RelativeLayout یک گروه نمایش است که نماهای فرزند را در موقعیت های نسبی نمایش می دهد. موقعیت هر نما را می توان نسبت به عناصر خواهر و برادر (مانند سمت چپ یا پایین نمای دیگر) یا در موقعیت های مربوط به ناحیه RelativeLayout والد (مانند تراز در پایین، چپ یا مرکز) مشخص کرد.
توجه: برای عملکرد بهتر و پشتیبانی ابزار، در عوض باید طرح خود را با ConstraintLayout بسازید .

RelativeLayout یک ابزار بسیار قدرتمند برای طراحی یک رابط کاربری است زیرا می تواند گروه های نمایش تودرتو را حذف کند و سلسله مراتب طرح بندی شما را صاف نگه دارد، که عملکرد را بهبود می بخشد. اگر متوجه شدید که از چندین گروه LinearLayout تو در تو استفاده می کنید، ممکن است بتوانید آنها را با یک RelativeLayout جایگزین کنید.
نماهای موقعیت یابی
RelativeLayout به نماهای فرزند اجازه می دهد موقعیت خود را نسبت به نمای والد یا یکدیگر (مشخص شده توسط ID) مشخص کنند. بنابراین می توانید دو عنصر را با حاشیه سمت راست تراز کنید، یا یکی در زیر دیگری، در مرکز صفحه، در مرکز سمت چپ، و غیره ایجاد کنید. بهطور پیشفرض، همه نماهای فرزند در بالا سمت چپ طرحبندی ترسیم میشوند، بنابراین باید موقعیت هر نما را با استفاده از ویژگیهای طرحبندی مختلف موجود در RelativeLayout.LayoutParams تعیین کنید.
برخی از بسیاری از ویژگیهای طرحبندی موجود برای نماها در یک RelativeLayout عبارتند از:
android:layout_alignParentTop- اگر
"true"، لبه بالایی این نمای را با لبه بالای والد مطابقت می دهد. android:layout_centerVertical- اگر
"true"، این کودک را به صورت عمودی در والد خود متمرکز می کند. -
android:layout_below - لبه بالایی این نما را در زیر نمای مشخص شده با شناسه منبع قرار می دهد.
-
android:layout_toRightOf - لبه سمت چپ این نما را در سمت راست نمای مشخص شده با شناسه منبع قرار می دهد.
اینها فقط چند نمونه هستند. تمام ویژگیهای طرحبندی در RelativeLayout.LayoutParams مستند شدهاند.
مقدار هر ویژگی layout یا یک بولی برای فعال کردن یک موقعیت طرح نسبت به RelativeLayout والد یا یک شناسه است که به نمای دیگری در طرح ارجاع می دهد که نمای باید در مقابل آن قرار گیرد.
در چیدمان XML شما، وابستگی ها در برابر سایر نماهای موجود در چیدمان را می توان به هر ترتیبی اعلام کرد. به عنوان مثال، می توانید اعلام کنید که "view1" در زیر "view2" قرار می گیرد حتی اگر "view2" آخرین نمای اعلام شده در سلسله مراتب باشد. مثال زیر چنین سناریویی را نشان می دهد.
مثال
بر هر یک از ویژگی هایی که موقعیت نسبی هر دیدگاه را کنترل می کنند، تأکید می شود.
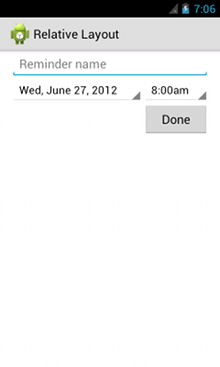
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/reminder" /> <Spinner android:id="@+id/dates" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/times" /> <Spinner android:id="@id/times" android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <Button android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/times" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:text="@string/done" /> </RelativeLayout>
برای جزئیات در مورد تمام ویژگی های طرح بندی موجود برای هر نمای فرزند از یک RelativeLayout ، RelativeLayout.LayoutParams را ببینید.


