Android 12 (API 수준 31)부터 다음을 사용할 수 있습니다.
RoundedCorner 및
WindowInsets.getRoundedCorner(int
position)만 더 지출하세요.
기기 화면의 둥근 모서리의 반경과 중심점입니다. 이러한 API는
모서리가 둥근 화면에서 앱의 UI 요소가 잘리지 않도록 합니다.
있습니다. 이 프레임워크는
getPrivacyIndicatorBounds() 드림
API: 보이는 마이크와 카메라의 제한된 직사각형을 반환합니다.
표시기를 참고하세요.
앱에서 구현될 때 이러한 API는 화면이 둥글지 않은 기기에는 영향을 미치지 않습니다.
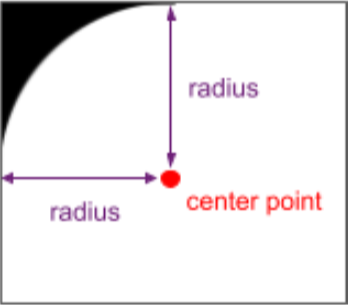
이 기능을 구현하려면 다음을 사용하여 RoundedCorner 정보를 가져옵니다.
WindowInsets.getRoundedCorner(int position)의 경계 기준
애플리케이션입니다. 앱이 전체 화면을 차지하지 않으면 API는
둥근 모서리의 중심점을 창을 기준으로 하여 둥근 모서리
경계선에 위치해 있습니다.
다음 코드 스니펫은 앱에서 UI가 잘리는 것을 방지하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
RoundedCorner의 정보를 기반으로 뷰의 여백을 설정합니다. 이
오른쪽 상단의 둥근 모서리입니다.
Kotlin
// Get the top-right rounded corner from WindowInsets. val insets = rootWindowInsets val topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT) ?: return // Get the location of the close button in window coordinates. val location = IntArray(2) closeButton!!.getLocationInWindow(location) val buttonRightInWindow = location[0] + closeButton.width val buttonTopInWindow = location[1] // Find the point on the quarter circle with a 45-degree angle. val offset = (topRight.radius * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(45.0))).toInt() val topBoundary = topRight.center.y - offset val rightBoundary = topRight.center.x + offset // Check whether the close button exceeds the boundary. if (buttonRightInWindow < rightBoundary << buttonTopInWindow > topBoundary) { return } // Set the margin to avoid truncating. val parentLocation = IntArray(2) getLocationInWindow(parentLocation) val lp = closeButton.layoutParams as FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp.rightMargin = Math.max(buttonRightInWindow - rightBoundary, 0) lp.topMargin = Math.max(topBoundary - buttonTopInWindow, 0) closeButton.layoutParams = lp
자바
// Get the top-right rounded corner from WindowInsets. final WindowInsets insets = getRootWindowInsets(); final RoundedCorner topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(POSITION_TOP_RIGHT); if (topRight == null) { return; } // Get the location of the close button in window coordinates. int [] location = new int[2]; closeButton.getLocationInWindow(location); final int buttonRightInWindow = location[0] + closeButton.getWidth(); final int buttonTopInWindow = location[1]; // Find the point on the quarter circle with a 45-degree angle. final int offset = (int) (topRight.getRadius() * Math.sin(Math.toRadians(45))); final int topBoundary = topRight.getCenter().y - offset; final int rightBoundary = topRight.getCenter().x + offset; // Check whether the close button exceeds the boundary. if (buttonRightInWindow < rightBoundary << buttonTopInWindow > topBoundary) { return; } // Set the margin to avoid truncating. int [] parentLocation = new int[2]; getLocationInWindow(parentLocation); FrameLayout.LayoutParams lp = (FrameLayout.LayoutParams) closeButton.getLayoutParams(); lp.rightMargin = Math.max(buttonRightInWindow - rightBoundary, 0); lp.topMargin = Math.max(topBoundary - buttonTopInWindow, 0); closeButton.setLayoutParams(lp);
잘리지 않도록 주의하세요
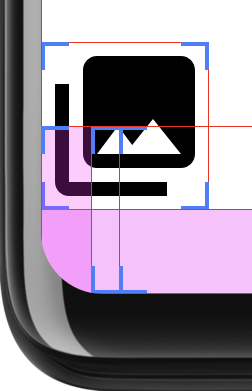
UI가 화면 전체를 채우는 경우 모서리가 둥근 경우 콘텐츠에 문제가 발생할 수 있습니다. 클리핑입니다. 예를 들어, 그림 2는 디스플레이 모서리에 있는 아이콘을 보여줍니다. 시스템 표시줄 뒤에 그려지는 레이아웃:

둥근 모서리를 확인하고 패딩을 적용하여 앱의 콘텐츠를 기기 모서리 밖으로 제거하세요. 예:
Kotlin
class InsetsLayout(context: Context, attrs: AttributeSet) : FrameLayout(context, attrs) { override fun onLayout(changed: Boolean, left: Int, top: Int, right: Int, bottom: Int) { val insets = rootWindowInsets if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && insets != null) { applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets) } super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom) } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.S) private fun applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets: WindowInsets) { val topLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_LEFT) val topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT) val bottomLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT) val bottomRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT) val leftRadius = max(topLeft?.radius ?: 0, bottomLeft?.radius ?: 0) val topRadius = max(topLeft?.radius ?: 0, topRight?.radius ?: 0) val rightRadius = max(topRight?.radius ?: 0, bottomRight?.radius ?: 0) val bottomRadius = max(bottomLeft?.radius ?: 0, bottomRight?.radius ?: 0) val windowManager = context.getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE) as WindowManager val windowBounds = windowManager.currentWindowMetrics.bounds val safeArea = Rect( windowBounds.left + leftRadius, windowBounds.top + topRadius, windowBounds.right - rightRadius, windowBounds.bottom - bottomRadius ) val location = intArrayOf(0, 0) getLocationInWindow(location) val leftMargin = location[0] - windowBounds.left val topMargin = location[1] - windowBounds.top val rightMargin = windowBounds.right - right - location[0] val bottomMargin = windowBounds.bottom - bottom - location[1] val layoutBounds = Rect( location[0] + paddingLeft, location[1] + paddingTop, location[0] + width - paddingRight, location[1] + height - paddingBottom ) if (layoutBounds != safeArea && layoutBounds.contains(safeArea)) { setPadding( calculatePadding(leftRadius, leftMargin, paddingLeft), calculatePadding(topRadius, topMargin, paddingTop), calculatePadding(rightRadius, rightMargin, paddingRight), calculatePadding(bottomRadius, bottomMargin, paddingBottom) ) } } private fun calculatePadding(radius1: Int?, radius2: Int?, margin: Int, padding: Int): Int = (max(radius1 ?: 0, radius2 ?: 0) - margin - padding).coerceAtLeast(0) }
자바
public class InsetsLayout extends FrameLayout { public InsetsLayout(@NonNull Context context) { super(context); } public InsetsLayout(@NonNull Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { super(context, attrs); } @Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { WindowInsets insets = getRootWindowInsets(); if (Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S && insets != null) { applyRoundedCornerPadding(insets); } super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom); } @RequiresApi(Build.VERSION_CODES.S) private void applyRoundedCornerPadding(WindowInsets insets) { RoundedCorner topLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_LEFT); RoundedCorner topRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_TOP_RIGHT); RoundedCorner bottomLeft = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_LEFT); RoundedCorner bottomRight = insets.getRoundedCorner(RoundedCorner.POSITION_BOTTOM_RIGHT); int radiusTopLeft = 0; int radiusTopRight = 0; int radiusBottomLeft = 0; int radiusBottomRight = 0; if (topLeft != null) radiusTopLeft = topLeft.getRadius(); if (topRight != null) radiusTopRight = topRight.getRadius(); if (bottomLeft != null) radiusBottomLeft = bottomLeft.getRadius(); if (bottomRight != null) radiusBottomRight = bottomRight.getRadius(); int leftRadius = Math.max(radiusTopLeft, radiusBottomLeft); int topRadius = Math.max(radiusTopLeft, radiusTopRight); int rightRadius = Math.max(radiusTopRight, radiusBottomRight); int bottomRadius = Math.max(radiusBottomLeft, radiusBottomRight); WindowManager windowManager = (WindowManager) getContext().getSystemService(Context.WINDOW_SERVICE); Rect windowBounds = windowManager.getCurrentWindowMetrics().getBounds(); Rect safeArea = new Rect( windowBounds.left + leftRadius, windowBounds.top + topRadius, windowBounds.right - rightRadius, windowBounds.bottom - bottomRadius ); int[] location = {0, 0}; getLocationInWindow(location); int leftMargin = location[0] - windowBounds.left; int topMargin = location[1] - windowBounds.top; int rightMargin = windowBounds.right - getRight() - location[0]; int bottomMargin = windowBounds.bottom - getBottom() - location[1]; Rect layoutBounds = new Rect( location[0] + getPaddingLeft(), location[1] + getPaddingTop(), location[0] + getWidth() - getPaddingRight(), location[1] + getHeight() - getPaddingBottom() ); if (!layoutBounds.equals(safeArea) && layoutBounds.contains(safeArea)) { setPadding( calculatePadding(radiusTopLeft, radiusBottomLeft, leftMargin, getPaddingLeft()), calculatePadding(radiusTopLeft, radiusTopRight, topMargin, getPaddingTop()), calculatePadding(radiusTopRight, radiusBottomRight, rightMargin, getPaddingRight()), calculatePadding(radiusBottomLeft, radiusBottomRight, bottomMargin, getPaddingBottom()) ); } } private int calculatePadding(int radius1, int radius2, int margin, int padding) { return Math.max(Math.max(radius1, radius2) - margin - padding, 0); } }
이 레이아웃은 UI를 둥근 모서리 영역으로 확장할지 결정합니다. 해당 위치에 패딩을 추가합니다. 그림 3에는 'Show layoutbound'가 표시되고, 개발자 옵션을 사용 설정하여 패딩이 더 명확하게 적용됩니다.
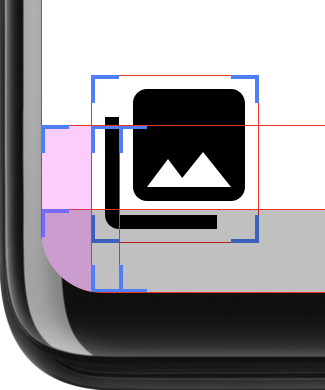
이 결정을 내리기 위해 이 레이아웃은 두 개의 직사각형을 계산합니다. safeArea는
layoutBounds는 둥근 모서리의 반지름 안의 면적
패딩을 뺀 값으로 계산됩니다. layoutArea이 safeArea를 완전히 포함하는 경우
레이아웃의 하위 요소가 잘릴 수도 있습니다. 이 경우 패딩은
추가를 통해 레이아웃이 safeArea 내에 유지되도록 합니다.
layoutBounds이 safeArea를 완전히 포함하는지 확인하면
패딩을 설정해야 합니다. 그림 4
탐색 메뉴 뒤에 그려지지 않은 경우 레이아웃을 표시합니다. 이 경우
레이아웃이 둥근 모서리 내에 있을 만큼 충분히 아래로 확장되지 않습니다.
탐색 메뉴가 차지하는 영역 내에 들어가야 합니다. 패딩은 필요하지 않습니다.