এই পাঠটি আপনাকে দেখায় কিভাবে CompatTab এবং TabHelper বিমূর্ত ক্লাসগুলি সাবক্লাস করতে হয় এবং নতুন API ব্যবহার করতে হয়। আপনার অ্যাপ্লিকেশানটি তাদের সমর্থন করে এমন একটি প্ল্যাটফর্ম সংস্করণ চলমান ডিভাইসগুলিতে এই বাস্তবায়ন ব্যবহার করতে পারে৷
নতুন API ব্যবহার করে ট্যাব প্রয়োগ করুন
CompatTab এবং TabHelper এর জন্য কংক্রিট ক্লাস যা নতুন API ব্যবহার করে একটি প্রক্সি বাস্তবায়ন। যেহেতু পূর্ববর্তী পাঠে সংজ্ঞায়িত বিমূর্ত ক্লাসগুলি নতুন APIs (শ্রেণির কাঠামো, পদ্ধতি স্বাক্ষর, ইত্যাদি) প্রতিফলিত করে, তাই এই নতুন APIগুলি ব্যবহার করে এমন কংক্রিট ক্লাসগুলি কেবল প্রক্সি পদ্ধতি কল এবং তাদের ফলাফলগুলি।
অলস ক্লাস লোডিংয়ের কারণে আপনি এই কংক্রিট ক্লাসগুলিতে সরাসরি নতুন API ব্যবহার করতে পারেন—এবং আগের ডিভাইসগুলিতে ক্র্যাশ হবে না৷ প্রথম অ্যাক্সেসে ক্লাসগুলি লোড করা হয় এবং আরম্ভ করা হয়—ক্লাসটি ইনস্ট্যান্টিয়েটিং বা প্রথমবারের জন্য এর একটি স্ট্যাটিক ক্ষেত্র বা পদ্ধতি অ্যাক্সেস করা। এইভাবে, যতক্ষণ না আপনি প্রাক-হানিকম্ব ডিভাইসগুলিতে হানিকম্ব-নির্দিষ্ট বাস্তবায়নগুলিকে ইনস্ট্যান্টিয়েট না করেন, ডালভিক ভিএম কোনও VerifyError ব্যতিক্রম ফেলবে না।
এই বাস্তবায়নের জন্য একটি ভাল নামকরণ কনভেনশন হল কংক্রিট ক্লাসগুলির জন্য প্রয়োজনীয় APIগুলির সাথে সংশ্লিষ্ট API স্তর বা প্ল্যাটফর্ম সংস্করণ কোড নাম যুক্ত করা। উদাহরণস্বরূপ, নেটিভ ট্যাব বাস্তবায়ন CompatTabHoneycomb এবং TabHelperHoneycomb ক্লাসগুলি দ্বারা সরবরাহ করা যেতে পারে, যেহেতু তারা Android 3.0 (API স্তর 11) বা তার পরে উপলব্ধ APIগুলির উপর নির্ভর করে৷
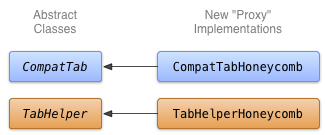
চিত্র 1. ট্যাবগুলির মৌচাক বাস্তবায়নের জন্য ক্লাস ডায়াগ্রাম।
CompatTabHoneycomb প্রয়োগ করুন
CompatTabHoneycomb হল CompatTab অ্যাবস্ট্রাক্ট ক্লাসের বাস্তবায়ন যা TabHelperHoneycomb পৃথক ট্যাবগুলিকে উল্লেখ করতে ব্যবহার করে। CompatTabHoneycomb এর মধ্যে থাকা ActionBar.Tab অবজেক্টে সমস্ত মেথড কল প্রক্সি করে।
নতুন ActionBar.Tab API ব্যবহার করে CompatTabHoneycomb প্রয়োগ করা শুরু করুন:
কোটলিন
class CompatTabHoneycomb internal constructor(val activity: Activity, tag: String) : CompatTab(tag) { ... // The native tab object that this CompatTab acts as a proxy for. private var mTab: ActionBar.Tab = // Proxy to new ActionBar.newTab API activity.actionBar.newTab() override fun setText(@StringRes textId: Int): CompatTab { // Proxy to new ActionBar.Tab.setText API mTab.setText(textId) return this } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
জাভা
public class CompatTabHoneycomb extends CompatTab { // The native tab object that this CompatTab acts as a proxy for. ActionBar.Tab mTab; ... protected CompatTabHoneycomb(FragmentActivity activity, String tag) { ... // Proxy to new ActionBar.newTab API mTab = activity.getActionBar().newTab(); } public CompatTab setText(int resId) { // Proxy to new ActionBar.Tab.setText API mTab.setText(resId); return this; } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
TabHelperHoneycomb প্রয়োগ করুন
TabHelperHoneycomb হল TabHelper অ্যাবস্ট্রাক্ট ক্লাসের বাস্তবায়ন যা প্রক্সি মেথড একটি প্রকৃত ActionBar কল করে, এটির অন্তর্ভুক্ত Activity থেকে প্রাপ্ত।
TabHelperHoneycomb প্রয়োগ করুন, ActionBar API-তে প্রক্সি পদ্ধতি কল করুন:
কোটলিন
class TabHelperHoneycomb internal constructor(activity: FragmentActivity) : TabHelper(activity) { private var mActionBar: ActionBar? = null override fun setUp() { mActionBar = mActionBar ?: mActivity.actionBar.apply { navigationMode = ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS } } override fun addTab(tab: CompatTab) { // Tab is a CompatTabHoneycomb instance, so its // native tab object is an ActionBar.Tab. mActionBar?.addTab(tab.getTab() as ActionBar.Tab) } }
জাভা
public class TabHelperHoneycomb extends TabHelper { ActionBar actionBar; ... protected void setUp() { if (actionBar == null) { actionBar = activity.getActionBar(); actionBar.setNavigationMode( ActionBar.NAVIGATION_MODE_TABS); } } public void addTab(CompatTab tab) { ... // Tab is a CompatTabHoneycomb instance, so its // native tab object is an ActionBar.Tab. actionBar.addTab((ActionBar.Tab) tab.getTab()); } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }

