Material Design هو دليل شامل للتصميم المرئي والحركة والتفاعل عبر الأنظمة الأساسية والأجهزة. لاستخدام التصميم المتعدد الأبعاد في تطبيقات Android، اتبع الإرشادات المحددة في مواصفات Material Design. إذا كان تطبيقك يستخدم مكتبة Compose في Jetpack، يمكنك استخدام مكتبة Compose Material 3. إذا كان تطبيقك طرق العرض، يمكنك استخدام مكونات Android Material المكتبة.
يوفّر Android الميزات التالية لمساعدتك في إنشاء تطبيقات Material Design:
- مظهر تطبيق Material Design لتصميم جميع تطبيقات واجهة المستخدم المصغّرة
- التطبيقات المصغّرة للمشاهدات المعقّدة، مثل القوائم والبطاقات
- واجهات برمجة التطبيقات للظلال والصور المتحرّكة المخصّصة
نسق المواد والتطبيقات المصغّرة
للاستفادة من ميزات Material، مثل تصميم أدوات واجهة المستخدم القياسية، وتبسيط تعريف نمط التطبيق، وتطبيق مظهر قائم على المواد في تطبيقك.
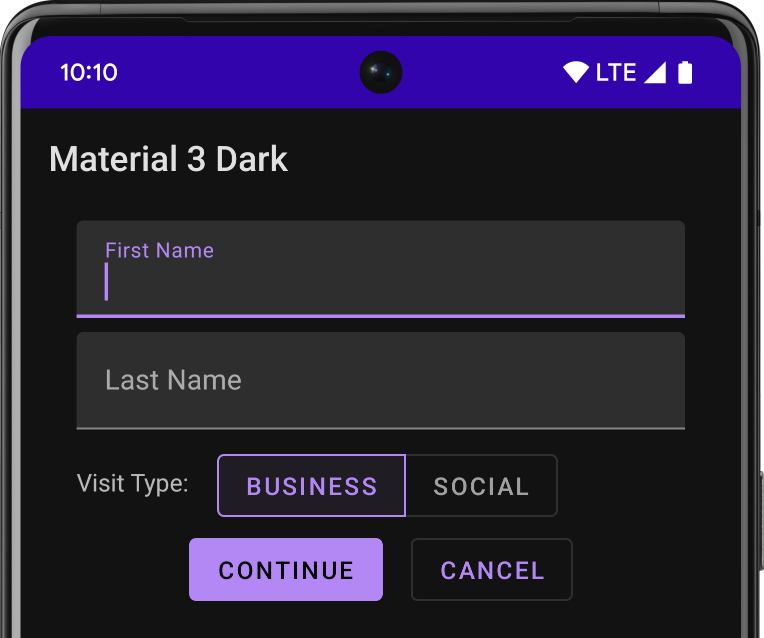
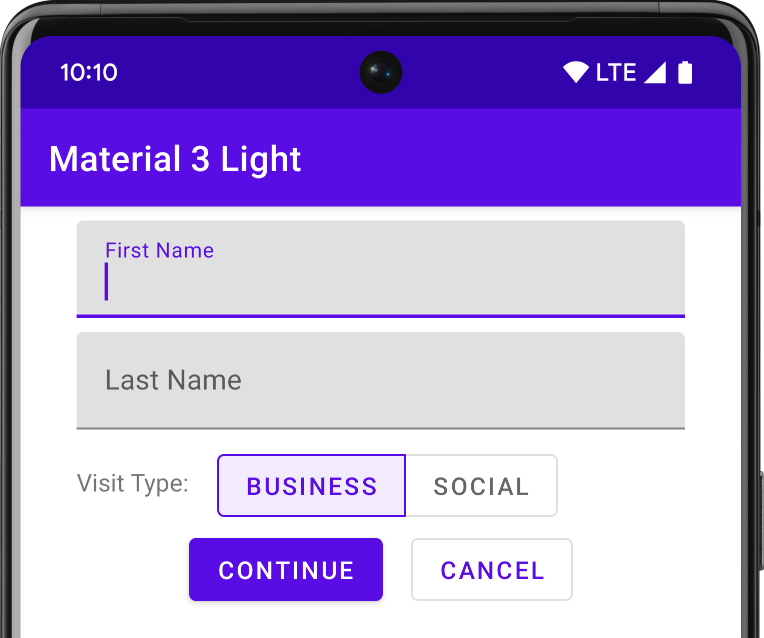
إذا كنت تستخدم "استوديو Android" لإنشاء مشروع Android، سيتم تلقائيًا تطبيق "مظهر متعدد الأبعاد". للتعرّف على كيفية تعديل مظهر مشروعك، يمكنك الاطّلاع على الأنماط والمظاهر:
لمنح المستخدمين تجربة مألوفة، استخدم أنماط تجربة المستخدم الأكثر شيوعًا في Material:
- شجِّع المستخدمين على اتّخاذ الإجراء الرئيسي في واجهة المستخدم باستخدام زر إجراء عائم.
- يمكنك عرض علامتك التجارية وعناصر التنقل والبحث والإجراءات الأخرى باستخدام شريط التطبيقات.
- يمكنك إظهار التنقل في تطبيقك وإخفاؤه باستخدام درج التنقل.
- يمكنك الاختيار من بين العديد من مكونات Material الأخرى لتخطيط التطبيق والتنقل، مثل أشرطة الأدوات وعلامات التبويب وشريط التنقل السفلي والمزيد. للاطّلاع على كلّها، يمكنك الاطّلاع على كتالوج مكونات Material Design لنظام التشغيل Android.
استخدِم رموز Material Icons المحدّدة مسبقًا كلّما أمكن. على سبيل المثال، بالنسبة إلى التنقل "القائمة" زر بالنسبة إلى لائحة التنقل، استخدِم "الهامبرغر" القياسي . عرض رموز التصميم المتعدد الأبعاد لقائمة من الأيقونات المتاحة. يمكنك أيضًا استيراد رموز SVG من مكتبة Material Icon باستخدام Vector Asset Studio:
بطاقات وظلال الارتفاع
بالإضافة إلى الموقعَين X وY، تمتلك الملفات الشخصية في Android السمة Z. يمثل هذا الموقع ارتفاع الملف الشخصي، والذي يحدد ما يلي:
- حجم الظل: تؤدي المشاهدات ذات قيم Z الأعلى إلى ظهور ظلال أكبر.
- ترتيب الرسم: تظهر المشاهدات ذات قيم Z الأعلى أعلى الملفات الشخصية الأخرى.
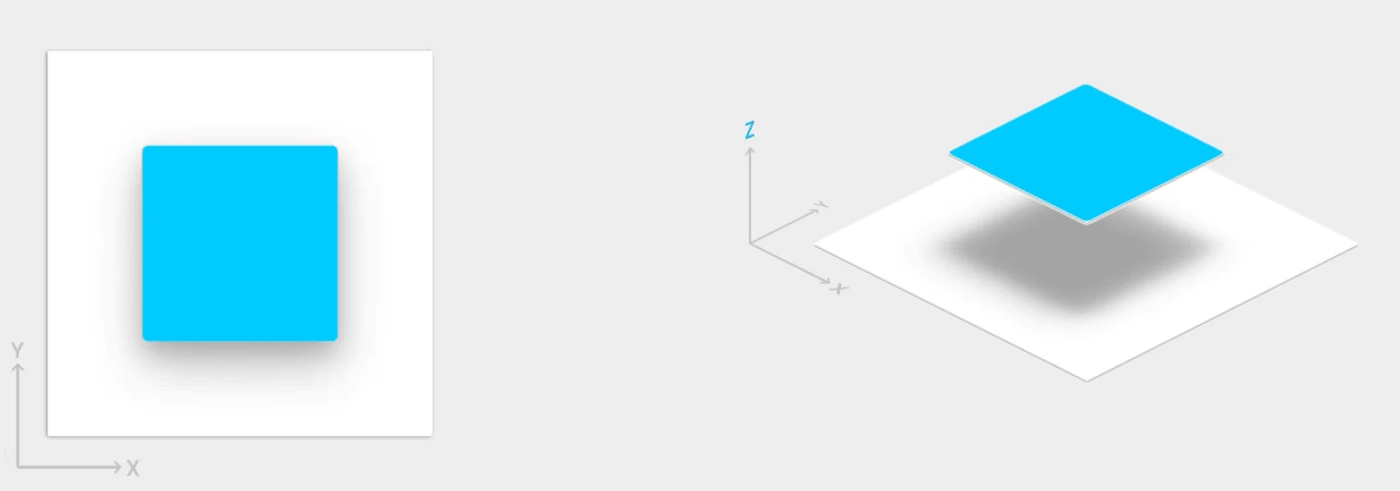
يمكنك تطبيق المسقط الرأسي على تخطيط يستند إلى بطاقة، مما يساعدك في عرض أجزاء مهمة من
المعلومات داخل البطاقات التي توفر مظهر Material. يمكنك استخدام التطبيق المصغّر
CardView ل
إنشاء بطاقات بارتفاع تلقائي. لمزيد من المعلومات، يُرجى مراجعة
إنشاء تنسيق مستند إلى بطاقة:
للحصول على معلومات عن إضافة ارتفاع إلى طرق العرض الأخرى، يُرجى الاطّلاع على إنشاء الظلال وطرق عرض المقاطع.
الصور المتحركة
تتيح لك واجهات برمجة تطبيقات الصور المتحركة إنشاء رسوم متحركة مخصصة للتعليقات باللمس في عناصر التحكم في واجهة المستخدم، والتغييرات في حالة العرض وتحولات الأنشطة.
تتيح لك واجهات برمجة التطبيقات هذه ما يلي:
- ويمكنك الرد على أحداث اللمس في طرق العرض باستخدام صور تعليقات اللمس المتحركة.
- إخفاء طرق العرض وإظهارها باستخدام الصور المتحركة للاكتشاف الدائري
- التبديل بين الأنشطة باستخدام رسوم متحركة مخصّصة لانتقال الأنشطة
- أنشئ صورًا متحركة أكثر طبيعية باستخدام الحركة المنحنية.
- يمكنك تحريك التغييرات في خاصية عرض واحدة أو أكثر باستخدام الصور المتحركة تغيير حالة العرض.
- عرض الصور المتحركة في عناصر قائمة الحالة بين تغييرات حالة العرض
تم دمج الصور المتحركة للملاحظات باللمس في العديد من طرق العرض العادية، مثل الأزرار. واجهات برمجة تطبيقات الرسوم المتحركة تخصيص هذه الرسوم المتحركة وإضافتها إلى طرق العرض المخصصة الخاصة بك.
لمزيد من المعلومات، يمكنك الاطّلاع على مقدّمة عن الصور المتحركة.
عناصر الرسم
تساعدك إمكانات عناصر الرسم هذه في تنفيذ تطبيقات Material Design:
- قابلة للرسم قابلة للتطوير بدون فقدان التعريف، وهي مثالية أيقونات أحادية اللون داخل التطبيق. مزيد من المعلومات حول ملفات المتجهات القابلة للرسم.
- يتيح لك التلوين القابل للرسم تحديد الصور النقطية كقناع ألفا وتلوينها باستخدام لون في وقت التشغيل. الاطّلاع على كيفية إضافة درجة اللون إلى العناصر القابلة للرسم
- تتيح لك ميزة استخراج الألوان استخراج الألوان البارزة تلقائيًا من صورة bitmap . اطّلِع على كيفية اختيار الألوان باستخدام Palette API.


