RelativeLayout은 상대 위치에 하위 뷰를 표시하는 뷰 그룹입니다. 각 뷰의 위치는 동위 요소(예: 다른 뷰의 왼쪽 또는 아래)에 상대적이거나 상위 RelativeLayout 영역(예: 맨 아래, 왼쪽 또는 중앙으로 정렬됨)에 상대적인 위치로 지정될 수 있습니다.
참고: 더 나은 성능과 도구 지원을 위해 ConstraintLayout을 사용하여 레이아웃을 빌드해야 합니다.

RelativeLayout은 중첩된 뷰 그룹을 없애고 레이아웃 계층 구조를 평면으로 유지하여 성능을 개선하므로 사용자 인터페이스 설계에 매우 유용한 유틸리티입니다. 여러 개의 중첩된 LinearLayout 그룹을 사용한다면 단일 RelativeLayout으로 대체할 수 있습니다.
뷰 위치 지정
RelativeLayout을 사용하면 하위 뷰는 상위 뷰 또는 서로 다른 뷰(ID로 구분)에 상대적인 위치를 지정할 수 있습니다. 따라서 두 요소를 오른쪽 테두리로 정렬하거나 위아래로 나란히, 화면 중앙에, 왼쪽 가운데 등으로 정렬할 수 있습니다. 기본적으로 모든 하위 뷰는 레이아웃의 왼쪽 상단에 그려지므로 RelativeLayout.LayoutParams에서 사용할 수 있는 다양한 레이아웃 속성을 사용하여 각 뷰의 위치를 정의해야 합니다.
RelativeLayout의 뷰에 사용할 수 있는 많은 레이아웃 속성 중 몇 가지는 다음과 같습니다.
android:layout_alignParentTop"true"면 이 뷰의 상단 가장자리를 상위 뷰의 상단 가장자리와 일치시킵니다.android:layout_centerVertical"true"면 이 하위 요소를 상위 요소 내에 세로로 중앙에 배치합니다.android:layout_below- 이 뷰의 상단 가장자리를 리소스 ID로 지정한 뷰 아래에 배치합니다.
android:layout_toRightOf- 이 뷰의 왼쪽 가장자리를 리소스 ID로 지정된 뷰의 오른쪽에 배치합니다.
다음은 몇 가지 예입니다. 모든 레이아웃 속성은 RelativeLayout.LayoutParams에 기술되어 있습니다.
각 레이아웃 속성의 값은 상위 RelativeLayout에 상대적인 레이아웃 위치를 사용 설정하는 부울 또는 뷰가 배치되어야 하는 레이아웃의 다른 뷰를 참조하는 ID입니다.
XML 레이아웃에서 레이아웃의 다른 뷰에 관한 종속 항목은 순서와 관계없이 선언할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 'view2'가 계층 구조에서 선언된 마지막 뷰라고 해도 'view1'을 'view2' 아래에 배치하도록 선언할 수 있습니다. 아래 예는 이러한 시나리오를 보여줍니다.
예
각 뷰의 상대 위치를 제어하는 각 속성이 강조되어 있습니다.
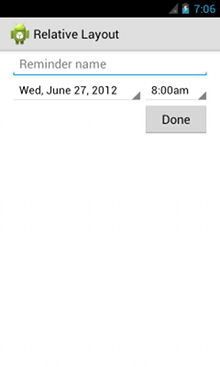
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/reminder" /> <Spinner android:id="@+id/dates" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/times" /> <Spinner android:id="@id/times" android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <Button android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/times" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:text="@string/done" /> </RelativeLayout>
RelativeLayout의 각 하위 뷰에서 사용 가능한 모든 레이아웃 속성에 관한 자세한 내용은 RelativeLayout.LayoutParams를 참고하세요.

