透過 Android 拖曳架構,您可在應用程式中加入互動式拖曳功能。透過拖曳功能,使用者可以複製或移動文字、圖片、物件以及任何由 URI 表示的內容、從一個 View 到另一個應用程式,或在多視窗模式的應用程式之間。
|
|
|
|
|
架構包含拖曳事件類別、拖曳事件監聽器,以及輔助類別和方法。雖然這個架構主要是啟用資料移轉功能,但您仍可將此架構用於其他 UI 動作。舉例來說,您可以建立應用程式,當使用者將某個顏色圖示拖曳到其他圖示上方時,可組合不同顏色。但是,文件的其餘部分會說明資料移轉架構中的拖曳架構。
總覽
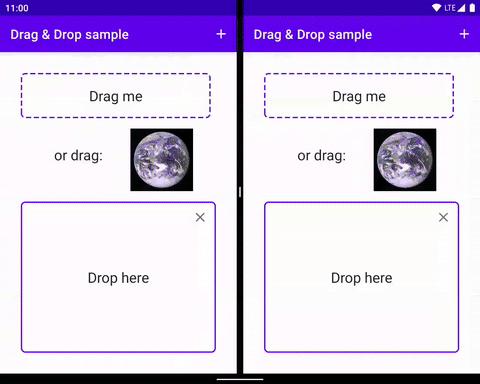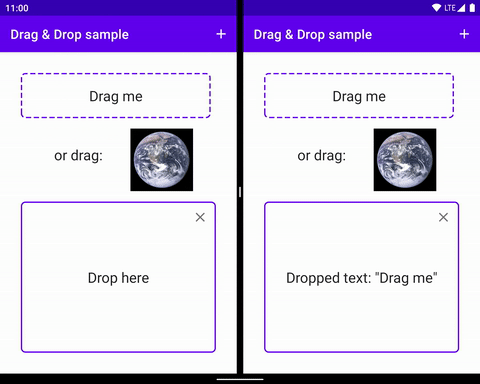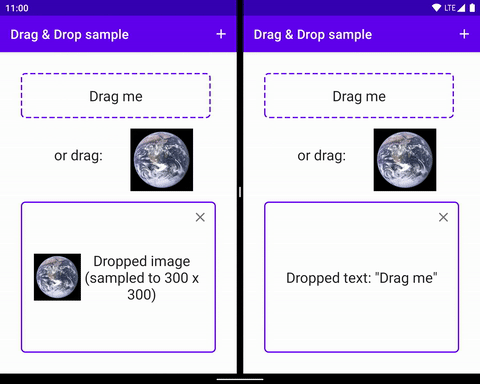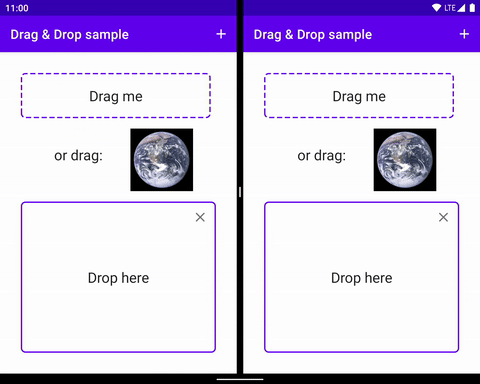
拖曳程序涉及幾個元素。
拖曳來源:拖曳程序的起點檢視畫面。
放置目標:可接受拖曳資料的檢視畫面。
拖曳陰影:拖曳陰影代表拖曳的資料,使用者可以看到這些資料。
拖曳事件:使用者將拖曳陰影移動到應用程式版面配置上時,系統會將拖曳事件傳送至與版面配置中
View物件相關聯的拖曳事件監聽器和回呼方法。
當使用者做出 UI 手勢,讓您的應用程式識別為開始拖曳資料的信號時,拖曳作業就會開始執行。作為回應,應用程式會通知系統拖曳作業開始。系統會呼叫應用程式以取得拖曳陰影,並在拖曳過程中向使用者顯示。
當使用者將拖曳陰影移至應用程式版面配置時,系統會將拖曳事件傳送至與版面配置中 View 物件相關聯的拖曳事件監聽器和回呼方法。如果使用者在放置目標上放開拖曳陰影,系統會傳送資料至該目標。無論拖曳陰影是否在放置目標上方,拖曳作業都會在使用者放開拖曳陰影時結束。
主題
- 重要概念
- 瞭解拖曳過程。
- 使用 DropHelper 可簡化拖曳作業
- 瞭解如何使用
DropHelper實作拖曳功能。 - 透過檢視區塊實作拖曳功能
- 或者,使用 Android 檢視區塊實作拖曳功能,這可讓開發人員進一步控管詳細資料。
- 在多視窗模式下拖曳
- 在多視窗模式下支援拖曳功能,可讓物件在不同應用程式中移動。
其他資源
- 使用檢視畫面拖曳程式碼研究室
- 拖曳即可流暢處理多工處理影片
- 拖曳範例:內含各種實作拖曳功能以及接受互動式多媒體的方式。

