RelativeLayout は、子ビューを相対位置に表示するビューグループです。各ビューの位置は、兄弟要素に対する相対位置(別のビューの左側や下など)として指定することも、親の RelativeLayout 領域に対する相対位置(下揃え、左揃え、中央揃えなど)で指定することもできます。
注: パフォーマンスやツールのサポートを改善するには、ConstraintLayout を使用してレイアウトを作成する必要があります。

RelativeLayout は、ユーザー インターフェースを設計するための非常に強力なユーティリティです。このユーティリティを使用すると、ネストされたビューグループを排除し、レイアウト階層をフラットに保つことで、パフォーマンスを改善できます。複数のネストされた LinearLayout グループを使用している場合、それらを 1 つの RelativeLayout で置換できることがあります。
ビューの配置
RelativeLayout を使用すると、子ビューの親ビューに対する相対位置を指定することも、相互(ID で指定)の相対位置を指定することもできます。そのため、2 つの要素を右枠線で整列したり、画面中央や左中央などで上下に並べたりできます。デフォルトでは、すべての子ビューがレイアウトの左上に描画されるため、RelativeLayout.LayoutParams で使用できる各種のレイアウト プロパティを使って各ビューの位置を定義する必要があります。
RelativeLayout のビューで使用できる各種のレイアウト プロパティの一部を以下に示します。
android:layout_alignParentTop-
"true"の場合、このビューの上端が親の上端と一致するように配置されます。 android:layout_centerVertical-
"true"の場合、この子が親内の縦方向中央に配置されます。 android:layout_below- リソース ID で指定されたビューの下にこのビューの上端が来るように配置されます。
android:layout_toRightOf- リソース ID で指定されたビューの右側にこのビューの左端が来るように配置されます。
これらはほんの一例です。すべてのレイアウト属性が RelativeLayout.LayoutParams に記載されています。
各レイアウト プロパティの値には、親の RelativeLayout に対する相対的なレイアウト位置を有効にするブール値か、ビューを配置するレイアウト内の別のビューを参照する ID のいずれかを指定します。
XML レイアウトでは、レイアウト内の他のビューに対する依存関係を任意の順序で宣言できます。 たとえば、「view2」が階層内で宣言されている最後のビューでも、「view1」を「view2」の下に配置するように宣言できます。次の例は、このようなシナリオを示しています。
例
各ビューの相対位置を制御する各属性が太字で示されています。
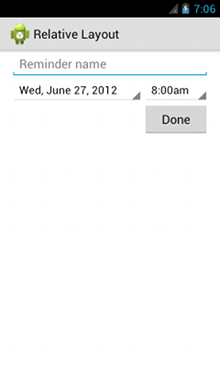
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/reminder" /> <Spinner android:id="@+id/dates" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/times" /> <Spinner android:id="@id/times" android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <Button android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/times" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:text="@string/done" /> </RelativeLayout>
RelativeLayout の各子ビューで使用できるすべてのレイアウト属性の詳細については、RelativeLayout.LayoutParams をご覧ください。

