طرحبندیهای نمایش برنامه پیمایش شامل لیستها ( TransformingLazyColumn ) و دیالوگها است. این طرحبندیها اکثر صفحهنمایش برنامهها را تشکیل میدهند و مجموعهای از مؤلفهها را نشان میدهند که باید با اندازههای صفحه نمایش بزرگتر سازگار شوند. بررسی کنید که مؤلفهها پاسخگو باشند—یعنی عرض موجود را پر کنند و هنگامی که ارتفاع بیشتری از صفحه در دسترس است، تنظیمات TransformingLazyColumn انجام دهند. این طرحبندیها قبلاً بهصورت پاسخگو ساخته شدهاند، و ما توصیههای دیگری برای استفاده بیشتر از املاک و مستغلات داریم.
طراحی های پاسخگو و بهینه بسازید
برای کمک به انطباق طرحبندیهای طراحی شما با اندازههای صفحهنمایش بزرگتر، ما رفتار طرحبندیها و اجزای خود را بهروزرسانی کردهایم تا رفتار پاسخگوی داخلی، از جمله حاشیهها و بالشتکهای مبتنی بر درصد داشته باشیم. برای رسیدگی به این موضوع، طرحبندیها و مؤلفههای کتابخانه رابط کاربری Android خود را با رفتار پاسخگوی داخلی، از جمله حاشیهها و بالشتکهای مبتنی بر درصد بهروزرسانی کردهایم. اگر از مؤلفه های Compose ما استفاده می کنید، می توانید به طور خودکار این پاسخگویی را به ارث ببرید.
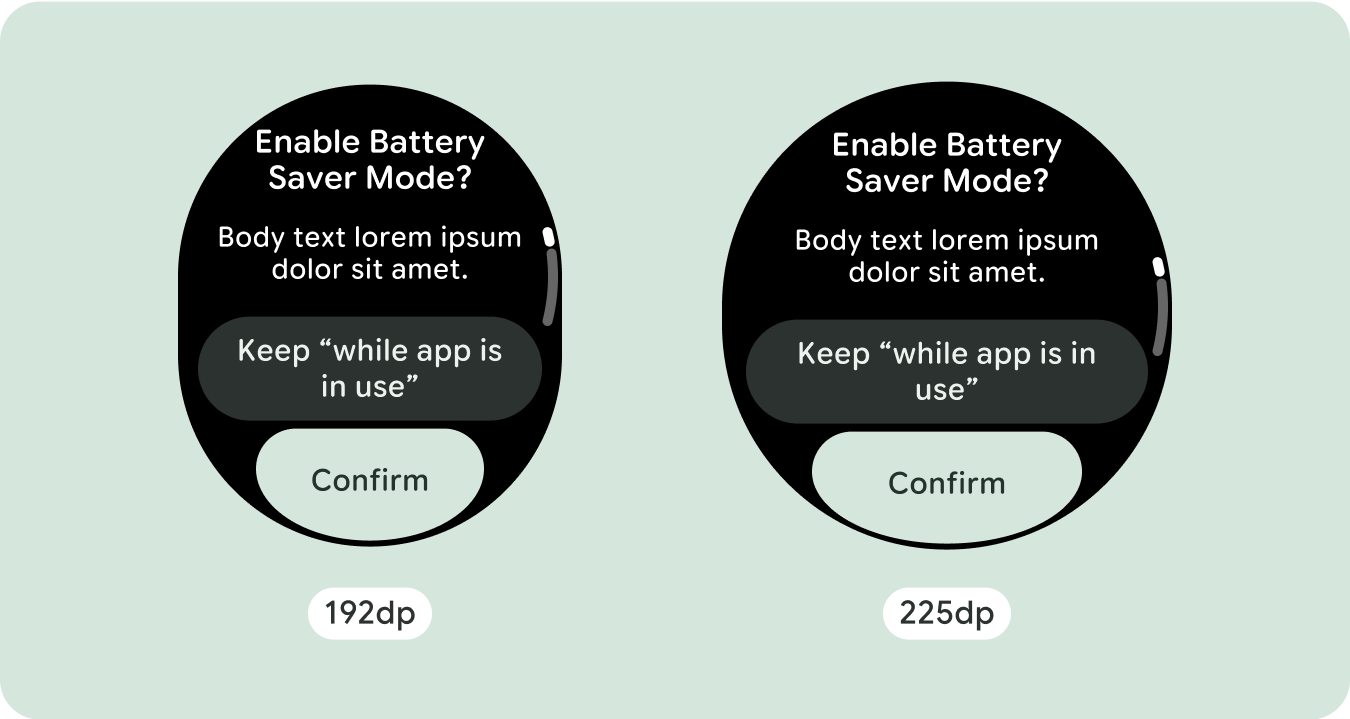
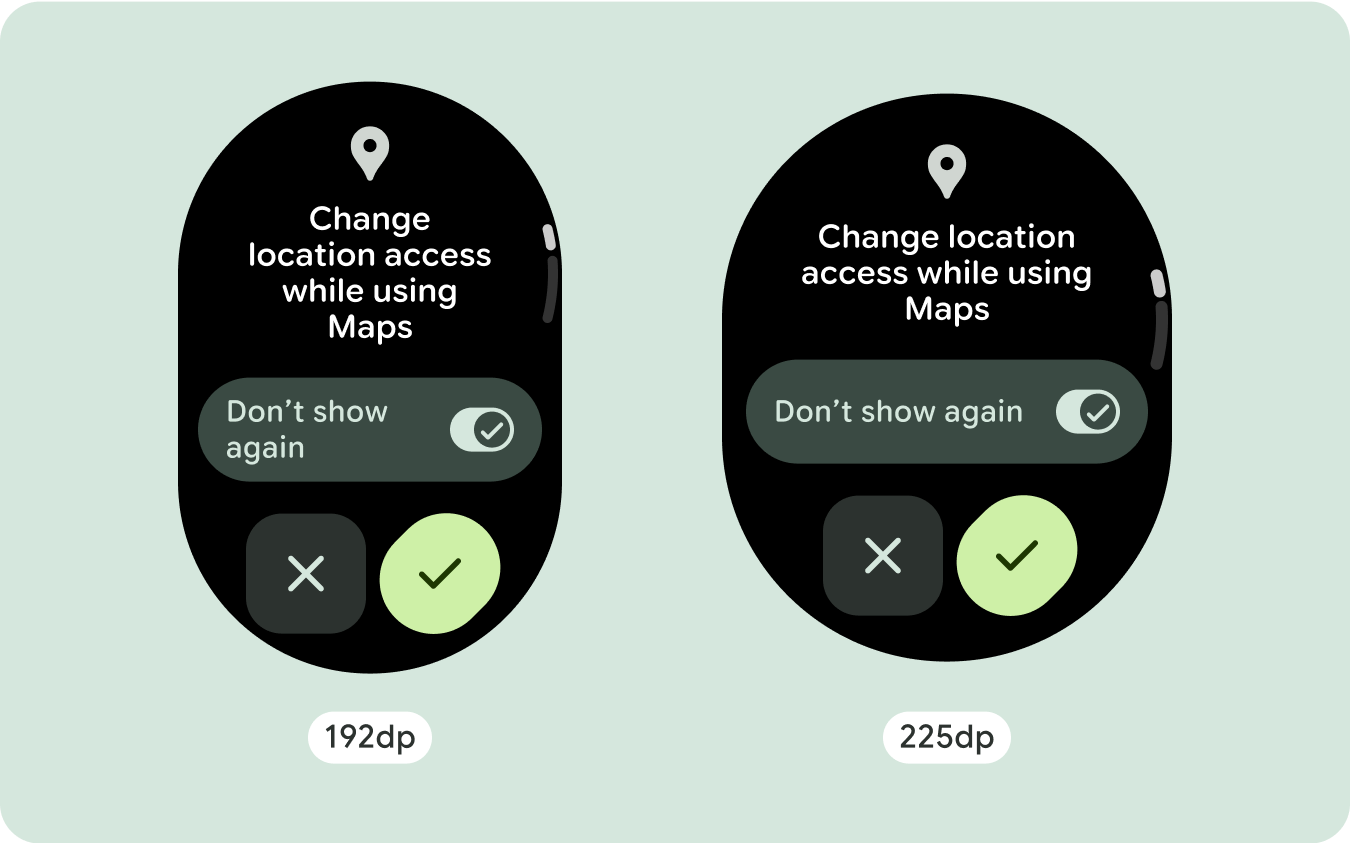
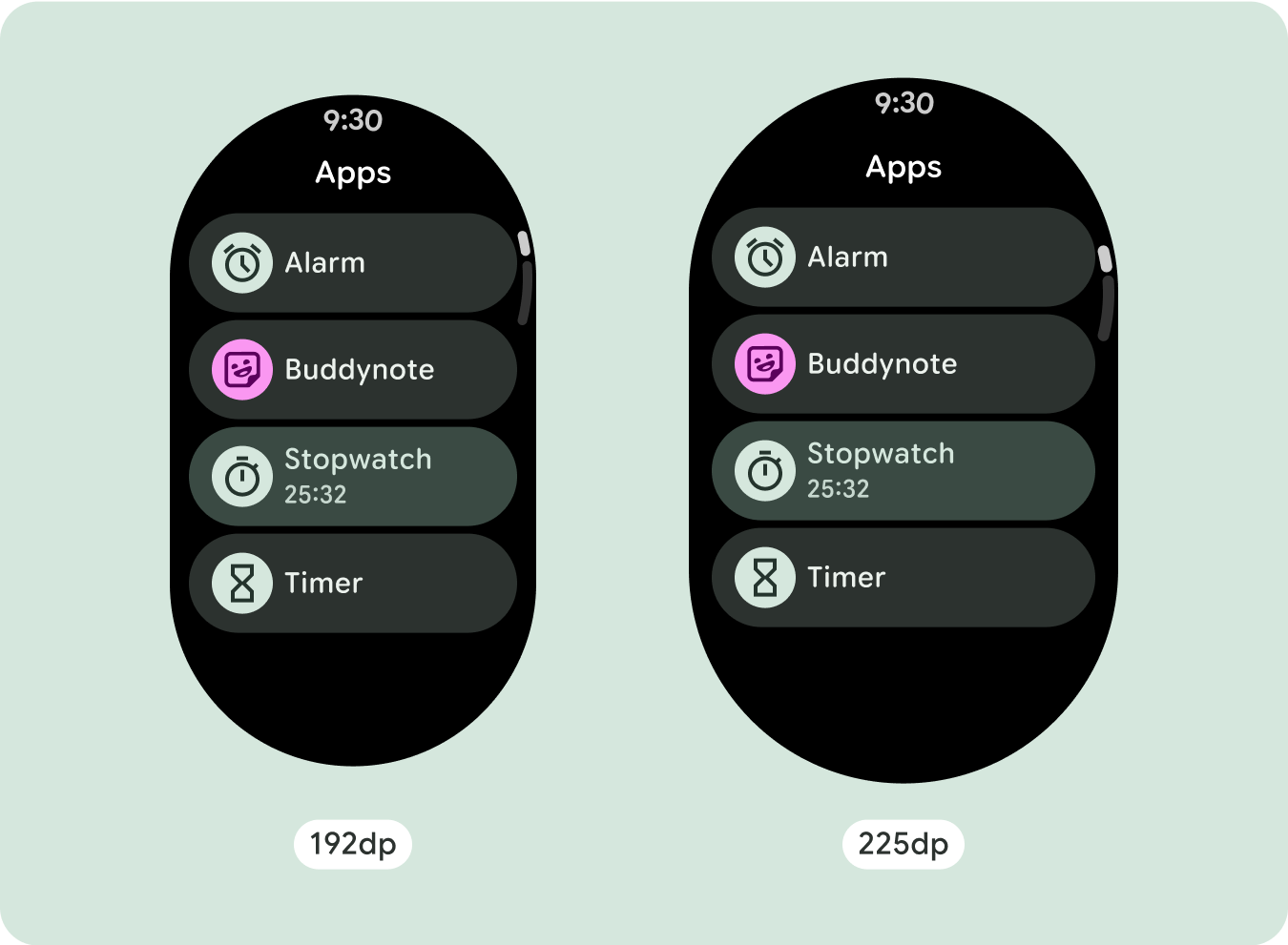
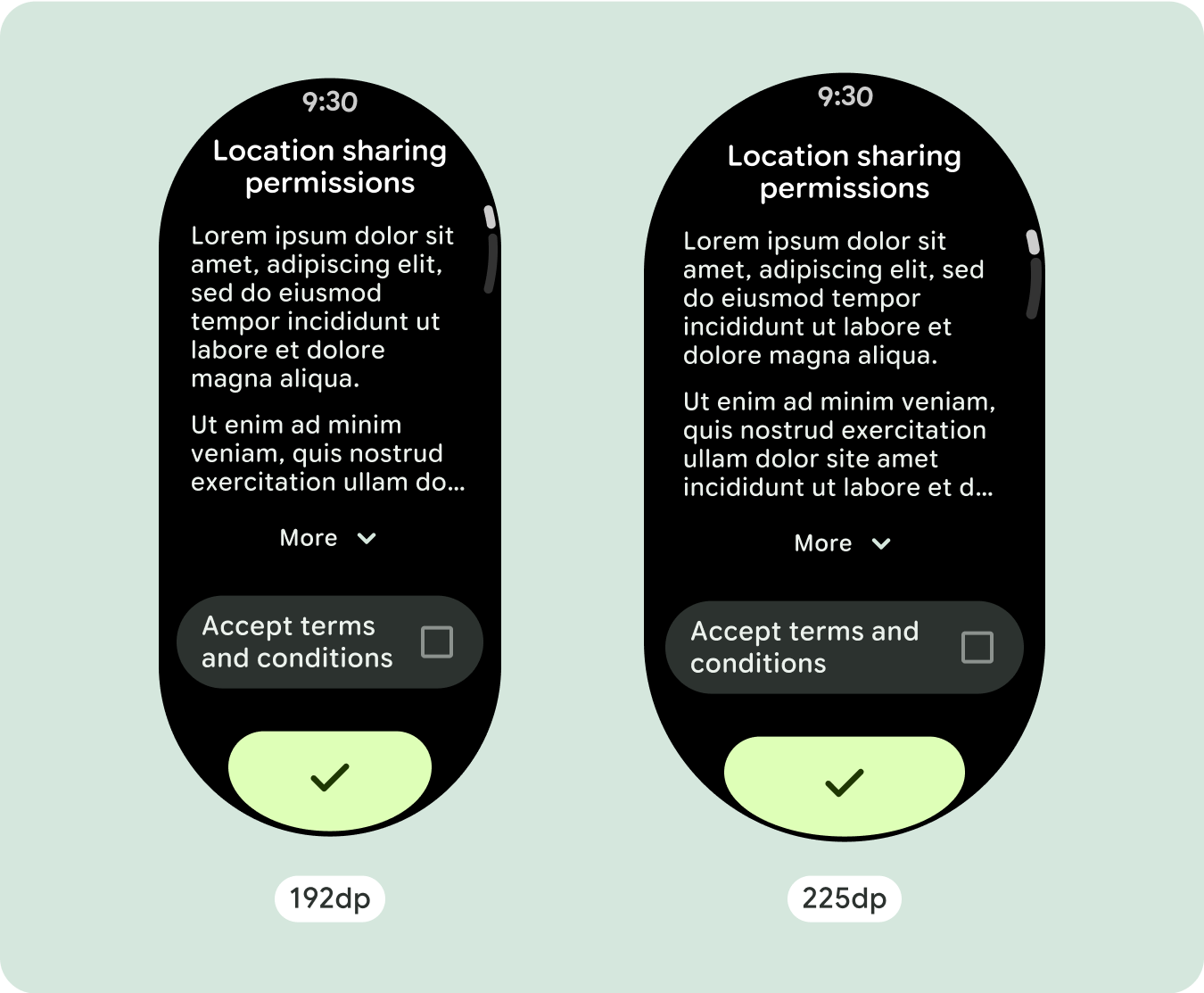
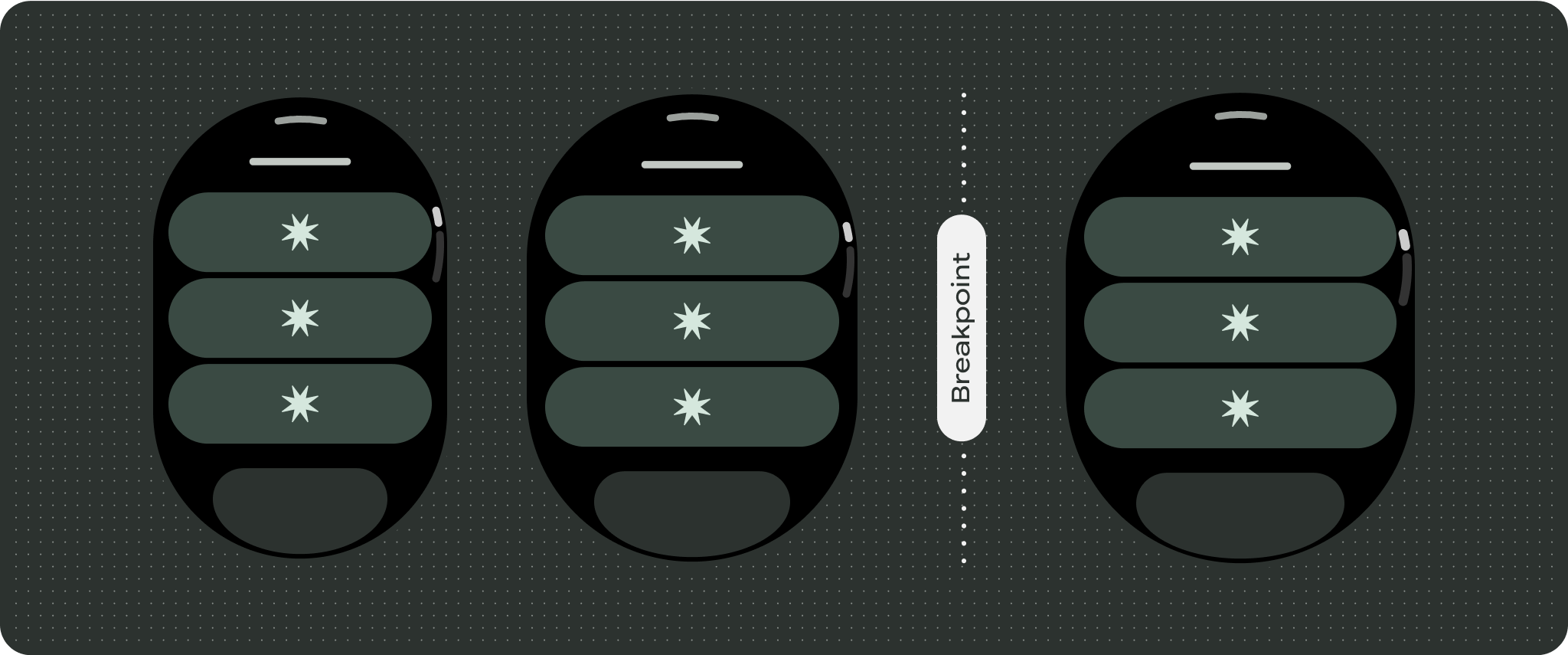
برای طراحیهای منحصربهفرد صفحهنمایش، اندازههای مختلف صفحهنمایش را بهطور کامل تست کنید، اطمینان حاصل کنید که اجزا و عناصر بهخوبی منطبق میشوند و از بریده شدن محتوا جلوگیری میکنند. حاشیههای درصدی ما به مقیاسبندی مؤثر فاصلهدهندهها کمک میکند، و توصیه میکنیم از نقطه شکست 225dp برای معرفی اطلاعات بیشتر و عملکرد بهبودیافته در صفحههای ساعت بزرگتر استفاده کنید.
بررسی کنید که اجزای عرض موجود را پر کنند
همه اجزا به صورت پاسخگو ساخته می شوند، به این معنی که عرض و ارتفاع موجود را پر می کنند. مطمئن شوید که حاشیههای لازم را دارید تا مطمئن شوید که محتوا توسط صفحه گرد بریده نمیشود.
نمایش کاراکترهای متنی اضافی
اکثر اجزا دارای کادرهای متنی هستند که عرض موجود را پر می کنند. این بدان معنی است که با افزایش عرض صفحه نمایش، آنها به طور خودکار تعداد کاراکترها را به دست می آورند.
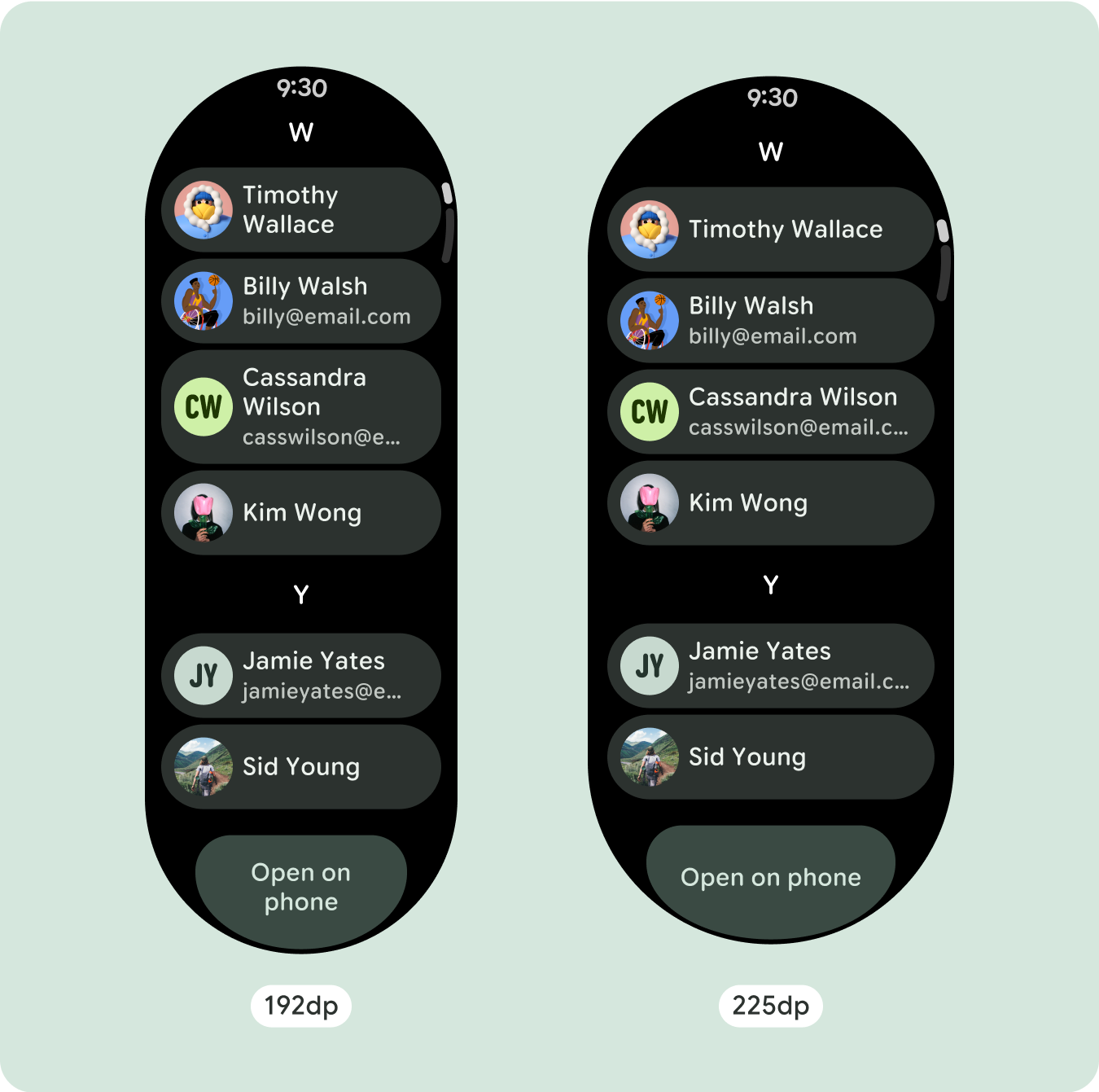

طراحی های تطبیقی و متمایز بسازید
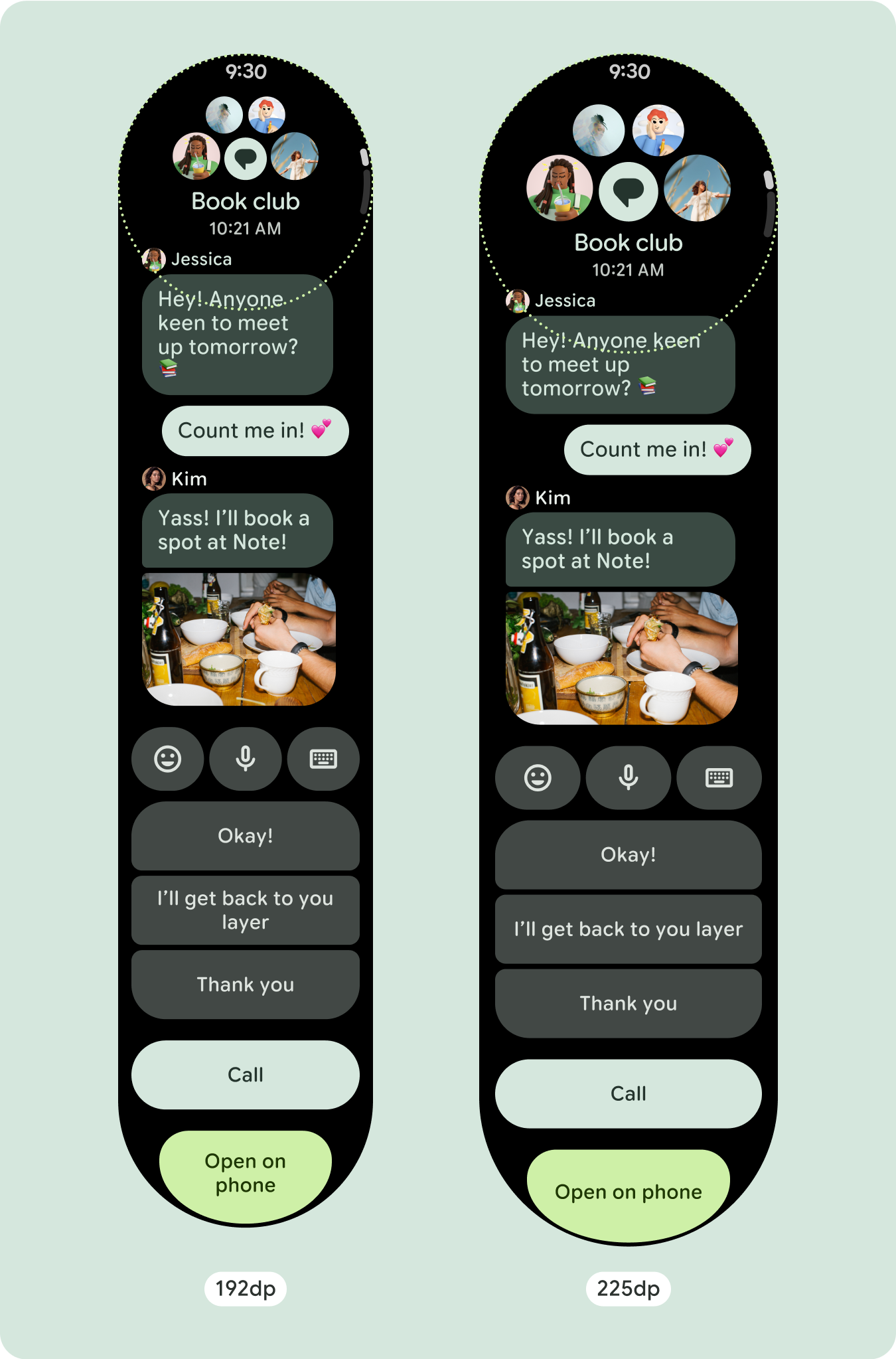
از آنجایی که طرحبندیهای پیمایش بهطور خودکار موارد بیشتری را که قبلاً در زیر صفحه پنهان شده بود نشان میدهند، برای افزودن ارزش نیازی به انجام کار زیادی نیست. هر مؤلفه پهنای موجود را پر میکند، و در برخی موارد، ممکن است یک مؤلفه ردیفهای اضافی متن (مانند کارتها) به دست آورد یا مؤلفهها برای پر کردن عرض موجود (مانند دکمههای نماد) کشیده شوند.
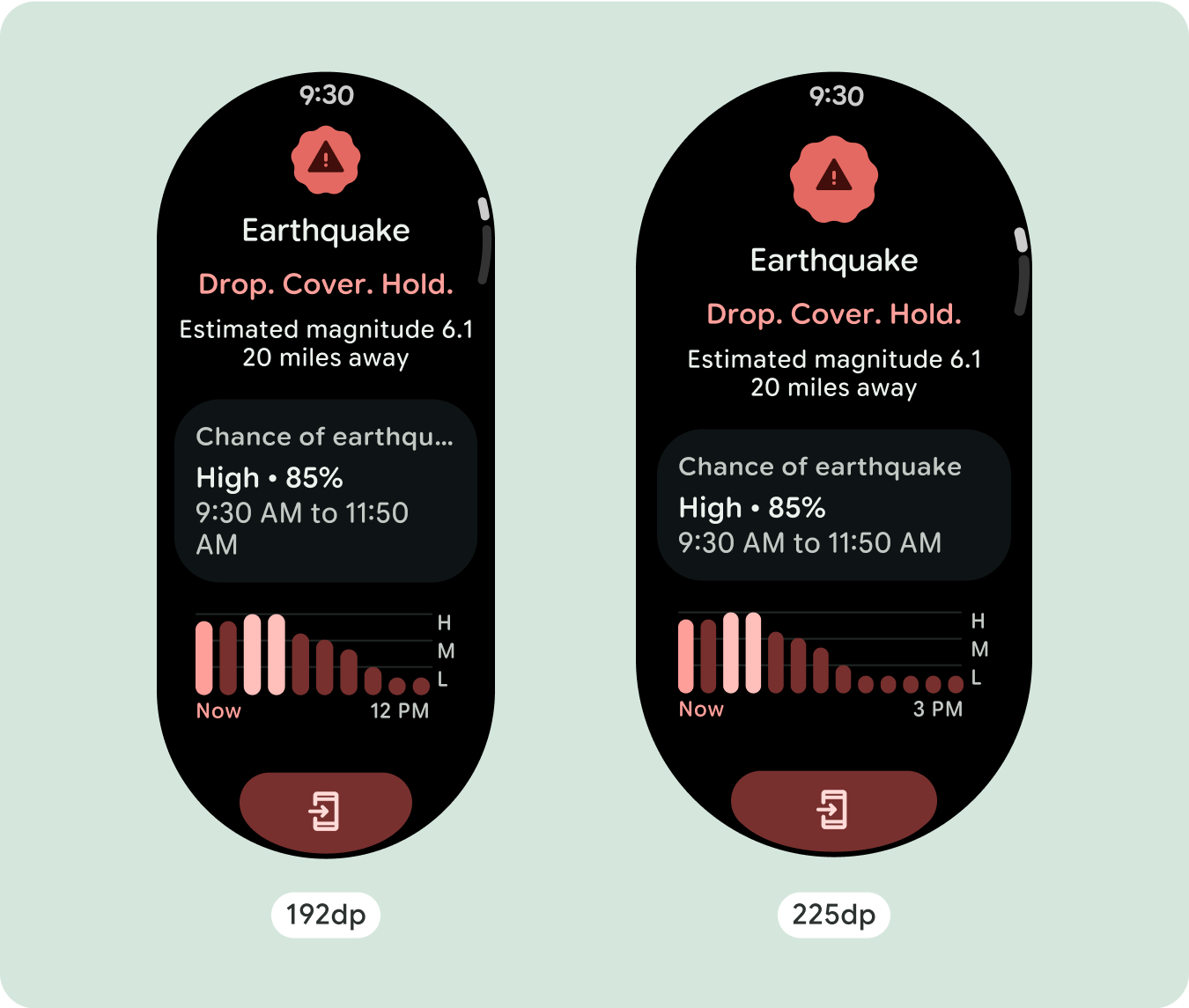
برای استفاده بهینه از فضای اضافی در اندازه های بزرگتر صفحه نمایش، یک نقطه شکست اندازه در 225dp اضافه کنید. این نقطه شکست امکان نمایش محتوای اضافی، اضافه کردن دکمهها یا دادههای بیشتر، یا تغییر طرحبندی را برای مطابقت بهتر با صفحه نمایش بزرگتر ممکن میسازد. این نیاز به طراحی متفاوتی برای هر نقطه شکست دارد. طراحی صفحه نمایش بزرگتر (225+) می تواند شامل عناصر اضافی زیر باشد:
اندازه را افزایش دهید یا وضعیت اجزای موجود را تغییر دهید
این می تواند به منظور نشان دادن جزئیات بیشتر یا قابل مشاهده تر کردن محتوا انجام شود.

چیدمان های بهینه شده و متفاوت
چیدمان میتواند پس از نقطه شکست 225dp کمی تغییر کند، به طوری که محتوای بالای صفحه در نمای پیشفرض بهینهسازی میشود، با این حال، تمام محتوای یکسان زیر تاشو باید بدون توجه به اندازه صفحه همچنان در دسترس باشند.
رفتار پاسخگو و سازگار
همه مؤلفههای موجود در کتابخانه Compose بهطور خودکار با اندازه گستردهتر صفحه سازگار میشوند و عرض و ارتفاع را افزایش میدهند. نماهای اسکرول که از شیوههای طراحی واکنشگرا استفاده میکنند، معمولاً با طیف وسیعی از اندازههای صفحه سازگار میشوند. با این حال، در برخی موارد خاص، میتوانید از یک نقطه شکست برای نادیده گرفتن ابعاد و تقویت طرحبندیها استفاده کنید که عملکرد را افزایش میدهد، قابلیت نگاه را بهبود میبخشد یا محتوا را بهتر روی صفحه نمایش میدهد.
تمام حاشیههای بالا، پایین و کناری باید بر حسب درصد تعریف شوند تا از بریده شدن و ایجاد مقیاسبندی متناسب عناصر جلوگیری شود. در نظر بگیرید که PositionIndicator زمانی که کاربر پیمایش می کند ظاهر می شود و بدون توجه به اندازه آن، به طور خودکار قاب صفحه را در آغوش می گیرد.
چک لیست
- حاشیه های بالا، پایین و کناری توصیه شده را اعمال کنید.
- حاشیه های بیرونی را در مقادیر درصد تعریف کنید تا از برش در ابتدا و انتهای ظرف قابل پیمایش جلوگیری کنید.
- حاشیه ها را در مقادیر ثابت DP بین عناصر UI اعمال کنید.
- استفاده از نقطه شکست در 225dp را در نظر بگیرید تا محتوای اضافی را معرفی کنید یا محتوای موجود را در اندازههای صفحه بزرگتر قابل مشاهدهتر کنید.
تجربیات متمایز ایجاد کنید
نماهای اسکرول بسیار قابل تنظیم هستند، با قابلیت افزودن هر ترکیبی از اجزا به هر ترتیب. حاشیه های بالا و پایین بسته به اینکه کدام اجزا در بالا و پایین قرار می گیرند می توانند تغییر کنند. این برای جلوگیری از بریده شدن محتوا توسط منحنی رو به رشد صفحه است.


