تنظیمات بخشی از Android Jetpack .
تنظیمات به کاربران امکان می دهد عملکرد و رفتار یک برنامه را تغییر دهند. تنظیمات میتوانند بر رفتار پسزمینه تأثیر بگذارند، مانند تعداد دفعاتی که برنامه دادهها را با ابر همگامسازی میکند، یا میتوانند گستردهتر باشند، مانند تغییر محتویات و ارائه رابط کاربری.
برای ادغام تنظیمات قابل پیکربندی کاربر در برنامه خود، از کتابخانه ترجیحی AndroidX استفاده کنید. این کتابخانه رابط کاربری را مدیریت میکند و با فضای ذخیرهسازی تعامل میکند، به طوری که شما فقط تنظیمات فردی را که کاربر میتواند پیکربندی کند، تعریف کنید. این کتابخانه با موضوع طراحی مواد ارائه میشود که تجربه کاربری ثابتی را در دستگاهها و نسخههای سیستمعامل ارائه میدهد.
شروع کنید
یک Preference بلوک اصلی ساختمان کتابخانه Preference است. صفحه تنظیمات حاوی یک سلسله مراتب Preference است. شما می توانید این سلسله مراتب را به عنوان یک منبع XML تعریف کنید، یا می توانید یک سلسله مراتب را در کد ایجاد کنید .
بخشهای زیر نحوه ساخت یک صفحه تنظیمات ساده با استفاده از کتابخانه ترجیحی AndroidX را شرح میدهند.
قبل از شروع، وابستگی کتابخانه Preference را به فایل build.gradle خود اضافه کنید:
شیار
dependencies { implementation "androidx.preference:preference-ktx:1.2.0" }
کاتلین
dependencies { implementation("androidx.preference:preference-ktx:1.2.0") }
پس از Gradle Sync، میتوانید به بخش XML کار بروید.
یک سلسله مراتب ایجاد کنید
در پروژه خود، به پوشه res/xml بروید، یک فایل preferences.xml ایجاد کنید و کد زیر را به آن اضافه کنید:
<PreferenceScreen xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"> <SwitchPreferenceCompat app:key="notifications" app:title="Enable message notifications"/> <Preference app:key="feedback" app:title="Send feedback" app:summary="Report technical issues or suggest new features"/> </PreferenceScreen>
این سلسله مراتب شامل دو شیء Preference است: یک SwitchPreferenceCompat که به کاربران امکان می دهد تنظیمات را روشن و خاموش کنند، و یک Preference اصلی بدون ویجت.
هنگام ساخت یک سلسله مراتب، هر Preference باید یک کلید منحصر به فرد داشته باشد.
سلسله مراتب را متورم کنید
برای افزایش یک سلسله مراتب از یک ویژگی XML، یک PreferenceFragmentCompat ایجاد کنید، onCreatePreferences() را لغو کنید و منبع XML را برای inflate فراهم کنید، همانطور که در مثال زیر نشان داده شده است:
کاتلین
class MySettingsFragment : PreferenceFragmentCompat() { override fun onCreatePreferences(savedInstanceState: Bundle?, rootKey: String?) { setPreferencesFromResource(R.xml.preferences, rootKey) } }
جاوا
public class MySettingsFragment extends PreferenceFragmentCompat { @Override public void onCreatePreferences(Bundle savedInstanceState, String rootKey) { setPreferencesFromResource(R.xml.preferences, rootKey); } }
سپس میتوانید این Fragment به Activity خود اضافه کنید، همانطور که با هر Fragment دیگری انجام میدهید:
کاتلین
class MySettingsActivity : AppCompatActivity() { override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState) supportFragmentManager .beginTransaction() .replace(R.id.settings_container, MySettingsFragment()) .commit() } }
جاوا
public class MySettingsActivity extends AppCompatActivity { @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); getSupportFragmentManager() .beginTransaction() .replace(R.id.settings_container, new MySettingsFragment()) .commit(); } }
نتیجه در تصویر زیر نشان داده شده است: 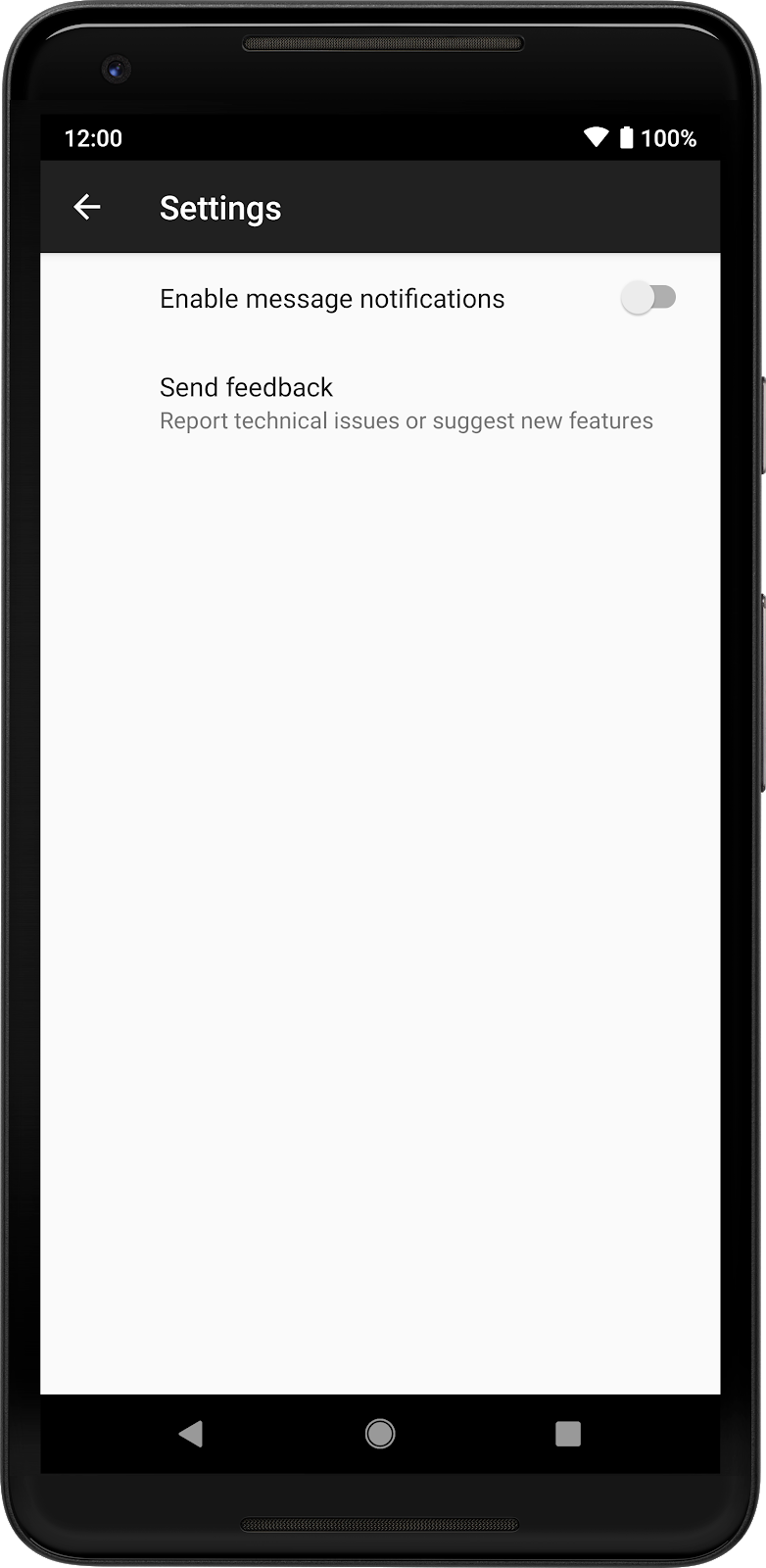
Preference .
بر ترجیحات نظارت کنید
با ثبت یک شنونده برای آن، می توانید رویدادی را هنگامی که یک اولویت تغییر می کند، دریافت کنید:
کاتلین
findPreference<SwitchPreferenceCompat>("notifications") ?.setOnPreferenceChangeListener { _, newValue -> Log.d("Preferences", "Notifications enabled: $newValue") true // Return true if the event is handled. } findPreference<Preference>("feedback") ?.setOnPreferenceClickListener { Log.d("Preferences", "Feedback was clicked") true // Return true if the click is handled. }
جاوا
SwitchPreferenceCompat notificationsPref = findPreference("notifications"); if (notificationsPref != null) { notificationsPref.setOnPreferenceChangeListener((preference, newValue) -> { Log.d("Preferences", String.format("Notifications enabled: %s", newValue)); return true; // Return true if the event is handled. }); } Preference feedbackPref = findPreference("feedback"); if (feedbackPref != null) { feedbackPref.setOnPreferenceClickListener((preference) -> { Log.d("Preferences", "Feedback was clicked"); return true; // Return true if the event is handled. }); }
مقدار ترجیحی فعلی را بخوانید
PreferenceFragmentCompat بسیاری از ماشین آلات مربوط به ذخیره و خواندن تنظیمات برگزیده را پنهان می کند. با این حال، همه چیز با استفاده از SharedPreferences ذخیره میشود و میتوانید این مقادیر را همانطور که معمولاً با SharedPreferences انجام میدهید بخوانید:
کاتلین
val preferences = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(this).all preferences.forEach { Log.d("Preferences", "${it.key} -> ${it.value}") }
جاوا
var preferences = PreferenceManager.getDefaultSharedPreferences(context).getAll(); preferences.forEach((key, value) ->{ Log.d("Preferences", String.format("%s -> %s", key, value)); });
قطعه قبلی نمونه ای از SharedPreferences پیش فرض را برای برنامه به دست می آورد، به تمام مقادیر ذخیره شده دسترسی پیدا می کند، روی آنها حلقه می زند و آنها را در Logcat چاپ می کند.

