讓物件根據旋轉三角形等預設程式移動物件,有助於
吸引註意,但如果想讓使用者與您的 OpenGL ES 圖形互動,該怎麼做?
讓 OpenGL ES 應用程式具有互動性的關鍵是擴大實作
GLSurfaceView 可覆寫
onTouchEvent() 會監聽觸控事件。
本課程將說明如何監聽觸控事件,讓使用者旋轉 OpenGL ES 物件。
設定觸控事件監聽器
如要讓 OpenGL ES 應用程式回應觸控事件,您必須實作
onTouchEvent()方法中的
GLSurfaceView 類別。以下實作範例說明如何監聽
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE 事件並轉譯為
形狀的旋轉角度。
Kotlin
private const val TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR: Float = 180.0f / 320f ... private var previousX: Float = 0f private var previousY: Float = 0f override fun onTouchEvent(e: MotionEvent): Boolean { // MotionEvent reports input details from the touch screen // and other input controls. In this case, you are only // interested in events where the touch position changed. val x: Float = e.x val y: Float = e.y when (e.action) { MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> { var dx: Float = x - previousX var dy: Float = y - previousY // reverse direction of rotation above the mid-line if (y > height / 2) { dx *= -1 } // reverse direction of rotation to left of the mid-line if (x < width / 2) { dy *= -1 } renderer.angle += (dx + dy) * TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR requestRender() } } previousX = x previousY = y return true }
Java
private final float TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR = 180.0f / 320; private float previousX; private float previousY; @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) { // MotionEvent reports input details from the touch screen // and other input controls. In this case, you are only // interested in events where the touch position changed. float x = e.getX(); float y = e.getY(); switch (e.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: float dx = x - previousX; float dy = y - previousY; // reverse direction of rotation above the mid-line if (y > getHeight() / 2) { dx = dx * -1 ; } // reverse direction of rotation to left of the mid-line if (x < getWidth() / 2) { dy = dy * -1 ; } renderer.setAngle( renderer.getAngle() + ((dx + dy) * TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR)); requestRender(); } previousX = x; previousY = y; return true; }
請注意,計算旋轉角度之後,這個方法會呼叫
requestRender() 用來通知
轉譯器轉譯影格。這種方法本例中最有效
因為除非旋轉角度發生變更,否則不需要重新繪製頁框。不過
「不會」影響效率,除非您同時要求轉譯器只在
使用 setRenderMode() 處理資料變更
方法,因此請確保這一行在轉譯器中未加註:
Kotlin
class MyGlSurfaceView(context: Context) : GLSurfaceView(context) { init { // Render the view only when there is a change in the drawing data renderMode = GLSurfaceView.RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY } }
Java
public MyGLSurfaceView(Context context) { ... // Render the view only when there is a change in the drawing data setRenderMode(GLSurfaceView.RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY); }
公開旋轉角度
上述程式碼範例要求您必須透過轉譯器公開旋轉角度,
並新增公開成員轉譯器程式碼在主使用者以外的另一個執行緒上執行
應用程式的介面執行緒,您必須將此公開變數宣告為 volatile。
下列程式碼可宣告變數,並公開 getter 和 setter 組合:
Kotlin
class MyGLRenderer4 : GLSurfaceView.Renderer { @Volatile var angle: Float = 0f }
Java
public class MyGLRenderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer { ... public volatile float mAngle; public float getAngle() { return mAngle; } public void setAngle(float angle) { mAngle = angle; } }
套用旋轉效果
如要套用觸控輸入產生的旋轉效果,請將產生角度和 新增一個變數,其中包含觸控輸入產生的角度:
Kotlin
override fun onDrawFrame(gl: GL10) { ... val scratch = FloatArray(16) // Create a rotation for the triangle // long time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() % 4000L; // float angle = 0.090f * ((int) time); Matrix.setRotateM(rotationMatrix, 0, angle, 0f, 0f, -1.0f) // Combine the rotation matrix with the projection and camera view // Note that the mvpMatrix factor *must be first* in order // for the matrix multiplication product to be correct. Matrix.multiplyMM(scratch, 0, mvpMatrix, 0, rotationMatrix, 0) // Draw triangle triangle.draw(scratch) }
Java
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) { ... float[] scratch = new float[16]; // Create a rotation for the triangle // long time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() % 4000L; // float angle = 0.090f * ((int) time); Matrix.setRotateM(rotationMatrix, 0, mAngle, 0, 0, -1.0f); // Combine the rotation matrix with the projection and camera view // Note that the vPMatrix factor *must be first* in order // for the matrix multiplication product to be correct. Matrix.multiplyMM(scratch, 0, vPMatrix, 0, rotationMatrix, 0); // Draw triangle mTriangle.draw(scratch); }
完成上述步驟後,請執行程式,然後用手指拖曳 旋轉三角形:
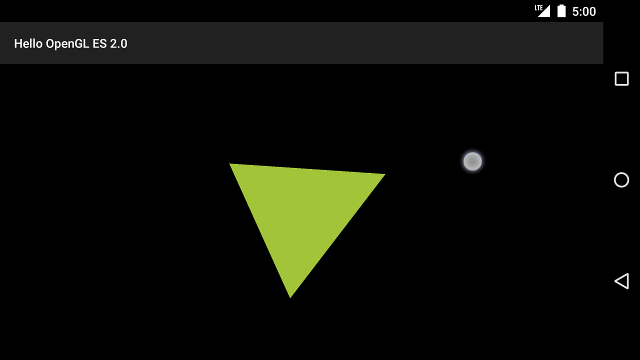
圖 1. 以觸控輸入方式旋轉的三角形 (圓圈顯示觸控處) 或 HTTP/HTTPS 位置)
