Android 12(API レベル 31)以降では、
RoundedCorner、
WindowInsets.getRoundedCorner(int
position):
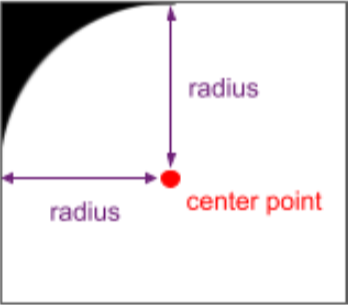
デバイス画面の角丸の半径と中心点。これらの API
丸みを帯びた画面でアプリの UI 要素が切り取られないようにする
可能です。このフレームワークでは
getPrivacyIndicatorBounds()
表示されるすべてのマイクやカメラの境界付き長方形を返す API が
インジケーターをご覧ください。
これらの API をアプリに実装しても、角の丸くない画面では効果がありません。
この機能を実装するには、次のコマンドを使用して RoundedCorner 情報を取得します。
WindowInsets.getRoundedCorner(int position)
説明します。アプリが画面全体を占有していない場合、API は
窓の角丸の中心点を基準にして角丸をつける
指定することもできます。
次のコード スニペットは、
RoundedCorner の情報に基づいてビューのマージンを設定します。この
右上の角が丸い部分です
Kotlin
// Get the top-right rounded corner from WindowInsets. val insets = rootWindowInsets val topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT) ?: return // Get the location of the close button in window coordinates. val location = IntArray(2) closeButton!!.getLocationInWindow(location) val buttonRightInWindow = location[0] + closeButton.width val buttonTopInWindow = location[1] // Find the point on the quarter circle with a 45-degree angle. val offset = (topRight.radius * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(45.0))).toInt() val topBoundary = topRight.center.y - offset val rightBoundary = topRight.center.x + offset // Check whether the close button exceeds the boundary. if (buttonRightInWindow < rightBoundary << buttonTopInWindow > topBoundary) { return } // Set the margin to avoid truncating. val parentLocation = IntArray(2) getLocationInWindow(parentLocation) val lp = closeButton.layoutParams as FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp.rightMargin = Math.max(buttonRightInWindow - rightBoundary, 0) lp.topMargin = Math.max(topBoundary - buttonTopInWindow, 0) closeButton.layoutParams = lp
Java
// Get the top-right rounded corner from WindowInsets. final WindowInsets insets = getRootWindowInsets(); final RoundedCorner topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(POSITION_TOP_RIGHT); if (topRight == null) { return; } // Get the location of the close button in window coordinates. int [] location = new int[2]; closeButton.getLocationInWindow(location); final int buttonRightInWindow = location[0] + closeButton.getWidth(); final int buttonTopInWindow = location[1]; // Find the point on the quarter circle with a 45-degree angle. final int offset = (int) (topRight.getRadius() * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(45))); final int topBoundary = topRight.getCenter().y - offset; final int rightBoundary = topRight.getCenter().x + offset; // Check whether the close button exceeds the boundary. if (buttonRightInWindow < rightBoundary << buttonTopInWindow > topBoundary) { return; } // Set the margin to avoid truncating. int [] parentLocation = new int[2]; getLocationInWindow(parentLocation); FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp = (FrameLayout.LayoutParams) closeButton.getLayoutParams(); lp.rightMargin = Math.max(buttonRightInWindow - rightBoundary, 0); lp.topMargin = Math.max(topBoundary - buttonTopInWindow, 0); closeButton.setLayoutParams(lp);
クリッピングに注意する
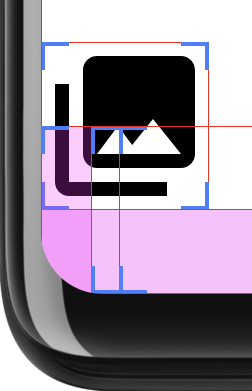
UI がディスプレイ全体に表示される場合、角が丸いとコンテンツに問題が生じる可能性があります。 あります。たとえば、図 2 は、ディスプレイの隅にあるアイコンで、 システムバーの背後に描画されるレイアウト:

これを回避するには、角の丸みを確認し、パディングを適用して アプリのコンテンツをデバイスの角から遠ざけてください。 例:
Kotlin
class InsetsLayout(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet) : FrameLayout(context, attrs) { override fun onLayout(changed: Boolean, left: Int, top: Int, right: Int, bottom: Int) { val insets = rootWindowInsets if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && insets != null) { applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets) } super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom) } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.S) private fun applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets: WindowInsets) { val topLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_LEFT) val topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT) val bottomLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT) val bottomRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT) val leftRadius = max(topLeft?.radius ?: 0, bottomLeft?.radius ?: 0) val topRadius = max(topLeft?.radius ?: 0, topRight?.radius ?: 0) val rightRadius = max(topRight?.radius ?: 0, bottomRight?.radius ?: 0) val bottomRadius = max(bottomLeft?.radius ?: 0, bottomRight?.radius ?: 0) val windowManager = context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) as WindowManager val windowBounds = windowManager.currentWindowMetrics.bounds val safeArea = Rect( windowBounds.left + leftRadius, windowBounds.top + topRadius, windowBounds.right - rightRadius, windowBounds.bottom - bottomRadius ) val location = intArrayOf(0, 0) getLocationInWindow(location) val leftMargin = location[0] - windowBounds.left val topMargin = location[1] - windowBounds.top val rightMargin = windowBounds.right - right - location[0] val bottomMargin = windowBounds.bottom - bottom - location[1] val layoutBounds = Rect( location[0] + paddingLeft, location[1] + paddingTop, location[0] + width - paddingRight, location[1] + height - paddingBottom ) if (layoutBounds != safeArea && layoutBounds.contains(safeArea)) { setPadding( calculatePadding(leftRadius, leftMargin, paddingLeft), calculatePadding(topRadius, topMargin, paddingTop), calculatePadding(rightRadius, rightMargin, paddingRight), calculatePadding(bottomRadius, bottomMargin, paddingBottom) ) } } private fun calculatePadding(radius1: Int?, radius2: Int?, margin: Int, padding: Int): Int = (max(radius1 ?: 0, radius2 ?: 0) - margin - padding).coerceAtLeast(0) }
Java
public class InsetsLayout extends FrameLayout { public InsetsLayout(@NonNull Context context) { super(context); } public InsetsLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { WindowInsets insets = getRootWindowInsets(); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && insets != null) { applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets); } super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom); } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.S) private void applyRoundedCornerPadding(WindowInsets insets) { RoundedCorner topLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_LEFT); RoundedCorner topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT); RoundedCorner bottomLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT); RoundedCorner bottomRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT); int radiusTopLeft = 0; int radiusTopRight = 0; int radiusBottomLeft = 0; int radiusBottomRight = 0; if (topLeft != null) radiusTopLeft = topLeft.getRadius(); if (topRight != null) radiusTopRight = topRight.getRadius(); if (bottomLeft != null) radiusBottomLeft = bottomLeft.getRadius(); if (bottomRight != null) radiusBottomRight = bottomRight.getRadius(); int leftRadius = Math.max(radiusTopLeft, radiusBottomLeft); int topRadius = Math.max(radiusTopLeft, radiusTopRight); int rightRadius = Math.max(radiusTopRight, radiusBottomRight); int bottomRadius = Math.max(radiusBottomLeft, radiusBottomRight); WindowManager windowManager = (WindowManager) getContext().getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE); Rect windowBounds = windowManager.getCurrentWindowMetrics().getBounds(); Rect safeArea = new Rect( windowBounds.left + leftRadius, windowBounds.top + topRadius, windowBounds.right - rightRadius, windowBounds.bottom - bottomRadius ); int[] location = {0, 0}; getLocationInWindow(location); int leftMargin = location[0] - windowBounds.left; int topMargin = location[1] - windowBounds.top; int rightMargin = windowBounds.right - getRight() - location[0]; int bottomMargin = windowBounds.bottom - getBottom() - location[1]; Rect layoutBounds = new Rect( location[0] + getPaddingLeft(), location[1] + getPaddingTop(), location[0] + getWidth() - getPaddingRight(), location[1] + getHeight() - getPaddingBottom() ); if (!layoutBounds.equals(safeArea) && layoutBounds.contains(safeArea)) { setPadding( calculatePadding(radiusTopLeft, radiusBottomLeft, leftMargin, getPaddingLeft()), calculatePadding(radiusTopLeft, radiusTopRight, topMargin, getPaddingTop()), calculatePadding(radiusTopRight, radiusBottomRight, rightMargin, getPaddingRight()), calculatePadding(radiusBottomLeft, radiusBottomRight, bottomMargin, getPaddingBottom()) ); } } private int calculatePadding(int radius1, int radius2, int margin, int padding) { return Math.max(Math.max(radius1, radius2) - margin - padding, 0); } }
このレイアウトでは、UI を角丸の領域まで拡張するかどうかを指定します。 その場所にパディングを追加します図 3 に「Show layout bounds」が表示されている開発者 オプションを有効にして、適用されているパディングをより明確に表示することもできます。
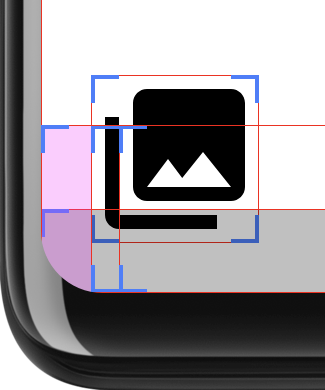
この判断を行うために、このレイアウトでは 2 つの長方形を計算します。safeArea
丸い角の半径内の面積、layoutBounds はサイズ、
パディングを差し引いた値になります。layoutArea に safeArea が完全に含まれている場合、次のようになります。
レイアウトの子はクリップされることがあります。その場合、パディングは
レイアウトが safeArea 内に収まるようにするために追加しました。
layoutBounds が safeArea を完全に囲んでいるかどうかを確認することで、
パディングを増やす方法について説明します。図 4
ナビゲーション バーの背後に描画されていないときにレイアウトを表示します。この例では
レイアウトが角丸に収まらないほど広くありません。これは、
ナビゲーション バーの表示領域内に収まるように調整します。パディングは不要です。