हर टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड में किसी खास तरह का टेक्स्ट इनपुट डाला जा सकता है. जैसे, ईमेल पता, फ़ोन नंबर या सादा टेक्स्ट. आपको अपने ऐप्लिकेशन में हर टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड के लिए इनपुट टाइप बताना होगा, ताकि सिस्टम सही सॉफ़्ट इनपुट तरीका दिखा सके. जैसे, ऑन-स्क्रीन कीबोर्ड.
इनपुट के तरीके के साथ उपलब्ध बटन के अलावा, इनके व्यवहार के बारे में भी बताया जा सकता है. जैसे, इनपुट का तरीका, वर्तनी के सुझाव देता है या नहीं, नए वाक्यों को कैपिटल लेटर में लिखता है या नहीं, और कैरिज रिटर्न बटन को हो गया या आगे बढ़ें जैसे ऐक्शन बटन से बदलता है या नहीं. इस पेज पर, इन विशेषताओं के बारे में बताने का तरीका बताया गया है.
कीबोर्ड का टाइप बताना
अपने टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड के लिए इनपुट का तरीका हमेशा बताएं. इसके लिए, <EditText> एलिमेंट में android:inputType एट्रिब्यूट जोड़ें.
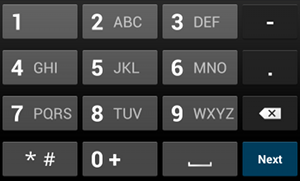
phone इनपुट का टाइप.उदाहरण के लिए, अगर आपको फ़ोन नंबर डालने के लिए कोई इनपुट तरीका चाहिए, तो "phone" वैल्यू का इस्तेमाल करें:
<EditText android:id="@+id/phone" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/phone_hint" android:inputType="phone" />
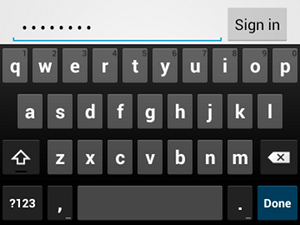
textPassword इनपुट का टाइप.अगर टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड पासवर्ड के लिए है, तो "textPassword" वैल्यू का इस्तेमाल करें, ताकि टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड में उपयोगकर्ता का इनपुट छिपा रहे:
<EditText android:id="@+id/password" android:hint="@string/password_hint" android:inputType="textPassword" ... />
android:inputType एट्रिब्यूट के साथ कई वैल्यू दी जा सकती हैं. इनमें से कुछ वैल्यू को जोड़कर, इनपुट के तरीके के दिखने के तरीके और अन्य व्यवहारों के बारे में बताया जा सकता है.
स्पेलिंग के सुझाव और अन्य सुविधाएं चालू करना
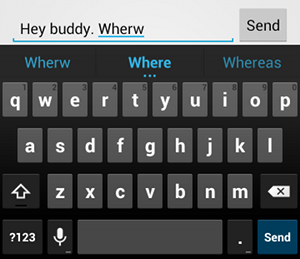
textAutoCorrect जोड़ने पर, गलत तरीके से लिखे गए शब्दों को अपने-आप ठीक किया जाता है.android:inputType एट्रिब्यूट की मदद से, इनपुट के तरीके के लिए अलग-अलग व्यवहार तय किए जा सकते हैं. सबसे अहम बात यह है कि अगर आपका टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड, टेक्स्ट मैसेज जैसे बुनियादी टेक्स्ट इनपुट के लिए है, तो "textAutoCorrect" वैल्यू की मदद से, स्पेलिंग अपने-आप ठीक होने की सुविधा चालू करें.
android:inputType एट्रिब्यूट की मदद से, अलग-अलग व्यवहार और इनपुट के तरीकों की स्टाइल को जोड़ा जा सकता है. उदाहरण के लिए, यहां एक ऐसा टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड बनाने का तरीका बताया गया है जो किसी वाक्य के पहले शब्द को कैपिटल लेटर में बदलता है. साथ ही, गलत स्पेलिंग को अपने-आप ठीक करता है:
<EditText android:id="@+id/message" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:inputType= "textCapSentences|textAutoCorrect" ... />
इनपुट के तरीके से जुड़ी कार्रवाई तय करना
ज़्यादातर सॉफ़्ट इनपुट के तरीकों में, सबसे नीचे कोने में उपयोगकर्ता ऐक्शन बटन होता है. यह बटन, मौजूदा टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड के लिए सही होता है. डिफ़ॉल्ट रूप से, सिस्टम इस बटन का इस्तेमाल आगे बढ़ें या हो गया कार्रवाई के लिए करता है. ऐसा तब तक होता है, जब तक आपका टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड कई लाइन वाले टेक्स्ट के साथ काम करता है. जैसे, android:inputType="textMultiLine" के साथ. इस मामले में, ऐक्शन बटन एक कैरिज रिटर्न होता है. हालांकि, आपके पास ऐसी अन्य कार्रवाइयां तय करने का विकल्प होता है जो आपके टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड के लिए ज़्यादा सही हो सकती हैं. जैसे, भेजें या जाओ.
कीबोर्ड ऐक्शन बटन की जानकारी देने के लिए, "actionSend" या "actionSearch" जैसी ऐक्शन वैल्यू के साथ android:imeOptions एट्रिब्यूट का इस्तेमाल करें. उदाहरण के लिए:

android:imeOptions="actionSend" का एलान करने पर, भेजें बटन दिखता है.<EditText android:id="@+id/search" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/search_hint" android:inputType="text" android:imeOptions="actionSend" />
इसके बाद, EditText एलिमेंट के लिए TextView.OnEditorActionListener तय करके, ऐक्शन बटन पर होने वाली दबाव की जानकारी सुनी जा सकती है. अपने लिसनर में, EditorInfo क्लास में बताए गए सही IME ऐक्शन आईडी का जवाब दें. जैसे, IME_ACTION_SEND, जैसा कि नीचे दिए गए उदाहरण में दिखाया गया है:
Kotlin
findViewById<EditText>(R.id.search).setOnEditorActionListener { v, actionId, event -> return@setOnEditorActionListener when (actionId) { EditorInfo.IME_ACTION_SEND -> { sendMessage() true } else -> false } }
Java
EditText editText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.search); editText.setOnEditorActionListener(new OnEditorActionListener() { @Override public boolean onEditorAction(TextView v, int actionId, KeyEvent event) { boolean handled = false; if (actionId == EditorInfo.IME_ACTION_SEND) { sendMessage(); handled = true; } return handled; } });
अपने-आप पूरा होने वाले सुझाव दिखाना
अगर आपको उपयोगकर्ताओं को टाइप करते समय सुझाव देने हैं, तो EditText के एक सबक्लास का इस्तेमाल किया जा सकता है. इसे AutoCompleteTextView कहा जाता है.
ऑटोकंप्लीट की सुविधा लागू करने के लिए, आपको एक ऐसा Adapter तय करना होगा जो टेक्स्ट के सुझाव देता हो. डेटा सोर्स के आधार पर, कई अडैप्टर उपलब्ध होते हैं. जैसे, डेटाबेस या ऐरे से.
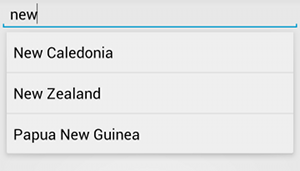
AutoCompleteTextView का उदाहरण.यहां दिए गए तरीके से, AutoCompleteTextView को सेट अप करने का तरीका बताया गया है. यह ArrayAdapter का इस्तेमाल करके, किसी कलेक्शन से सुझाव देता है:
- अपने लेआउट में
AutoCompleteTextViewजोड़ें. यहां सिर्फ़ टेक्स्ट फ़ील्ड वाला लेआउट दिया गया है:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <AutoCompleteTextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/autocomplete_country" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
- वह कलेक्शन तय करें जिसमें टेक्स्ट के सभी सुझाव शामिल हों. उदाहरण के लिए, यहां देशों के नामों का एक कलेक्शन दिया गया है:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string-array name="countries_array"> <item>Afghanistan</item> <item>Albania</item> <item>Algeria</item> <item>American Samoa</item> <item>Andorra</item> <item>Angola</item> <item>Anguilla</item> <item>Antarctica</item> ... </string-array> </resources>
- अपने
ActivityयाFragmentमें, सुझाव देने वाले अडैप्टर की जानकारी देने के लिए, यहां दिए गए कोड का इस्तेमाल करें:Kotlin
// Get a reference to the AutoCompleteTextView in the layout. val textView = findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_country) as AutoCompleteTextView // Get the string array. val countries: Array<out String> = resources.getStringArray(R.array.countries_array) // Create the adapter and set it to the AutoCompleteTextView. ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, countries).also { adapter -> textView.setAdapter(adapter) }
Java
// Get a reference to the AutoCompleteTextView in the layout. AutoCompleteTextView textView = (AutoCompleteTextView) findViewById(R.id.autocomplete_country); // Get the string array. String[] countries = getResources().getStringArray(R.array.countries_array); // Create the adapter and set it to the AutoCompleteTextView. ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, countries); textView.setAdapter(adapter);
पिछले उदाहरण में,
countries_arrayस्ट्रिंग कलेक्शन में मौजूद हर आइटम कोsimple_list_item_1लेआउट में मौजूदTextViewसे जोड़ने के लिए, एक नयाArrayAdapterशुरू किया जाता है. यह Android का एक लेआउट है, जो सूची में टेक्स्ट के लिए स्टैंडर्ड दिखावट देता है. -
setAdapter()को कॉल करके, अडैप्टर कोAutoCompleteTextViewको असाइन करें.

