LinearLayout
è un gruppo di viste che allinea tutti gli elementi secondari in un'unica direzione, verticalmente
in orizzontale. Puoi specificare la direzione del layout con
android:orientation
.
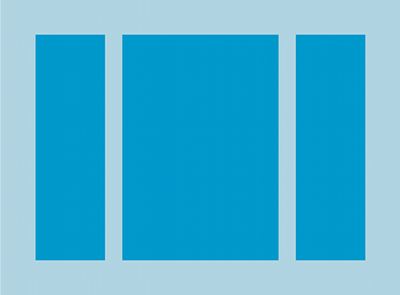
LinearLayout con tre orizzontalmente
orientati ai bambini.
Tutti gli elementi secondari di LinearLayout vengono sovrapposti uno dopo l'altro,
pertanto un elenco verticale ha un solo elemento secondario per riga, indipendentemente dalla loro larghezza. R
dell'elenco orizzontale
è alto una sola riga ed è l'altezza del profilo secondario più alto,
più spaziatura interna. Un LinearLayout rispetta i margini tra
bambini e la gravità (destra, centro o sinistra)
di ogni elemento figlio.
Spessore layout
LinearLayout supporta anche l'assegnazione di un peso a
singoli bambini con
android:layout_weight
. Questo attributo assegna un'"importanza" a una vista in termini di
da quanto spazio occupa sullo schermo. Un valore di ponderazione più grande consente di espandere
per riempire lo spazio rimanente nella vista genitore. Le viste secondarie possono specificare una ponderazione
e l'eventuale spazio rimanente nel gruppo di visualizzazioni viene assegnato agli elementi secondari
in modo proporzionale, in base al peso dichiarato. Il peso predefinito è zero.
Distribuzione uguale
Per creare un layout lineare in cui ogni asset secondario utilizzi la stessa quantità di spazio
sullo schermo, imposta
android:layout_height
di ogni vista a "0dp" per un layout verticale, oppure la
android:layout_width
di ogni vista a "0dp" per un layout orizzontale. Quindi imposta
android:layout_weight di ogni visualizzazione per "1".
Distribuzione disuguale
Puoi anche creare layout lineari in cui gli elementi secondari utilizzano diversi quantità di spazio libero sullo schermo. Considera i seguenti esempi:
- Supponi di avere tre campi di testo: due con un valore di ponderazione pari a 1 e un con il valore predefinito di 0. Il terzo campo di testo, con un valore di ponderazione pari a 0, occupa solo l'area richiesta dai suoi contenuti. L'altro due campi di testo, con valore di ponderazione pari a 1, si espandono equamente per riempire spazio rimanente dopo la misurazione dei contenuti di tutti e tre i campi.
- Se invece hai tre campi di testo di cui due hanno un valore di ponderazione pari a 1 mentre il terzo ha un peso pari a 2, lo spazio rimanente dopo contenuto di tutti e tre i campi viene allocato come segue: il campo con valore di ponderazione pari a 2 e metà diviso equamente tra con un valore di ponderazione pari a 1.
La figura e lo snippet di codice riportati di seguito mostrano come potrebbero funzionare le ponderazioni del layout in un "invia messaggio" attività. Il campo A, la riga Oggetto e Ogni pulsante Invia occupa solo l'altezza necessaria. L'area del messaggio occupa il resto dell'altezza dell'attività.

LinearLayout.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" android:orientation="vertical" > <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/to" /> <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/subject" /> <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:gravity="top" android:hint="@string/message" /> <Button android:layout_width="100dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="end" android:text="@string/send" /> </LinearLayout>
Per maggiori dettagli sugli attributi disponibili per ogni vista secondaria di un
LinearLayout, vedi
LinearLayout.LayoutParams.

