RelativeLayout היא קבוצת תצוגה שמציגה צפיות צאצא באופן יחסי
במיקומי המודעות החדשים. ניתן לציין את המיקום של כל תצוגה ביחס לרכיבי אח (למשל
מימין או מתחת לתצוגה אחרת) או במיקומים ביחס לאזור ההורה RelativeLayout (למשל מיושר למטה, שמאלה או למרכז).
הערה: כדי לקבל תמיכה טובה יותר בביצועים ובכלים, מומלץ ליצור את הפריסה באמצעות ConstraintLayout.

RelativeLayout הוא כלי עוצמתי מאוד לעיצוב ממשק משתמש
כי היא יכולה לבטל קבוצות של תצוגות בתוך קבוצות ולהשאיר את היררכיית הפריסה שטוחה, דבר ששיפור
או של ביצועים. אם מצאת את עצמך משתמש בכמה קבוצות LinearLayout מקוננות,
ייתכן שתהיה לך אפשרות להחליף אותם ב-RelativeLayout אחד.
ממקם את התצוגות
RelativeLayout מאפשר לתצוגות הצאצא לציין את המיקום שלהן ביחס
תצוגה מפורטת של ההורה או אחד לשני (מצוין לפי מזהה). כך אפשר ליישר שני רכיבים לפי גבול ימני,
להפוך אחת מתחת לאחרת, במרכז המסך, במרכז השמאלי וכן הלאה. כברירת מחדל, כל הצאצאים
התצוגות מצוירות בפינה השמאלית העליונה של הפריסה, כך שצריך להגדיר את המיקום של כל תצוגה
באמצעות מאפייני הפריסה השונים שזמינים מ-RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.
חלק ממאפייני הפריסה הרבים שזמינים לתצוגות ב-RelativeLayout
כוללים:
android:layout_alignParentTop- אם במקרה
"true", הקצה העליון של התצוגה הזו תואם לקצה העליון של תבנית ההורה. android:layout_centerVertical- אם
"true", הילד או הילדה מוגדרים בצורה אנכית בתוך ההורה שלהם. android:layout_below- ממקם את הקצה העליון של התצוגה הזו מתחת לתצוגה שצוינה באמצעות מזהה משאב.
android:layout_toRightOf- ממקם את הקצה השמאלי של התצוגה הזאת מימין לתצוגה שצוינה באמצעות מזהה משאב.
אלה רק כמה דוגמאות. כל מאפייני הפריסה מתועדים ב-RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.
הערך של כל נכס פריסה הוא בוליאני של
להפעיל מיקום פריסה ביחס לתבנית ההורה RelativeLayout או למזהה
מפנה לתצוגה אחרת בפריסה שאליה יש למקם את התצוגה.
בפריסת ה-XML אפשר להצהיר על יחסי תלות עם תצוגות אחרות בפריסה בכל סדר שתרצו. לדוגמה, אפשר להצהיר כי "view1" להיות ממוקם מתחת ל-"view2" גם אם "view2" היא האחרונה לתצוגה המוצהרת בהיררכיה. הדוגמה הבאה ממחישה תרחיש כזה.
דוגמה
מודגש כל אחד מהמאפיינים שקובעים את המיקום היחסי של כל תצוגה.
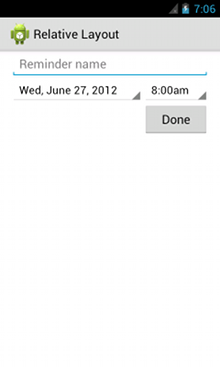
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/reminder" /> <Spinner android:id="@+id/dates" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/times" /> <Spinner android:id="@id/times" android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <Button android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/times" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:text="@string/done" /> </RelativeLayout>
בכתובת RelativeLayout.LayoutParams אפשר לקרוא פרטים על כל מאפייני הפריסה הזמינים לכל תצוגת צאצא של RelativeLayout.

