این درس نحوه ایجاد پیادهسازی را مورد بحث قرار میدهد که منعکسکننده APIهای جدیدتر و در عین حال از دستگاههای قدیمیتر پشتیبانی میکند.
در مورد راه حل جایگزین تصمیم بگیرید
چالش برانگیزترین کار در استفاده از ویژگی های رابط کاربری جدیدتر به روشی سازگار با عقب، تصمیم گیری و اجرای یک راه حل قدیمی تر (fallback) برای نسخه های پلتفرم قدیمی تر است. در بسیاری از موارد، این امکان وجود دارد که هدف این مؤلفههای رابط کاربری جدیدتر با استفاده از ویژگیهای چارچوب رابط کاربری قدیمیتر محقق شود. به عنوان مثال:
نوارهای اقدام را می توان با استفاده از یک
LinearLayoutافقی حاوی دکمه های تصویر، یا به عنوان نوار عنوان سفارشی یا به عنوان نما در طرح بندی فعالیت شما، پیاده سازی کرد. اقدامات سرریز را می توان در زیر دکمه منوی دستگاه ارائه کرد.برگههای Action Bar را میتوان با استفاده از یک
LinearLayoutافقی حاوی دکمهها یا با استفاده از عنصرTabWidgetUI پیادهسازی کرد.ویجت های
NumberPickerوSwitchرا می توان به ترتیب با استفاده از ابزارک هایSpinnerوToggleButtonپیاده سازی کرد.ویجت های
ListPopupWindowوPopupMenuرا می توان با استفاده از ابزارک هایPopupWindowپیاده سازی کرد.
به طور کلی راه حل یکسانی برای پسپورت کردن اجزای رابط کاربری جدیدتر به دستگاههای قدیمیتر وجود ندارد. مراقب تجربه کاربری باشید: در دستگاه های قدیمی تر، کاربران ممکن است با الگوهای طراحی جدیدتر و اجزای رابط کاربری آشنا نباشند. به این فکر کنید که چگونه می توان همان عملکرد را با استفاده از عناصر آشنا ارائه کرد. در بسیاری از موارد، این موضوع کمتر نگران کننده است - اگر اجزای رابط کاربری جدیدتر در اکوسیستم برنامه برجسته باشند (مانند نوار عمل)، یا مدل تعامل بسیار ساده و شهودی باشد (مانند نماها با کشیدن انگشت با استفاده از ViewPager ).
تب ها را با استفاده از API های قدیمی پیاده سازی کنید
برای ایجاد یک پیادهسازی قدیمیتر از برگههای نوار عمل، میتوانید از TabWidget و TabHost استفاده کنید (اگرچه میتوانید از ویجتهای Button با چیدمان افقی استفاده کنید). این را در کلاسهایی به نامهای TabHelperEclair و CompatTabEclair پیادهسازی کنید، زیرا این پیادهسازی از APIهایی استفاده میکند که حداکثر تا Android 2.0 (Eclair) معرفی شدهاند.
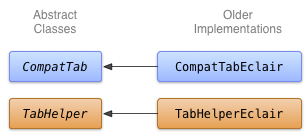
شکل 1. نمودار کلاس برای اجرای Eclair زبانه ها.
پیاده سازی CompatTabEclair ویژگی های برگه مانند متن برگه و نماد را در متغیرهای نمونه ذخیره می کند، زیرا یک شی ActionBar.Tab برای مدیریت این ذخیره سازی موجود نیست:
کاتلین
class CompatTabEclair internal constructor(val activity: FragmentActivity, tag: String) : CompatTab(tag) { // Store these properties in the instance, // as there is no ActionBar.Tab object. private var text: CharSequence? = null ... override fun setText(resId: Int): CompatTab { // Our older implementation simply stores this // information in the object instance. text = activity.resources.getText(resId) return this } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
جاوا
public class CompatTabEclair extends CompatTab { // Store these properties in the instance, // as there is no ActionBar.Tab object. private CharSequence text; ... public CompatTab setText(int resId) { // Our older implementation simply stores this // information in the object instance. text = activity.getResources().getText(resId); return this; } ... // Do the same for other properties (icon, callback, etc.) }
پیاده سازی TabHelperEclair از روش هایی در ویجت TabHost برای ایجاد اشیاء TabHost.TabSpec و نشانگرهای برگه استفاده می کند:
کاتلین
class TabHelperEclair internal constructor(activity: FragmentActivity) : TabHelper(activity) { private var tabHost: TabHost? = null ... override fun setUp() { // Our activity layout for pre-Honeycomb devices // must contain a TabHost. tabHost = tabHost ?: mActivity.findViewById<TabHost>(android.R.id.tabhost).apply { setup() } } override fun addTab(tab: CompatTab) { ... tabHost?.newTabSpec(tab.tag)?.run { setIndicator(tab.getText()) // And optional icon ... tabHost?.addTab(this) } } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
جاوا
public class TabHelperEclair extends TabHelper { private TabHost tabHost; ... protected void setUp() { if (tabHost == null) { // Our activity layout for pre-Honeycomb devices // must contain a TabHost. tabHost = (TabHost) mActivity.findViewById( android.R.id.tabhost); tabHost.setup(); } } public void addTab(CompatTab tab) { ... TabSpec spec = tabHost .newTabSpec(tag) .setIndicator(tab.getText()); // And optional icon ... tabHost.addTab(spec); } // The other important method, newTab() is part of // the base implementation. }
اکنون دو پیادهسازی CompatTab و TabHelper دارید: یکی که روی دستگاههای دارای Android نسخه 3.0 یا بالاتر کار میکند و از APIهای جدید استفاده میکند، و دیگری که روی دستگاههای دارای Android نسخه 2.0 یا بالاتر کار میکند و از APIهای قدیمیتر استفاده میکند. درس بعدی استفاده از این پیاده سازی ها در برنامه شما را مورد بحث قرار می دهد.

