LinearLayout
là một nhóm khung hiển thị căn chỉnh tất cả phần tử con theo một hướng, chiều dọc hoặc
theo chiều ngang. Bạn có thể chỉ định hướng bố cục bằng thuộc tính
android:orientation
.
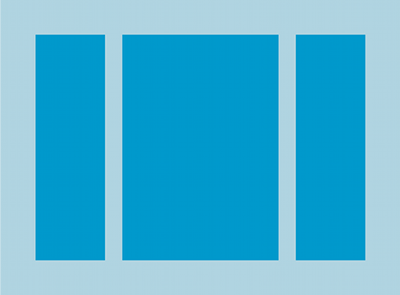
LinearLayout có 3 theo chiều ngang
trẻ em.
Tất cả phần tử con của LinearLayout được xếp chồng lần lượt nhau,
vì vậy, danh sách dọc chỉ có một phần tử con trên mỗi hàng, bất kể độ rộng của các phần tử đó. Đáp
danh sách ngang chỉ cao một hàng và đó là chiều cao của phần tử con cao nhất,
cộng với khoảng đệm. LinearLayout tuân theo lề giữa
phần tử con và trọng lực – bên phải, chính giữa hoặc bên trái
căn chỉnh—của từng phần tử con.
Trọng số bố cục
LinearLayout cũng hỗ trợ chỉ định trọng số cho
những con cá nhân có
android:layout_weight
. Thuộc tính này gán một "mức độ quan trọng" cho một lượt xem theo
nó chiếm bao nhiêu không gian trên màn hình. Giá trị trọng số lớn hơn cho phép quảng cáo mở rộng
để lấp đầy không gian còn lại trong khung hiển thị mẹ. Chế độ xem con có thể chỉ định trọng số
giá trị và mọi không gian còn lại trong nhóm khung hiển thị sẽ được gán cho các thành phần con
tương ứng, dựa trên trọng số đã khai báo. Trọng số mặc định là 0.
Phân bổ đồng đều
Để tạo bố cục tuyến tính, trong đó mỗi thành phần con sử dụng cùng một lượng không gian
trên màn hình, hãy đặt
android:layout_height
của mỗi thành phần hiển thị thành "0dp" cho bố cục dọc hoặc
android:layout_width
của mỗi thành phần hiển thị thành "0dp" cho bố cục ngang. Sau đó, đặt
android:layout_weight của mỗi chế độ xem đến "1".
Phân bổ không đồng đều
Bạn cũng có thể tạo bố cục tuyến tính trong đó các phần tử con sử dụng các kiểu bố cục khác nhau một lượng không gian trên màn hình. Hãy xem các ví dụ sau đây:
- Giả sử bạn có ba trường văn bản: hai trường có giá trị trọng số là 1 và một trường thứ ba có giá trị trọng số mặc định là 0. Trường văn bản thứ ba có giá trị trọng số bằng 0, chỉ chiếm diện tích cần thiết cho nội dung của hàm. Khác hai trường văn bản, với giá trị trọng số là 1, hãy mở rộng đều để lấp đầy khoảng trống còn lại sau khi nội dung của cả ba trường được đo.
- Nếu bạn có 3 trường văn bản, trong đó 2 trường có giá trị trọng số là 1 và phần tử thứ ba có trọng số là 2, thì phần còn lại sau phần tử nội dung của cả ba trường được phân bổ như sau: 1/2 đến 2 trường có giá trị trọng số là 2 và một nửa được chia đều cho có giá trị trọng số là 1.
Hình và đoạn mã sau đây cho thấy cách hoạt động của trọng số bố cục trong một "gửi tin nhắn" của bạn. Trường Tới, dòng Chủ đề và nút Gửi chỉ chiếm chiều cao mà các phần tử đó cần. Vùng thông báo chiếm phần còn lại trong chiều cao của hoạt động.

LinearLayout.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" android:orientation="vertical" > <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/to" /> <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/subject" /> <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:gravity="top" android:hint="@string/message" /> <Button android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="end" android:text="@string/send" /> </LinearLayout>
Để biết thông tin chi tiết về các thuộc tính có sẵn cho mỗi chế độ xem con của một
LinearLayout, xem
LinearLayout.LayoutParams

