باستخدام WindowInsetsCompat، يمكن لتطبيقك طلب البحث عن لوحة المفاتيح على الشاشة (المعروفة أيضًا باسم IME) والتحكّم فيها بطريقة مشابهة لطريقة تفاعله مع أشرطة النظام. يمكن لتطبيقك أيضًا استخدام
WindowInsetsAnimationCompat
لإنشاء انتقالات سلسة عند فتح لوحة المفاتيح البرمجية أو إغلاقها.
المتطلّبات الأساسية
قبل إعداد عناصر التحكّم والرسوم المتحركة للوحة المفاتيح البرمجية، اضبط تطبيقك على عرض المحتوى من الحافة إلى الحافة. ويتيح ذلك التعامل مع حواف نوافذ النظام، مثل أشرطة النظام ولوحة المفاتيح على الشاشة.
التحقّق من ظهور برنامج لوحة المفاتيح
استخدِم WindowInsets للتحقّق من ظهور لوحة المفاتيح
البرمجية.
Kotlin
val insets = ViewCompat.getRootWindowInsets(view) ?: return val imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) val imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom
Java
WindowInsetsCompat insets = ViewCompat.getRootWindowInsets(view); boolean imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()); int imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom;
بدلاً من ذلك، يمكنك استخدام
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener
لمراقبة التغييرات في إمكانية ظهور لوحة المفاتيح البرمجية.
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view) { _, insets -> val imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) val imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom insets }
Java
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view, (v, insets) -> { boolean imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()); int imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom; return insets; });
مزامنة الرسوم المتحركة مع لوحة المفاتيح البرمجية
عندما ينقر المستخدم على حقل إدخال نص، تنزلق لوحة المفاتيح إلى مكانها من أسفل الشاشة، كما هو موضّح في المثال التالي:
يوضّح المثال الذي يحمل التصنيف "غير متزامن" في الشكل 2 السلوك التلقائي في نظام التشغيل Android 10 (المستوى 29 من واجهة برمجة التطبيقات)، حيث يتم تثبيت حقل النص ومحتوى التطبيق في مكانهما بدلاً من مزامنتهما مع حركة لوحة المفاتيح، وهو سلوك قد يكون مزعجًا بصريًا.
في الإصدار 11 من نظام التشغيل Android (المستوى 30 لواجهة برمجة التطبيقات) والإصدارات الأحدث، يمكنك استخدام
WindowInsetsAnimationCompatلمزامنة انتقال التطبيق مع انزلاق لوحة المفاتيح للأعلى والأسفل من أسفل الشاشة. يبدو هذا أكثر سلاسة، كما هو موضّح في المثال الذي يحمل التصنيف "متزامن" في الشكل 2.
اضبط
WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback
باستخدام طريقة العرض التي ستتم مزامنتها مع الصورة المتحركة للوحة المفاتيح.
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setWindowInsetsAnimationCallback( view, object : WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback(DISPATCH_MODE_STOP) { // Override methods. } )
Java
ViewCompat.setWindowInsetsAnimationCallback( view, new WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback( WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback.DISPATCH_MODE_STOP ) { // Override methods. });
تتوفّر عدة طرق لتجاوز الإعدادات في WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback،
وهي
onPrepare()
وonStart()
وonProgress()
وonEnd().
ابدأ بالاتصال بـ onPrepare() قبل إجراء أي تغييرات على التنسيق.
يتم استدعاء onPrepare عند بدء حركة إدخال، وقبل إعادة تخطيط طرق العرض بسبب الحركة. يمكنك استخدامها لحفظ حالة البدء، وهي في هذه الحالة الإحداثي السفلي للعرض.
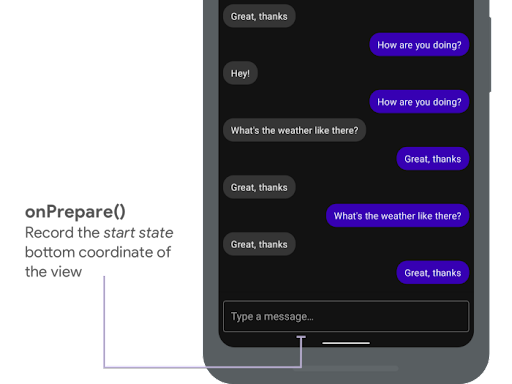
onPrepare() لتسجيل حالة البدء
يعرض المقتطف التالي نموذجًا لطلب onPrepare:
Kotlin
var startBottom = 0f override fun onPrepare( animation: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat ) { startBottom = view.bottom.toFloat() }
Java
float startBottom; @Override public void onPrepare( @NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation ) { startBottom = view.getBottom(); }
يتم استدعاء onStart عند بدء صورة متحركة للعناصر الناشئة. يمكنك استخدامها لضبط جميع خصائص العرض على الحالة النهائية لتغييرات التصميم. إذا كان لديك
OnApplyWindowInsetsListener دالة ردّ تم ضبطها على أي من طرق العرض، سيتم
استدعاؤها في هذه المرحلة. هذا هو الوقت المناسب لحفظ الحالة النهائية لخصائص العرض.
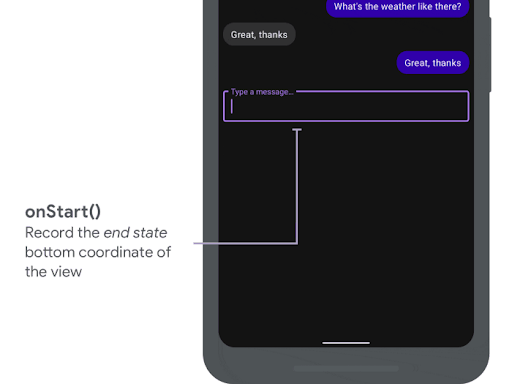
onStart() لتسجيل الحالة النهائية
يعرض المقتطف التالي نموذجًا لطلب onStart:
Kotlin
var endBottom = 0f override fun onStart( animation: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat, bounds: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat ): WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat { // Record the position of the view after the IME transition. endBottom = view.bottom.toFloat() return bounds }
Java
float endBottom; @NonNull @Override public WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat onStart( @NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation, @NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat bounds ) { endBottom = view.getBottom(); return bounds; }
يتم استدعاء onProgress عندما تتغير الحواف الداخلية كجزء من تشغيل صورة متحركة،
لذا يمكنك إلغاءها وتلقّي إشعار بشأن كل إطار أثناء
الصورة المتحركة للوحة المفاتيح. عدِّل خصائص طريقة العرض بحيث يتم تحريك طريقة العرض بشكل متزامن مع لوحة المفاتيح.
في هذه المرحلة، تكون جميع تغييرات التنسيق قد اكتملت. على سبيل المثال، إذا كنت تستخدم
View.translationY لنقل العرض، تنخفض القيمة تدريجيًا مع كل
استدعاء لهذه الطريقة، وتصل في النهاية إلى 0 في موضع التصميم الأصلي.
onProgress() لمزامنة الصور المتحركة.
يعرض المقتطف التالي نموذجًا لطلب onProgress:
Kotlin
override fun onProgress( insets: WindowInsetsCompat, runningAnimations: MutableList<WindowInsetsAnimationCompat> ): WindowInsetsCompat { // Find an IME animation. val imeAnimation = runningAnimations.find { it.typeMask and WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime() != 0 } ?: return insets // Offset the view based on the interpolated fraction of the IME animation. view.translationY = (startBottom - endBottom) * (1 - imeAnimation.interpolatedFraction) return insets }
Java
@NonNull @Override public WindowInsetsCompat onProgress( @NonNull WindowInsetsCompat insets, @NonNull List<WindowInsetsAnimationCompat> runningAnimations ) { // Find an IME animation. WindowInsetsAnimationCompat imeAnimation = null; for (WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation : runningAnimations) { if ((animation.getTypeMask() & WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) != 0) { imeAnimation = animation; break; } } if (imeAnimation != null) { // Offset the view based on the interpolated fraction of the IME animation. view.setTranslationY((startBottom - endBottom) * (1 - imeAnimation.getInterpolatedFraction())); } return insets; }
يمكنك اختياريًا إلغاء onEnd. يتم استدعاء هذه الطريقة بعد انتهاء الصورة المتحركة. هذا هو الوقت المناسب لإزالة أي تغييرات مؤقتة.
مراجع إضافية
- WindowInsetsAnimation على GitHub

