RelativeLayout คือกลุ่มมุมมองที่แสดงการดูของเด็กในแบบสัมพัทธ์
ตำแหน่ง ตำแหน่งของแต่ละมุมมองสามารถระบุเป็นสัมพัทธ์กับองค์ประกอบข้างเคียง (เช่น
ซ้ายของหรือด้านล่างมุมมองอื่น) หรือในตำแหน่งที่สัมพันธ์กับพื้นที่ RelativeLayout ระดับบนสุด (เช่น จัดชิดด้านล่าง ซ้าย หรือกึ่งกลาง)
หมายเหตุ หากต้องการการสนับสนุนด้านเครื่องมือและประสิทธิภาพที่ดีขึ้น คุณควรสร้างเลย์เอาต์ด้วย ConstraintLayout แทน

RelativeLayout เป็นยูทิลิตีที่ทรงพลังมากสำหรับการออกแบบอินเทอร์เฟซผู้ใช้
เนื่องจากสามารถกำจัดกลุ่มมุมมองที่ซ้อนกัน และทำให้ลำดับชั้นของเลย์เอาต์มีความคงที่ ซึ่งช่วยปรับปรุง
ด้านประสิทธิภาพ หากคุณพบว่าตนเองใช้กลุ่ม LinearLayout ที่ซ้อนกันหลายกลุ่ม
คุณอาจแทนที่ด้วย RelativeLayout เดียวได้
มุมมองการวางตำแหน่ง
RelativeLayout ทำให้มุมมองย่อยสามารถระบุอันดับที่สัมพันธ์กับ
มุมมองหลักหรือมุมมองของกันและกัน (ระบุโดยรหัส) คุณสามารถจัดเรียงองค์ประกอบ 2 รายการด้วยเส้นขอบด้านขวา หรือ
ทำให้วิดีโอหนึ่งอยู่ใต้หน้าจออีกแบบหนึ่ง กึ่งกลางหน้าจอ กึ่งกลางซ้าย และอื่นๆ โดยค่าเริ่มต้น ผู้เผยแพร่โฆษณาย่อยทั้งหมด
มุมมองจะวาดที่ด้านซ้ายบนของเลย์เอาต์ คุณจึงต้องกำหนดตำแหน่งของแต่ละมุมมอง
โดยใช้คุณสมบัติการจัดวางที่หลากหลายจาก RelativeLayout.LayoutParams
พร็อพเพอร์ตี้ของเลย์เอาต์บางส่วนที่มีให้ดูใน RelativeLayout
รวมข้อมูลต่อไปนี้
android:layout_alignParentTop- หาก
"true"จะทำให้ขอบด้านบนของมุมมองนี้ตรงกับขอบด้านบนของระดับบนสุด android:layout_centerVertical- หากเป็น
"true"ให้เด็กคนนี้อยู่กึ่งกลางในแนวตั้งภายในแนวตั้ง android:layout_below- จัดตำแหน่งขอบด้านบนของมุมมองนี้ใต้ข้อมูลพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ที่ระบุด้วยรหัสทรัพยากร
android:layout_toRightOf- จัดตำแหน่งขอบด้านซ้ายของมุมมองนี้ทางด้านขวาของข้อมูลพร็อพเพอร์ตี้ที่ระบุด้วยรหัสทรัพยากร
นี่เป็นเพียงตัวอย่างบางส่วน แอตทริบิวต์เลย์เอาต์ทั้งหมดจะบันทึกไว้ที่ RelativeLayout.LayoutParams
ค่าสำหรับคุณสมบัติการจัดวางแต่ละรายการเป็นบูลีนสำหรับ
เปิดใช้ตำแหน่งเลย์เอาต์ที่สัมพันธ์กับ RelativeLayout ระดับบนสุดหรือรหัสที่
อ้างอิงถึงมุมมองอื่นในการจัดวางที่ควรตำแหน่งของมุมมองนั้น
ในเลย์เอาต์ XML ของคุณ ทรัพยากร Dependency เทียบกับมุมมองอื่นๆ ในเลย์เอาต์จะประกาศในลำดับใดก็ได้ เช่น คุณสามารถประกาศว่า "view1" ให้อยู่ต่ำกว่า "มุมมอง 2" แม้ว่าจะเป็น "view2" เป็นอันสุดท้าย มุมมองที่ประกาศในลำดับชั้น ตัวอย่างด้านล่างจะแสดงให้เห็นสถานการณ์ดังกล่าว
ตัวอย่าง
โดยจะเน้นแอตทริบิวต์แต่ละอย่างที่ควบคุมตำแหน่งสัมพัทธ์ของมุมมองแต่ละรายการ
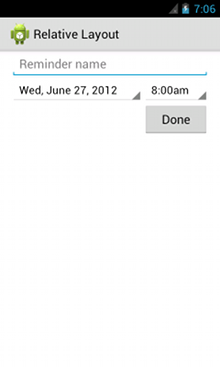
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/reminder" /> <Spinner android:id="@+id/dates" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/times" /> <Spinner android:id="@id/times" android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <Button android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/times" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:text="@string/done" /> </RelativeLayout>
โปรดดูรายละเอียดเกี่ยวกับแอตทริบิวต์เลย์เอาต์ทั้งหมดที่ใช้ได้สำหรับมุมมองย่อยแต่ละรายการของ RelativeLayout ที่หัวข้อ RelativeLayout.LayoutParams

