回転する三角形のようなプリセット プログラムに従ってオブジェクトを動かすと、
注目を集めていますが、ユーザーに OpenGL ES グラフィックスを操作してもらいたい場合はどうでしょうか。
OpenGL ES アプリをタッチ インタラクティブにするための鍵は、
GLSurfaceView:
onTouchEvent(): タッチイベントをリッスンします。
このレッスンでは、タッチイベントをリッスンしてユーザーによる OpenGL ES オブジェクトの回転を可能にする方法について紹介します。
タッチリスナーを設定する
OpenGL ES アプリがタッチイベントに応答できるようにするには、
onTouchEvent() メソッドを
GLSurfaceView クラス。以下の実装例は、
MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE のイベントを作成し、それを次の言語に翻訳する
図形の回転角度。
Kotlin
private const val TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR: Float = 180.0f / 320f ... private var previousX: Float = 0f private var previousY: Float = 0f override fun onTouchEvent(e: MotionEvent): Boolean { // MotionEvent reports input details from the touch screen // and other input controls. In this case, you are only // interested in events where the touch position changed. val x: Float = e.x val y: Float = e.y when (e.action) { MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> { var dx: Float = x - previousX var dy: Float = y - previousY // reverse direction of rotation above the mid-line if (y > height / 2) { dx *= -1 } // reverse direction of rotation to left of the mid-line if (x < width / 2) { dy *= -1 } renderer.angle += (dx + dy) * TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR requestRender() } } previousX = x previousY = y return true }
Java
private final float TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR = 180.0f / 320; private float previousX; private float previousY; @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) { // MotionEvent reports input details from the touch screen // and other input controls. In this case, you are only // interested in events where the touch position changed. float x = e.getX(); float y = e.getY(); switch (e.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: float dx = x - previousX; float dy = y - previousY; // reverse direction of rotation above the mid-line if (y > getHeight() / 2) { dx = dx * -1 ; } // reverse direction of rotation to left of the mid-line if (x < getWidth() / 2) { dy = dy * -1 ; } renderer.setAngle( renderer.getAngle() + ((dx + dy) * TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR)); requestRender(); } previousX = x; previousY = y; return true; }
このメソッドでは、回転角度の計算後、
requestRender():
フレームをレンダリングするタイミングであることを通知します。この例では、このアプローチが最も効率的です
これは、回転に変更がない限りフレームを再描画する必要がないためです。ただし、
ただし、次の場合にのみレンダラに再描画をリクエストしない限り、効率に影響はありません。
setRenderMode() を使用してデータが変更される
そのため、レンダラで次の行を必ずコメント化解除してください。
Kotlin
class MyGlSurfaceView(context: Context) : GLSurfaceView(context) { init { // Render the view only when there is a change in the drawing data renderMode = GLSurfaceView.RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY } }
Java
public MyGLSurfaceView(Context context) { ... // Render the view only when there is a change in the drawing data setRenderMode(GLSurfaceView.RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY); }
回転角度を公開する
上記のサンプルコードでは、回転角をレンダラで公開する必要があります。
公開メンバーの追加などですレンダラのコードはメインユーザーとは別のスレッドで実行されるため
渡すには、このパブリック変数を volatile として宣言する必要があります。
変数を宣言し、ゲッターとセッターを対で公開するコードを次に示します。
Kotlin
class MyGLRenderer4 : GLSurfaceView.Renderer { @Volatile var angle: Float = 0f }
Java
public class MyGLRenderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer { ... public volatile float mAngle; public float getAngle() { return mAngle; } public void setAngle(float angle) { mAngle = angle; } }
回転を適用する
タップ入力によって生成された回転を適用するには、角度を生成するコードをコメントアウトし、 タップ入力で生成された角度を含む変数を追加します。
Kotlin
override fun onDrawFrame(gl: GL10) { ... val scratch = FloatArray(16) // Create a rotation for the triangle // long time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() % 4000L; // float angle = 0.090f * ((int) time); Matrix.setRotateM(rotationMatrix, 0, angle, 0f, 0f, -1.0f) // Combine the rotation matrix with the projection and camera view // Note that the mvpMatrix factor *must be first* in order // for the matrix multiplication product to be correct. Matrix.multiplyMM(scratch, 0, mvpMatrix, 0, rotationMatrix, 0) // Draw triangle triangle.draw(scratch) }
Java
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) { ... float[] scratch = new float[16]; // Create a rotation for the triangle // long time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() % 4000L; // float angle = 0.090f * ((int) time); Matrix.setRotateM(rotationMatrix, 0, mAngle, 0, 0, -1.0f); // Combine the rotation matrix with the projection and camera view // Note that the vPMatrix factor *must be first* in order // for the matrix multiplication product to be correct. Matrix.multiplyMM(scratch, 0, vPMatrix, 0, rotationMatrix, 0); // Draw triangle mTriangle.draw(scratch); }
上記の手順が完了したら、プログラムを実行し、画面の上で指をドラッグして 三角形を回転させます。
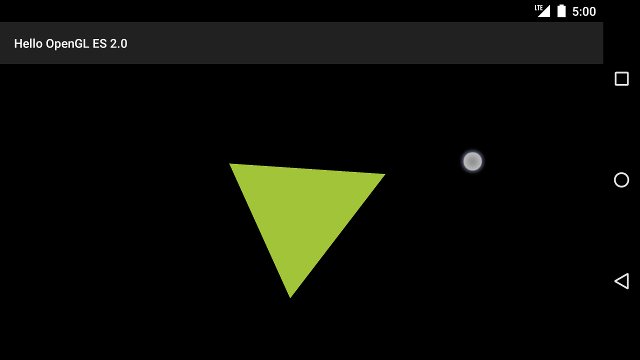
図 1. タップ入力で回転している三角形(円はタップを示しています) 設定されます。
