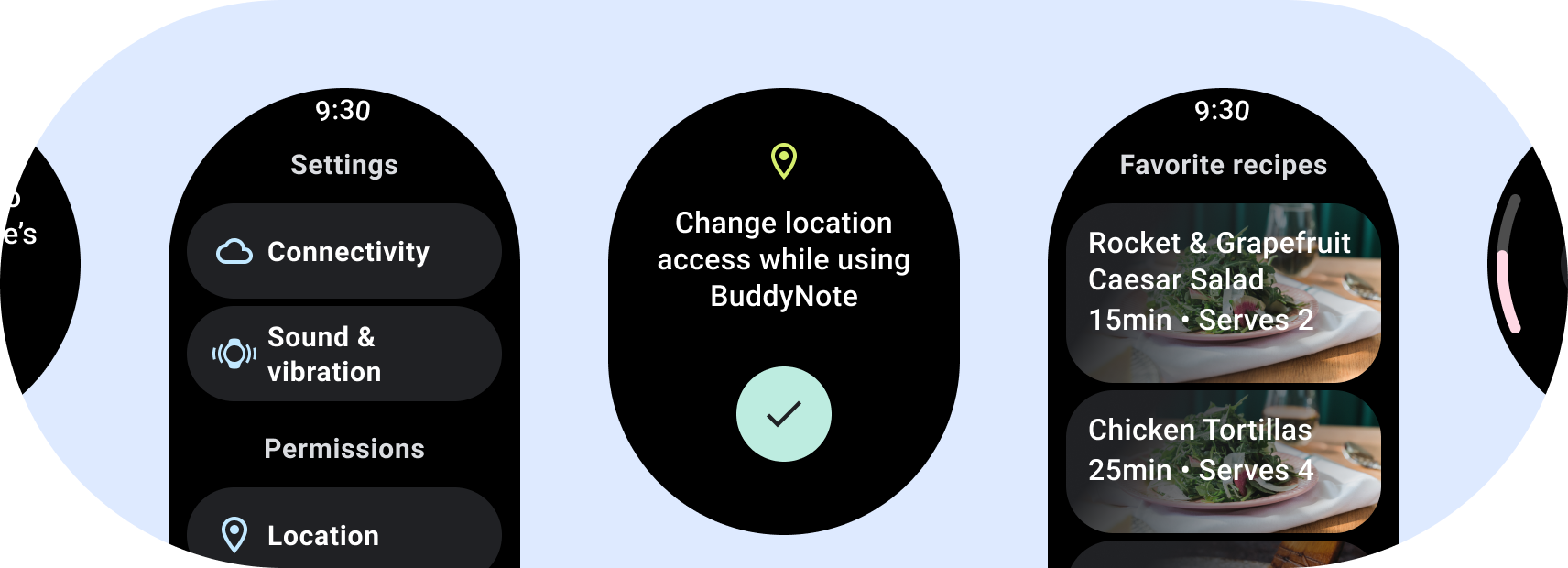
Wear OS용 앱을 디자인할 때는 어떤 레이아웃을 위한 것인지 신중하게 선택하세요. 경험해 볼 수 있습니다 Wear OS는 원형 디스플레이에서 실행되며 클리핑이 더 많기 때문입니다. 표준 레이아웃에는 두 가지 카테고리가 있습니다. 고려해야 합니다.
스크롤되지 않는 앱 레이아웃
스크롤되지 않은 레이아웃은 한눈에 확인할 수 있는 정보에 초점을 맞추고 다음과 같이 사용자에게 가치를 제공합니다. 발생할 수 있습니다 그렇기 때문에 Google Cloud의 다음 레이아웃에 넣을 수 있습니다.
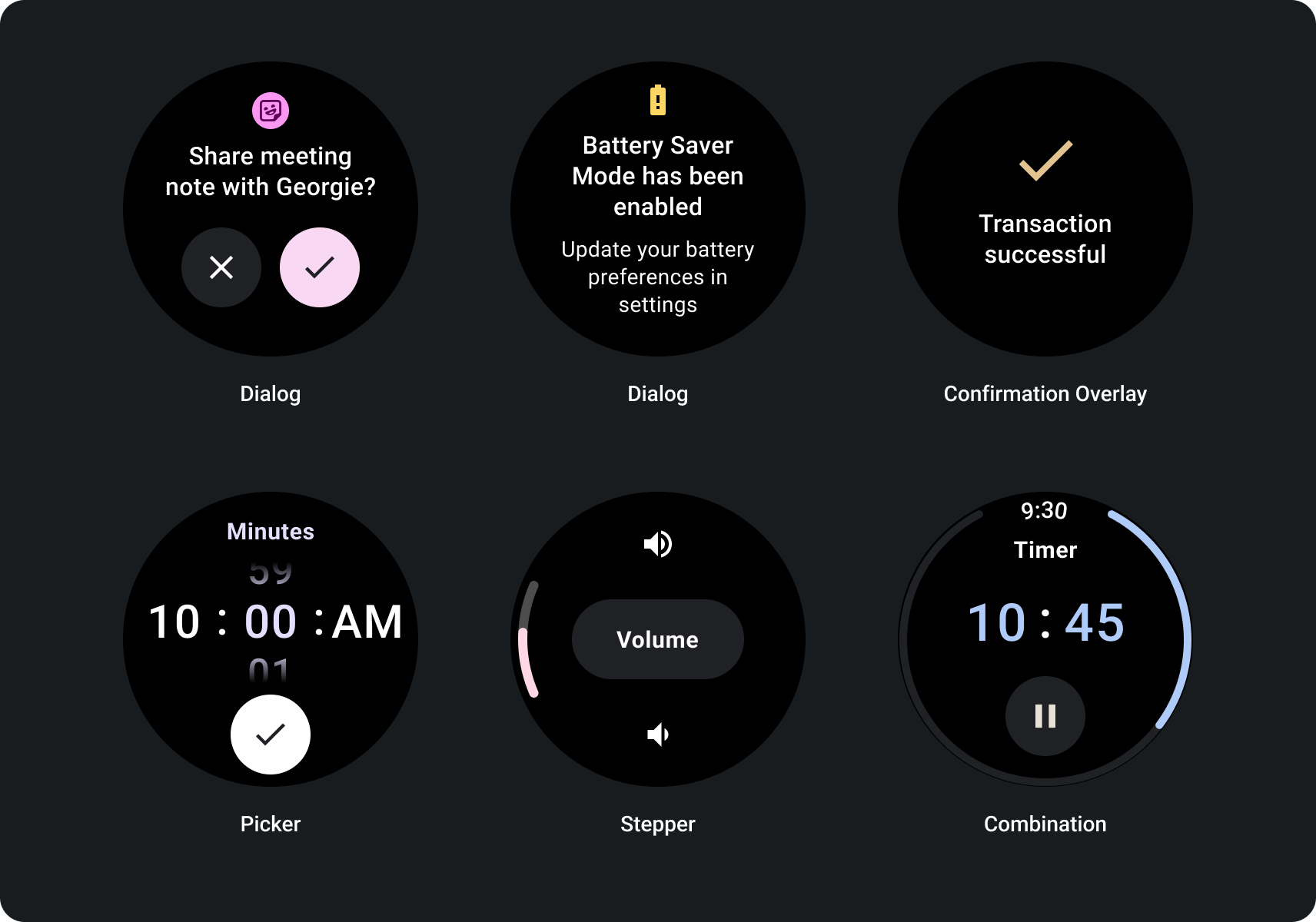
스크롤되지 않는 반응형 뷰 빌드
- 언어, 글꼴 크기 조정, 기기, 변수를 조합하여 테스트 있습니다.
- 콘텐츠가 알려졌거나 제어되는 경우에만 스크롤할 수 없는 레이아웃 사용 특정 디자인을 사용해야 하는 경우에 대비할 수 있습니다.
- 레이아웃에 권장되는 상단, 하단, 측면 여백을 적용합니다.
- 콘텐츠가 표시되지 않을 수 있는 위치에는 백분율로 여백을 정의합니다. 잘리지 않습니다.
- 요소를 정렬하여 여러 기기 크기 간에 균형을 유지합니다.
앱 레이아웃 스크롤
한 화면에 모두 표시할 수 있는 것보다 더 많은 정보가 포함된 페이지의 경우 보다 길고 몰입도 높은 여정을 지원하는 데 필요한 경우 스크롤 없이 볼 수 있는 부분인 합니다.
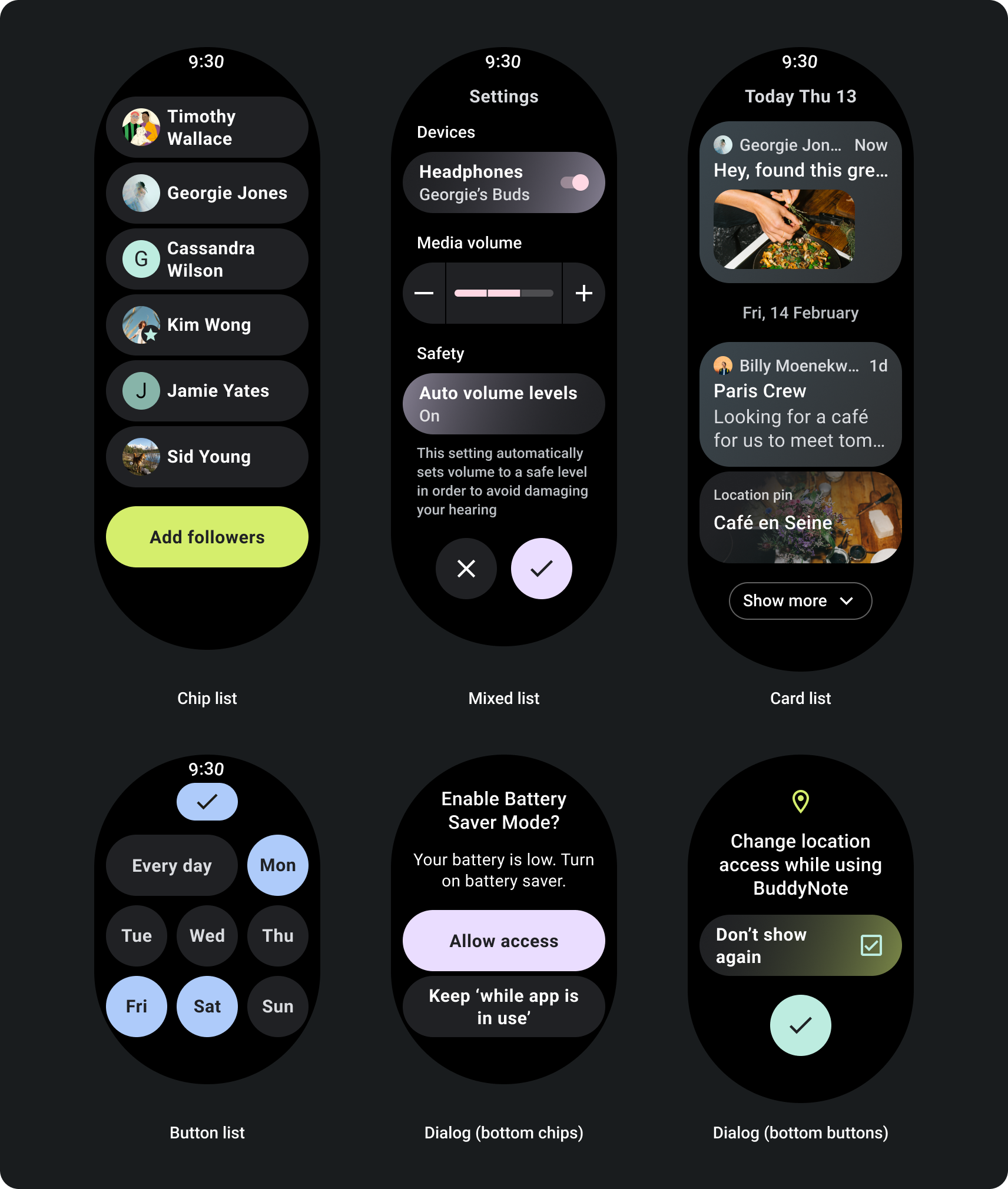
반응형 스크롤 뷰 빌드
- 권장되는 상단, 하단, 측면 여백을 적용합니다.
- 바깥쪽 여백을 백분율 값으로 정의하여 스크롤 가능한 컨테이너의 시작과 끝을 나타냅니다.
- UI 요소 사이의 고정된 DP 값에 여백을 적용합니다.
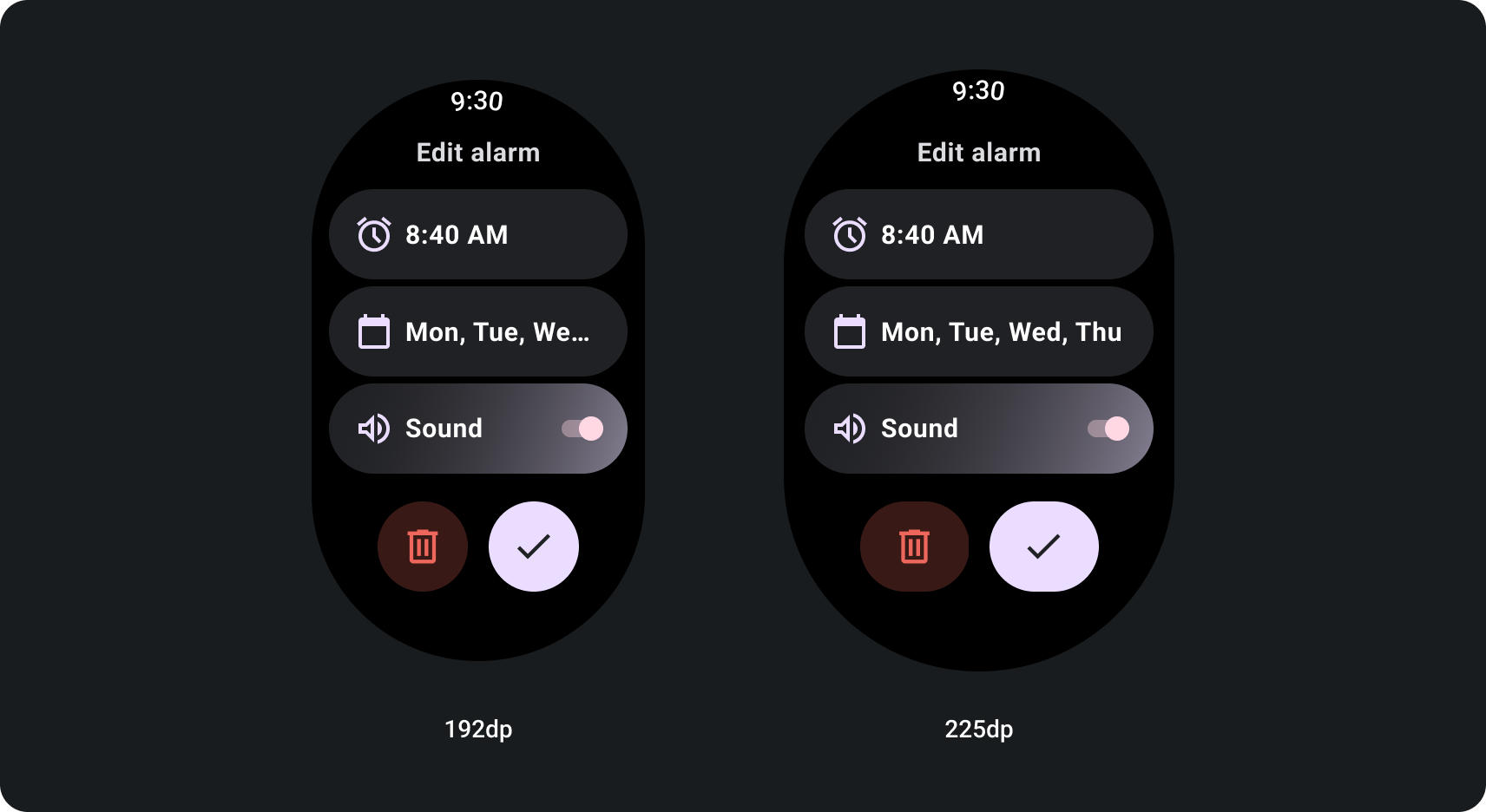
화면 크기 중단점을 사용하여 적응형 스크롤 뷰를 빌드하는 방법
반응형 디자인 방식을 사용하는 스크롤 뷰는 일반적으로 화면 크기 그러나 일부 특별한 경우에는 중단점을 사용하여 추가 옵션을 표시하고 크기를 재정의하고 레이아웃을 보강하여 콘텐츠를 화면에 더 잘 표시할 수 있습니다. 다음 예를 참고하세요. 큰 화면에서 아래쪽의 두 버튼이 넓어지는 방식을 보여줍니다.
Figma 디자인 키트
디자인 키트 다운로드 페이지를 방문하여 다양한 앱과 카드를 만들기 위한 구성요소, 옵션, 추천 설계하는 것이 중요합니다

