假設您要使用動作列分頁做為應用程式頂層導覽的主要形式。很抱歉,ActionBar API 僅適用於 Android 3.0 以上版本 (API 級別 11 以上)。因此,如果您要將應用程式發行到執行舊版平台的裝置,就必須提供支援新版 API 的實作,同時提供使用舊版 API 的備用機制。
在本課程中,您將建構分頁的使用者介面 (UI) 元件,此元件使用具備版本專屬實作的抽象類別,以提供回溯相容性。本課程將說明如何為新的分頁 API 建立抽象層,做為建構分頁元件的第一步。
為抽象層做好準備
Java 程式設計語言中的「抽象」包含建立一或多個介面或抽象類別,以隱藏實作詳細資料。如果是較新的 Android API,您可以使用抽象化機制來建構適用於較新版本的元件,在新型裝置上使用現有 API,並在舊裝置上改回使用較舊、更相容的 API。
使用這個方法時,您必須先決定要以回溯相容方式使用哪些新類別,然後根據較新類別的公用介面建立抽象類別。定義抽象介面時,請盡可能建立較新的 API 的鏡像。這可以提高前瞻相容性,方便日後在不再需要時捨棄抽象層。
為新的 API 建立抽象類別後,即可在執行階段建立及選擇任意數量的實作項目。為了回溯相容,這些實作方式可能因所需的 API 級別而異。因此,其中一種實作項目可能會使用最近發布的 API,而其他實作則可使用舊版 API。
建立抽象分頁介面
如要建立可回溯相容的分頁版本,您必須先確定應用程式所需的功能和特定 API。針對頂層版面分頁,假設您符合下列功能需求:
- 分頁指標應會顯示文字和圖示。
- 分頁可與片段執行個體建立關聯。
- 活動應能監聽分頁變更。
預先備妥這些需求後,您就能控管抽象層的範圍。這表示您能省下建立多個抽象層的實作時間,更快開始使用新的回溯相容實作。
分頁的主要 API 位於 ActionBar 和 ActionBar.Tab。這些 API 會抽象化,讓分頁更容易辨識。本範例專案的需求要求返回 Eclair (API 級別 5),同時利用 Honeycomb (API 級別 11) 的新分頁功能。以下顯示支援這兩種實作及其抽象基礎類別 (或介面) 的類別結構圖表。
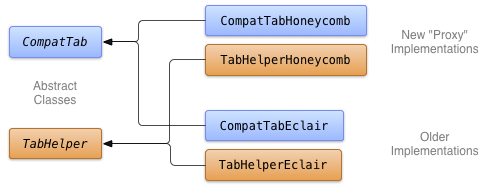
圖 1. 抽象基礎類別以及特定版本實作的類別圖表。
抽象動作列.Tab
如要開始建構分頁抽象層,請建立代表分頁的抽象類別,以鏡像 ActionBar.Tab 介面:
Kotlin
sealed class CompatTab(val tag: String) { ... abstract fun getText(): CharSequence abstract fun getIcon(): Drawable abstract fun getCallback(): CompatTabListener abstract fun getFragment(): Fragment abstract fun setText(text: String): CompatTab abstract fun setIcon(icon: Drawable): CompatTab abstract fun setCallback(callback: CompatTabListener): CompatTab abstract fun setFragment(fragment: Fragment): CompatTab ... }
Java
public abstract class CompatTab { ... public abstract CompatTab setText(int resId); public abstract CompatTab setIcon(int resId); public abstract CompatTab setTabListener( CompatTabListener callback); public abstract CompatTab setFragment(Fragment fragment); public abstract CharSequence getText(); public abstract Drawable getIcon(); public abstract CompatTabListener getCallback(); public abstract Fragment getFragment(); ... }
您可以使用抽象類別 (而非介面) 簡化常用功能的實作程序,例如分頁物件與活動的關聯 (不會顯示在程式碼片段中)。
抽象的 ActionBar 分頁方法
接著請定義抽象類別,用於在活動中建立並新增分頁,例如 ActionBar.newTab() 和 ActionBar.addTab():
Kotlin
sealed class TabHelper(protected val activity: FragmentActivity) { ... abstract fun setUp() fun newTab(tag: String): CompatTab { // This method is implemented in a later lesson. } abstract fun addTab(tab: CompatTab) ... }
Java
public abstract class TabHelper { ... public CompatTab newTab(String tag) { // This method is implemented in a later lesson. } public abstract void addTab(CompatTab tab); ... }
在後續課程中,您將建立 TabHelper 和 CompatTab 的實作方式,適用於舊版和新版平台。
