
Apps that are responsive and optimized utilize responsive layouts that automatically adapt to different screen sizes, offering some additional value to users and providing a productive, engaging user experience.
Add value through responsive design
Responsive layouts dynamically format and position elements such as buttons, text fields, and dialogs for an optimal user experience. Automatically offer users of your app additional value on larger screens by utilizing responsive design practices. Whether it's more text visible at a glance, more actions on screen, or larger, more accessible tap targets, responsive practices provide an enhanced experience for users of larger screens.

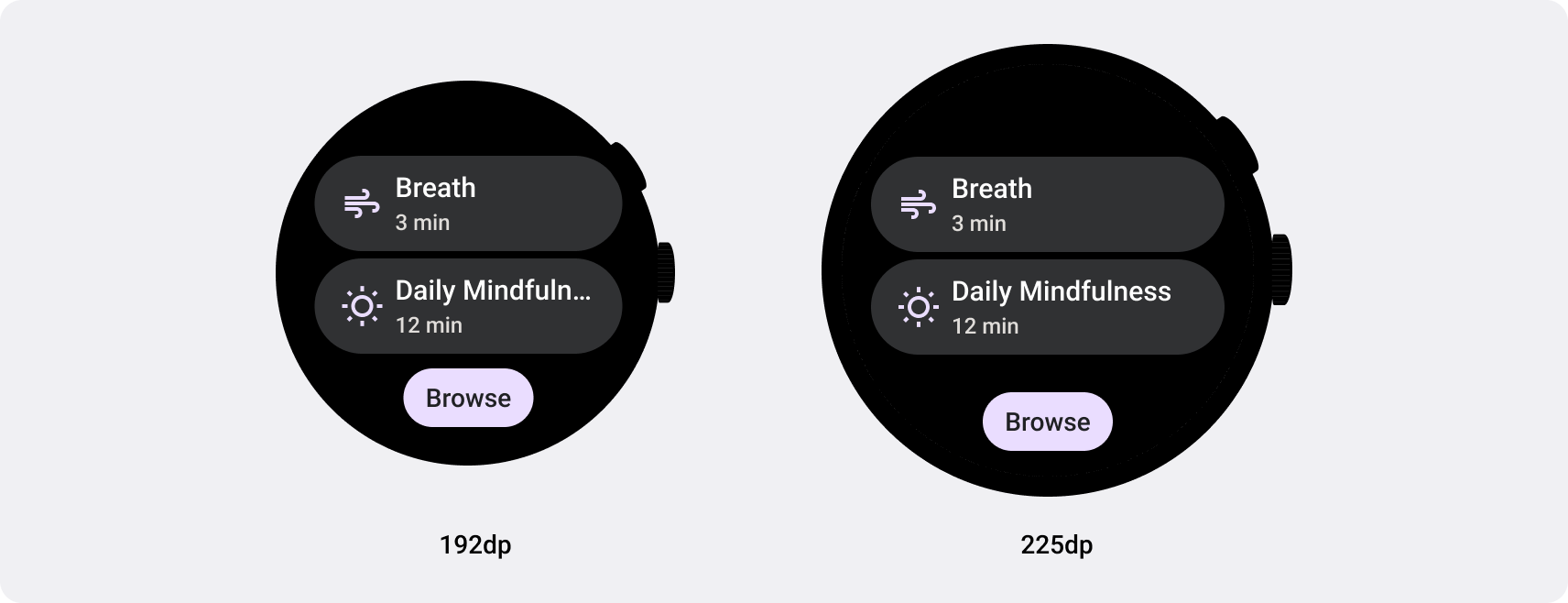
Build responsive apps and tiles for Wear OS
Responsive UIs stretch and change to make the best possible use of all available screen space, no matter what size screen they're rendered on. When designing responsive layouts on a round screen, scrolling and non-scrolling views each have unique requirements to maintain UI element scaling, as well as preserve a balanced layout and composition. For scrolling views, use percentages to define all top, bottom, and side margins to avoid clipping and provide proportional scaling of elements. For non-scrolling views, use percentages and vertical constraints for all margins. That way, the main content in the middle can stretch to fill the available area.
See the Compose and Tiles implementation guidance for responsive layouts.
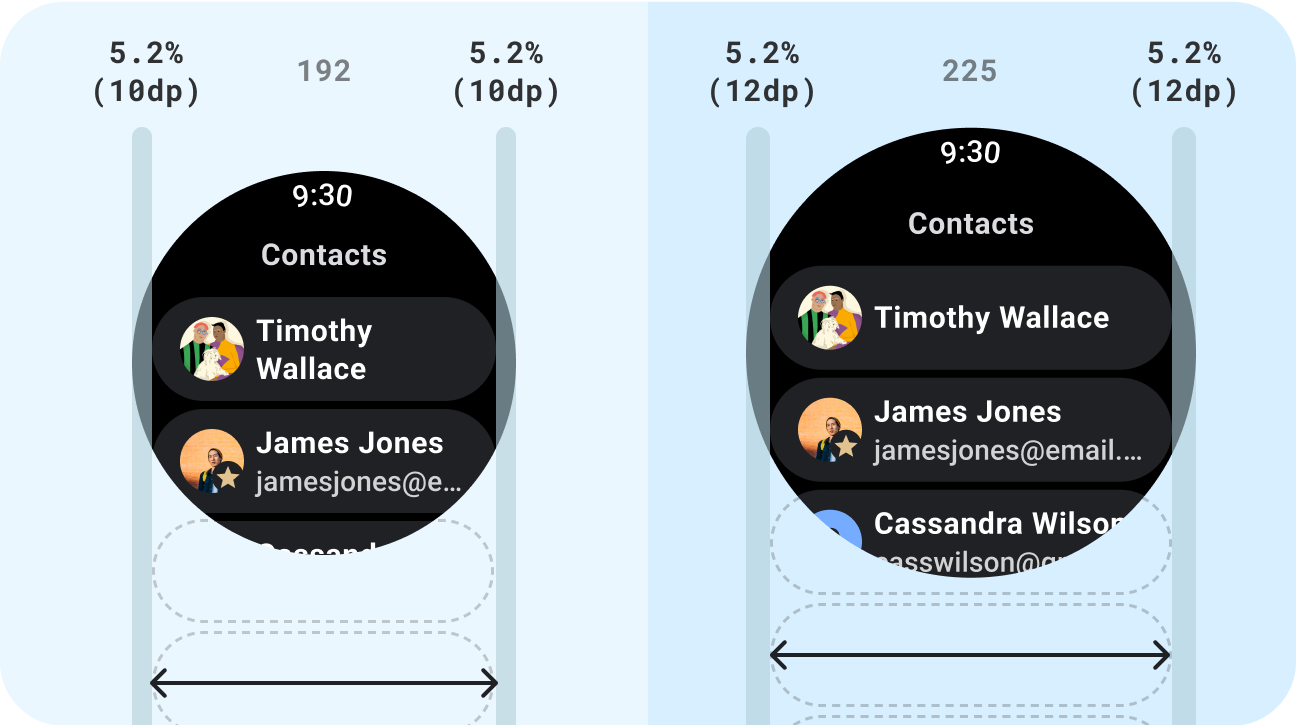
Do
- Use standard components which are designed for adaptation.
- Utilize adaptive layouts which adapt smoothly across screen sizes.
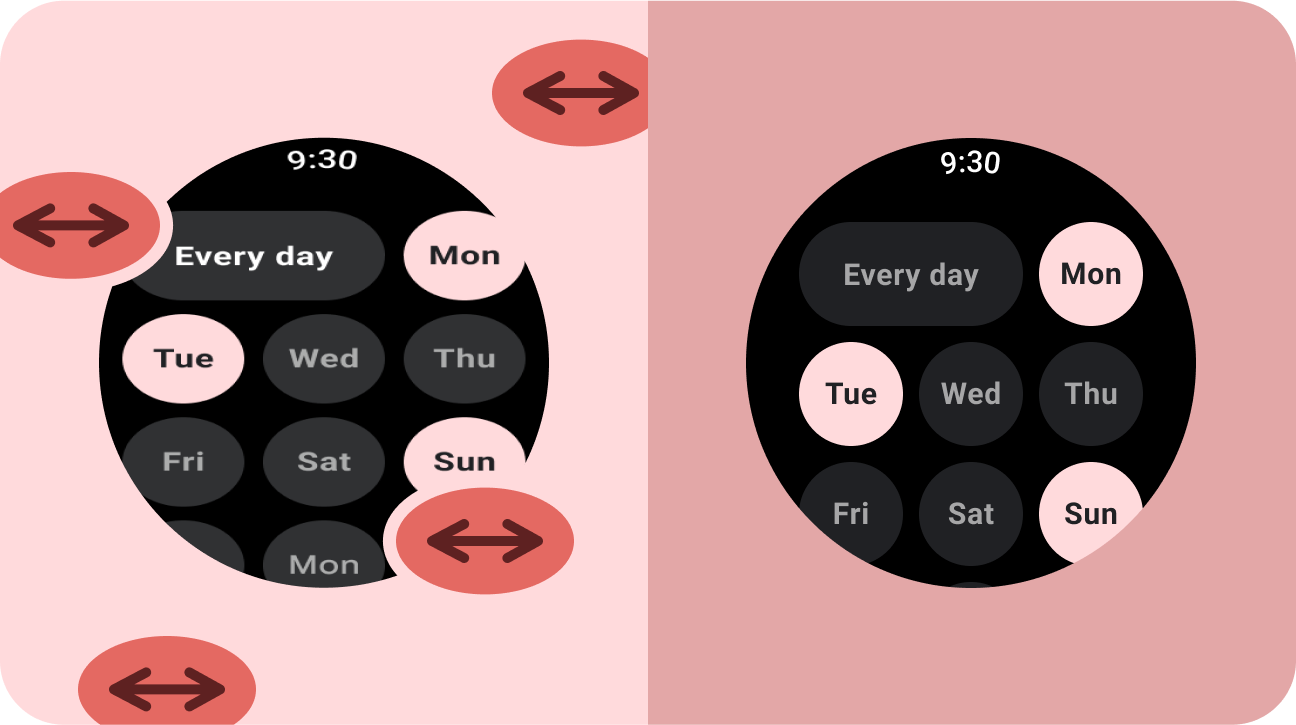
Don't
- Stretch UI elements (text fields, buttons, dialogs) to fill extra space.
- Increase the sizes of fonts (unless they're serving a primarily graphic purpose).
Next step: adaptive and differentiated
Apps that are adaptive and differentiated create a user experience that isn't possible on devices with smaller screens.
