RelativeLayout هو مجموعة عرض تعرض مشاهدات الأطفال بشكل نسبي.
المناصب. يمكن تحديد موضع كل طريقة عرض بالنسبة إلى العناصر التابعة (مثل
يسار أو أسفل عرض آخر) أو في مواضع بالنسبة إلى منطقة RelativeLayout الرئيسية (مثل المحاذاة إلى الأسفل أو اليسار أو الوسط).
ملاحظة: للحصول على أداء أفضل وإمكانية استخدام الأدوات، يجب بدلاً من ذلك إنشاء تنسيق باستخدام ConstraintLayout.

RelativeLayout هي أداة فعالة جدًا لتصميم واجهة مستخدم
لأنه يمكن أن يلغي مجموعات طرق العرض المتداخلة والإبقاء على التسلسل الهرمي للتصميم مسطحًا، مما يحسن
أدائه. إذا وجدت نفسك تستخدم عدة مجموعات LinearLayout مدمجة،
يمكنك استبدالها بـ RelativeLayout واحد.
طرق عرض المكانة في السوق
يتيح RelativeLayout لطرق العرض الفرعية تحديد موضعها بالنسبة إلى
الملف الشخصي للوالدَين أو لبعضهما البعض (يتم تحديد ذلك من خلال رقم التعريف) لذا يمكنك محاذاة عنصرين بواسطة الحد الأيمن، أو
جعل واحد أسفل الآخر، في وسط الشاشة، في منتصف اليسار، وهكذا. بشكل تلقائي، يمكن لجميع حسابات الأطفال
يتم رسم طرق العرض في أعلى يسار التخطيط، لذا يجب عليك تحديد موضع كل طريقة عرض
باستخدام خصائص التنسيق المختلفة المتاحة من RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.
بعض خصائص التنسيق الكثيرة المتاحة للعرض في RelativeLayout
تشمل:
android:layout_alignParentTop- إذا كانت
"true"، فستتطابق الحافة العلوية من هذا العرض مع الحافة العلوية للجهاز الرئيسي. android:layout_centerVertical- إذا كانت
"true"، يتم توسيط هذه المجموعة الفرعية عموديًا ضمن العنصر الرئيسي. android:layout_below- وضع الحافة العلوية لهذا العرض أسفل العرض المحدد برقم تعريف مورد.
android:layout_toRightOf- وضع الحافة اليسرى لهذا العرض على يمين العرض المحدد برقم تعريف مورد.
هذه بعض الأمثلة فقط. تم توثيق جميع سمات التنسيق على RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.
قيمة كل خاصية تخطيط إما منطقية
تفعيل موضع تنسيق بالنسبة إلى العنصر RelativeLayout الرئيسي أو رقم تعريف
إلى طريقة عرض أخرى في التنسيق الذي ينبغي وضع العرض وفقًا له.
في تنسيق XML، يمكن تعريف التبعيات مقابل طرق العرض الأخرى في التنسيق بأي ترتيب. على سبيل المثال، يمكنك الإفصاح عن أن "view1" أن يتم وضعها أسفل "view2" حتى إذا كانت "view2" هو الأخير تم تعريفها في التسلسل الهرمي. يوضح المثال التالي هذا السيناريو.
مثال
يتم التأكيد على كل سمة من السمات التي تتحكم في الموضع النسبي لكل طريقة عرض.
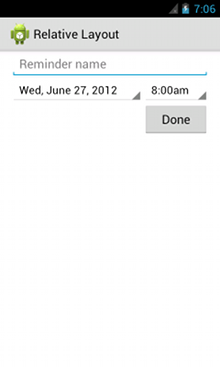
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/reminder" /> <Spinner android:id="@+id/dates" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/times" /> <Spinner android:id="@id/times" android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <Button android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/times" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:text="@string/done" /> </RelativeLayout>
للحصول على تفاصيل عن جميع سمات التنسيق المتاحة لكل طريقة عرض فرعية لـ "RelativeLayout"، يُرجى الاطّلاع على RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.

