كيفية إنشاء حقل نصي يقلب الحرف الأول من الجملة إلى كتابة كبيرة ويصحّح الأخطاء الإملائية تلقائيًا:
<EditText android:id="@+id/message" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:inputType= "textCapSentences|textAutoCorrect" ... />
تحديد إجراء أسلوب الإدخال
توفّر معظم طرق الإدخال السهلة زرّ إجراء للمستخدم في الزاوية السفلية يكون مناسبًا
لحقل النص الحالي. يستخدم النظام هذا الزر تلقائيًا لتنفيذ أحد الإجراءَين التالي أو
تم ما لم يكن حقل النص يتيح إدخال نص مكوّن من عدة أسطر، مثل
android:inputType="textMultiLine"، وفي هذه الحالة يكون زر الإجراء هو زر carriage
return. ومع ذلك، يمكنك تحديد إجراءات أخرى قد تكون أكثر ملاءمةً لحقل النص،
مثل إرسال أو الانتقال.
لتحديد زرّ إجراء لوحة المفاتيح، استخدِم السمة
android:imeOptions
مع قيمة إجراء مثل "actionSend" أو "actionSearch". على سبيل المثال:

android:imeOptions="actionSend".<EditText android:id="@+id/search" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/search_hint" android:inputType="text" android:imeOptions="actionSend" />
يمكنك بعد ذلك الاستماع إلى عمليات الضغط على زر الإجراء من خلال تحديد
TextView.OnEditorActionListener
لعنصر EditText. في ملف
المستمع، يجب الردّ على معرّف إجراء IME المناسب المحدّد في فئة
EditorInfo،
مثل
IME_ACTION_SEND،
كما هو موضّح في المثال التالي:
Kotlin
findViewById<EditText>(R.id.search).setOnEditorActionListener { v, actionId, event -> return@setOnEditorActionListener when (actionId) { EditorInfo.IME_ACTION_SEND -> { sendMessage() true } else -> false } }
Java
EditText editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.search); editText.setOnEditorActionListener(new OnEditorActionListener() { @Override public boolean onEditorAction(TextView v, int actionId, KeyEvent event) { boolean handled = false; if (actionId == EditorInfo.IME_ACTION_SEND) { sendMessage(); handled = true; } return handled; } });
تقديم اقتراحات للإكمال التلقائي
إذا كنت تريد تقديم اقتراحات للمستخدمين أثناء الكتابة، يمكنك استخدام فئة فرعية من
EditText تُسمى
AutoCompleteTextView.
لتنفيذ ميزة "الإكمال التلقائي"، يجب تحديد
Adapter يوفّر اقتراحات متنه. تتوفّر عدة محولات، استنادًا إلى مصدر البيانات، مثل
قاعدة بيانات أو صفيف.
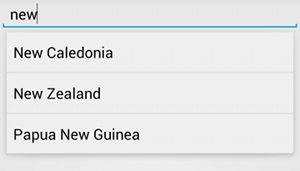
AutoCompleteTextView مع اقتراحات
نصيةتوضِّح الخطوات التالية كيفية إعداد AutoCompleteTextView الذي
يقدّم اقتراحات من صفيف باستخدام
ArrayAdapter:
- أضِف الرمز
AutoCompleteTextViewإلى التنسيق. في ما يلي تنسيق يتضمّن حقل النص فقط:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <AutoCompleteTextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/autocomplete_country" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
- حدِّد المصفوفة التي تحتوي على جميع اقتراحات النصوص. على سبيل المثال، إليك
صفيف من أسماء البلدان:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string-array name="countries_array"> <item>Afghanistan</item> <item>Albania</item> <item>Algeria</item> <item>American Samoa</item> <item>Andorra</item> <item>Angola</item> <item>Anguilla</item> <item>Antarctica</item> ... </string-array> </resources>
- في
ActivityأوFragment، استخدِم الرمز التالي لتحديد المحوِّل الذي يقدّم الاقتراحات:Kotlin
// Get a reference to the AutoCompleteTextView in the layout. val textView = findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_country) as AutoCompleteTextView // Get the string array. val countries: Array<out String> = resources.getStringArray(R.array.countries_array) // Create the adapter and set it to the AutoCompleteTextView. ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, countries).also { adapter -> textView.setAdapter(adapter) }
Java
// Get a reference to the AutoCompleteTextView in the layout. AutoCompleteTextView textView = (AutoCompleteTextView) findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_country); // Get the string array. String[] countries = getResources().getStringArray(R.array.countries_array); // Create the adapter and set it to the AutoCompleteTextView. ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, countries); textView.setAdapter(adapter);
في المثال السابق، يتمّ إعداد
ArrayAdapterجديد لربط كل عنصر في صفيف السلسلةcountries_arrayبأحد عناصرTextViewالمتوفّرة في تنسيقsimple_list_item_1. هذا تنسيق يوفّره Android ويمنح مظهرًا عاديًا للنص في القائمة. -
يمكنك إسناد المحوِّل إلى
AutoCompleteTextViewمن خلال الاتصال بالرقمsetAdapter().

