스마트시계는 휴대기기보다 화면 크기가 작으므로 사용자가 액세스할 수 있고 사용 가능한 화면 공간을 효율적으로 사용하는 방식으로 요소를 정렬하고 표시하는 것이 중요합니다. 항목이 화면에 맞도록 Material 가이드라인에 지정된 대로 패딩과 여백을 올바르게 사용합니다.
디자인이 화면에 맞더라도 사용자가 다음 중 하나를 실행하면 인터페이스 요소가 잘리거나 잘릴 수 있습니다.
- 표시 언어를 변경합니다.
- 텍스트 크기를 변경합니다.
- 텍스트 굵게 표시 시스템 설정을 사용 설정합니다.
이러한 고려사항을 염두에 두고 디자인을 테스트하여 다양한 사용자 환경에 맞게 원활하게 조정되는지 확인해야 합니다.
상호작용 요소가 완전히 표시되도록 유지
인터페이스에 상호작용 요소가 포함된 경우, 특히 이러한 요소가 페이지 가장자리에 배치된 경우 사용자가 이러한 요소를 완전히 스크롤하여 볼 수 있는지 확인합니다. 앱에서 Horologist 라이브러리를 사용한다면 responsive() 레이아웃 팩토리를 사용하세요. 아니면 스페이서를 사용하고 ScalingLazyColumn 객체의 상단과 하단에 여백을 추가하여 첫 번째 및 마지막 목록 항목이 항상 잘리지 않도록 합니다.
밀집형 레이아웃에는 카드 대신 칩 사용
더 밀도가 높은 레이아웃이 필요하면 카드 대신 CompactChip를 사용하세요. 카드의 노출 영역 영역이 넓으면 텍스트 잘림 및 콘텐츠 클리핑을 방지하기가 훨씬 더 어렵습니다.
잘림 및 잘림 시 화면 크기 효과 고려하기
Wear OS 기기의 화면 크기에 따라 추가 텍스트와 버튼을 표시할 공간이 더 작거나 커집니다.
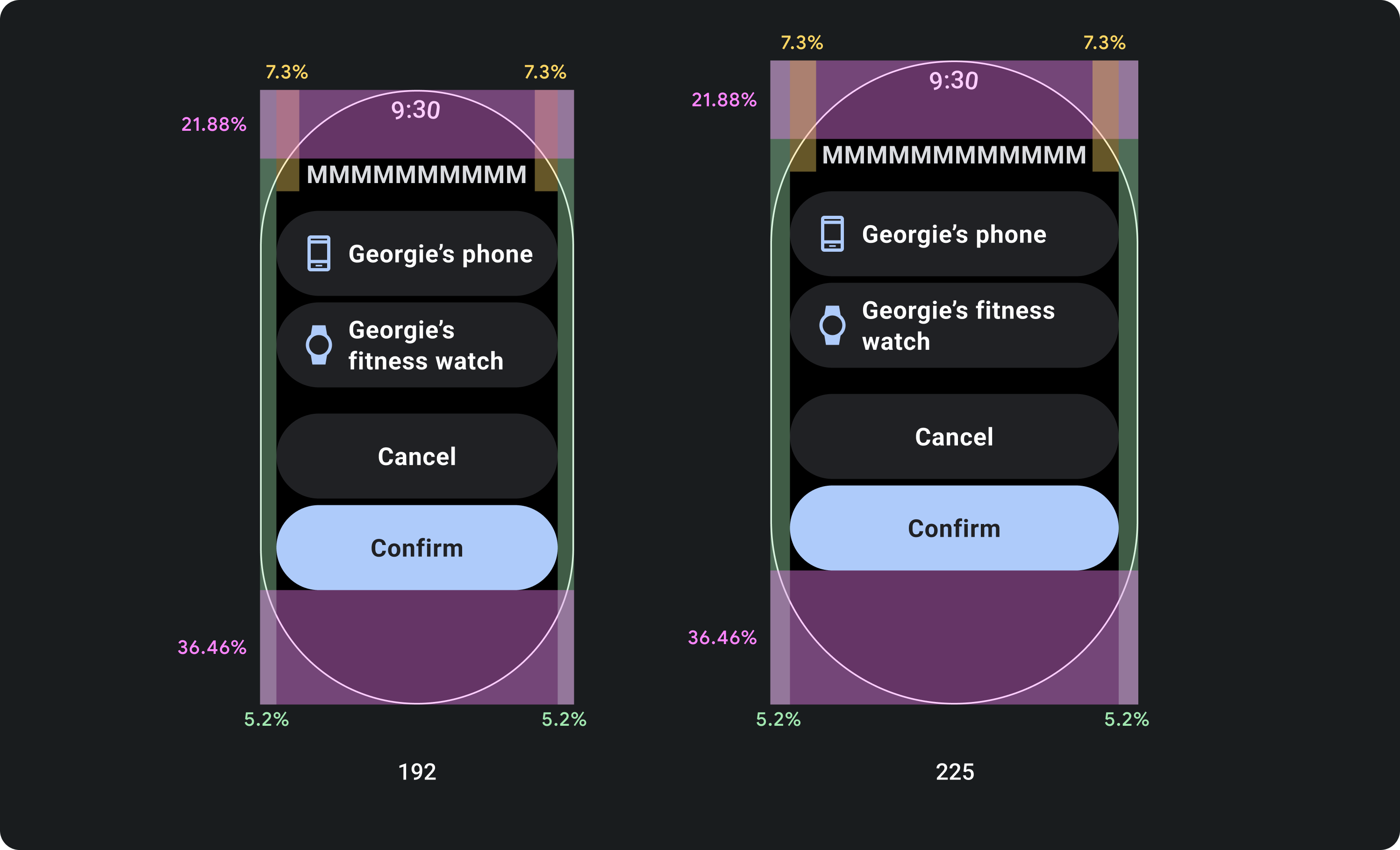
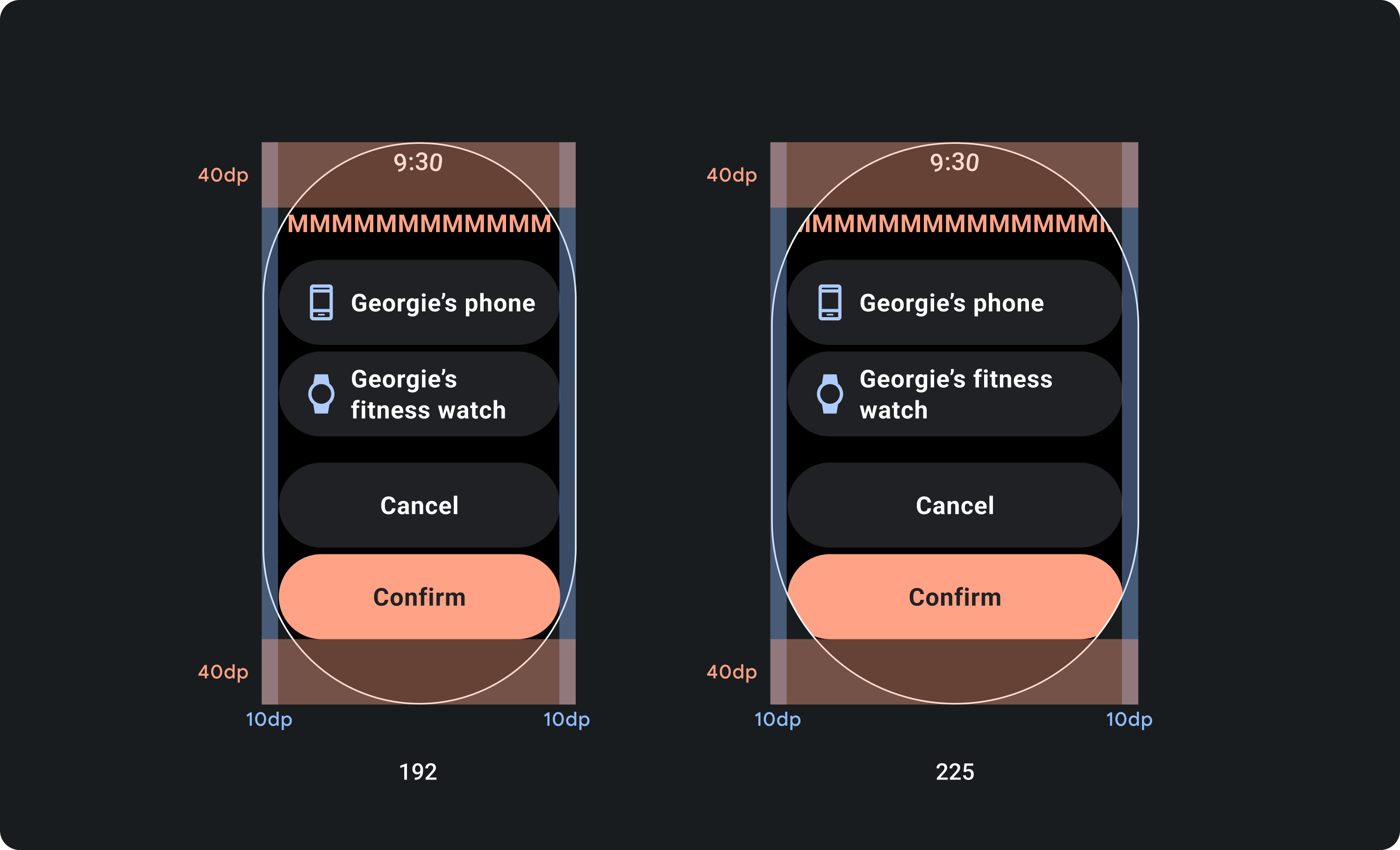
고정 마진이 아닌 비율 마진을 고려한 디자인
Wear OS 기기의 화면 크기에 맞게 조정되는 콘텐츠를 만들려면 각 여백의 크기가 화면 크기를 기준으로 하는 비율 여백을 적용하세요. 항목이 화면의 상단이나 하단에 배치되는 경우 추가 내부 패딩을 적용하여 화면의 곡선 가장자리에서 콘텐츠 잘림을 최소화합니다. 반대로 콘텐츠 그룹이 한 화면에 맞을 만큼 작으면 상단과 하단의 공간이 증가합니다.
의견을 제시하지
부적절한 예
작은 화면에 필요한 글자 수 제한을 적용하세요.
대부분의 경우 큰 화면에서는 잘리기 전에 텍스트와 콘텐츠가 더 많이 표시될 수 있습니다. 더 많은 가로 공간을 사용할 수 있더라도 항상 가장 작은 화면 크기에 맞게 디자인하여 여러 기기에서 일관된 환경을 만들 수 있습니다.
예를 들어 버튼은 큰 화면에서 잘리기 전에 더 많은 문자를 위한 공간이 있을 수 있지만, 사용자 환경에 중요한 클릭 유도 문구인 경우 작은 기기의 화면에 잘리지 않고 완전히 표시될 수 있을 정도로 짧은 텍스트를 사용하세요.
또는 카드에 서버에서 가져온 텍스트와 같은 가변 콘텐츠가 표시되는 경우 작은 화면에서는 이 텍스트가 잘릴 가능성을 계획하세요.

의견을 제시하지

