AppSearch 是一款高性能的设备端搜索解决方案,用于管理本地存储的结构化数据。其中包含用于将数据编入索引和使用全文搜索来检索数据的 API。应用可以使用 AppSearch 提供自定义应用内搜索功能,让用户即使在离线状态下也能搜索内容。
AppSearch 提供以下功能:
- 一种 I/O 占用率低的移动设备优先快速存储实现
- 快速高效地对大型数据集进行索引编制和查询
- 支持多种语言,例如英语和西班牙语
- 相关性排名和使用情况评分
与 SQLite 相比,AppSearch 的 I/O 用量较低,因此在对大型数据集进行索引编制和搜索时,延迟时间更短。AppSearch 通过支持单个查询来简化跨类型查询,而 SQLite 会合并来自多个表的结果。
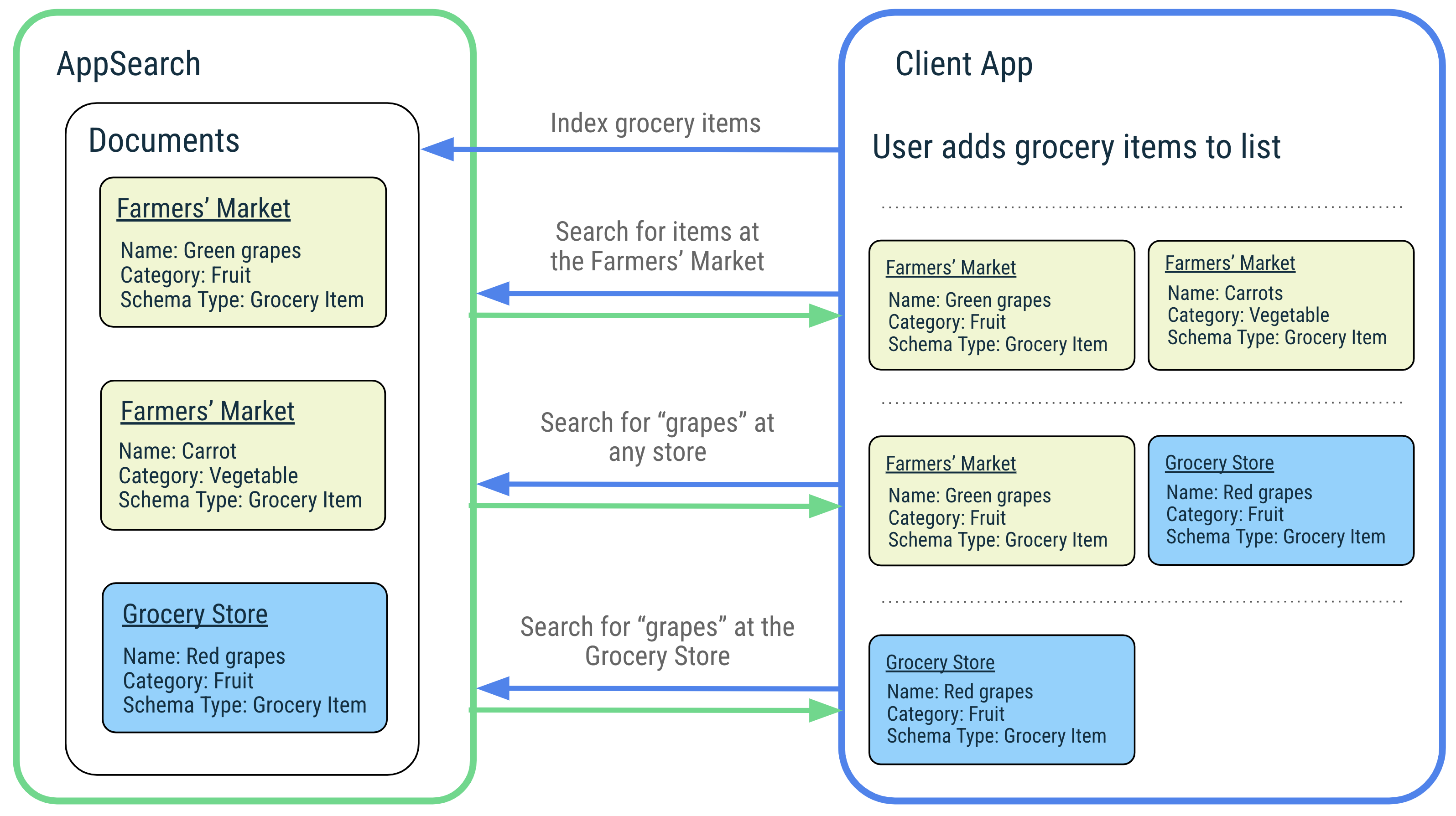
为了说明 AppSearch 的功能,我们以一个音乐应用为例,该应用可管理用户喜爱的歌曲,并让用户轻松搜索这些歌曲。用户可以欣赏世界各地的音乐,歌名以不同的语言显示,而 AppSearch 原生支持对这些歌名进行编入索引和查询。当用户按歌名或音乐人姓名搜索歌曲时,应用只需将请求传递给 AppSearch,即可快速高效地检索匹配的歌曲。应用会显示结果,让用户能够快速开始播放喜爱的歌曲。
设置
如需在应用中使用 AppSearch,请将以下依赖项添加到应用的 build.gradle 文件中:
Groovy
dependencies { def appsearch_version = "1.1.0" implementation "androidx.appsearch:appsearch:$appsearch_version" // Use kapt instead of annotationProcessor if writing Kotlin classes annotationProcessor "androidx.appsearch:appsearch-compiler:$appsearch_version" implementation "androidx.appsearch:appsearch-local-storage:$appsearch_version" // PlatformStorage is compatible with Android 12+ devices, and offers additional features // to LocalStorage. implementation "androidx.appsearch:appsearch-platform-storage:$appsearch_version" // PlayServicesStorage is compatible with all devices that support Google Play Services on // all API levels. It offers the same features as PlatformStorage and is the recommended // solution for lower API levels on which PlatformStorage is not supported. implementation "androidx.appsearch:appsearch-play-services-storage:$appsearch_version" }
Kotlin
dependencies { val appsearch_version = "1.1.0" implementation("androidx.appsearch:appsearch:$appsearch_version") // Use annotationProcessor instead of kapt if writing Java classes kapt("androidx.appsearch:appsearch-compiler:$appsearch_version") implementation("androidx.appsearch:appsearch-local-storage:$appsearch_version") // PlatformStorage is compatible with Android 12+ devices, and offers additional features // to LocalStorage. implementation("androidx.appsearch:appsearch-platform-storage:$appsearch_version") // PlayServicesStorage is compatible with all devices that support Google Play Services on // all API levels. It offers the same features as PlatformStorage and is the recommended // solution for lower API levels on which PlatformStorage is not supported. implementation("androidx.appsearch:appsearch-play-services-storage:$appsearch_version") }
AppSearch 概念
下图展示了 AppSearch 概念及其互动。
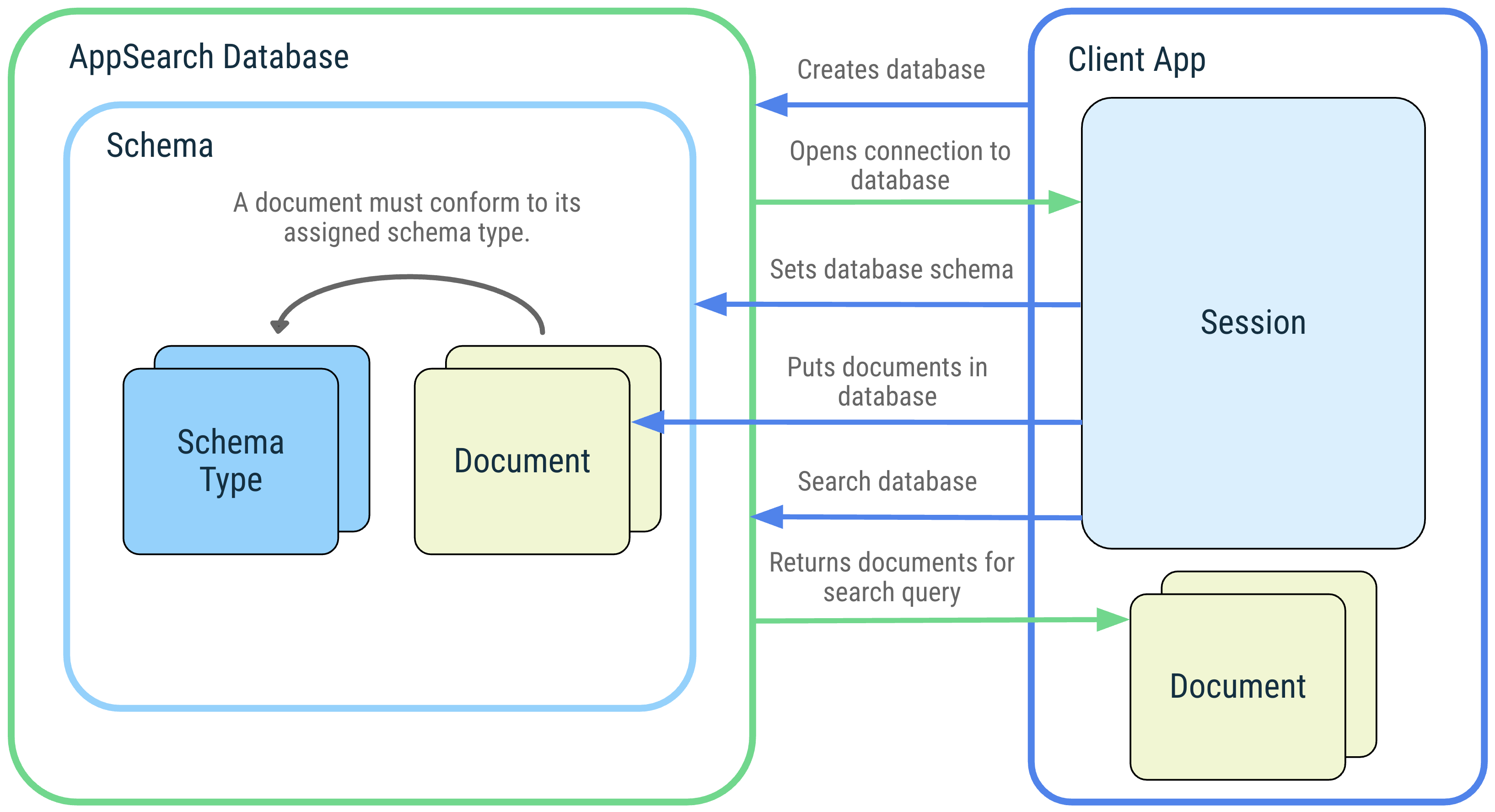 图 1. AppSearch 概念示意图:AppSearch 数据库、架构、架构类型、文档、会话和搜索。
图 1. AppSearch 概念示意图:AppSearch 数据库、架构、架构类型、文档、会话和搜索。
数据库和会话
AppSearch 数据库是符合数据库架构的文档集合。客户端应用通过提供其应用上下文和数据库名称来创建数据库。只有创建数据库的应用才能打开数据库。打开数据库后,系统会返回一个会话以与数据库交互。会话是调用 AppSearch API 的入口点,会一直保持打开状态,直到客户端应用将其关闭。
架构和架构类型
架构表示 AppSearch 数据库中数据的组织结构。
架构由表示数据的唯一类型的架构类型组成。架构类型由包含名称、数据类型和基数的属性组成。将架构类型添加到数据库架构后,就可以创建该架构类型的文档并将其添加到数据库中。
文档
在 AppSearch 中,数据单元表示为文档。AppSearch 数据库中的每个文档都通过其命名空间和 ID 进行唯一标识。当只需要查询一个来源(例如用户账号)时,命名空间用于分隔来自不同来源的数据。
文档包含创建时间戳、存活时间 (TTL) 和一个可用于检索期间排名的得分。文档还会被分配一个架构类型,该类型用于描述文档必须具有的其他数据属性。
文档类是对文档的抽象。它包含表示文档内容的带注释字段。默认情况下,文档类的名称会设置架构类型的名称。
搜索
系统会为文档编入索引,您可以通过提供查询来搜索文档。如果文档包含查询中的字词或与其他搜索规范匹配,则会被匹配并纳入搜索结果中。结果会根据其得分和排名策略进行排序。搜索结果由可按顺序检索的页面表示。
AppSearch 提供搜索自定义功能,例如过滤条件、页面大小配置和摘要。
平台存储空间、本地存储空间或 Play 服务存储空间
AppSearch 提供三种存储解决方案:LocalStorage、PlatformStorage 和 PlayServicesStorage。借助 LocalStorage,您的应用可以管理位于应用数据目录中的应用专用索引。同时使用 PlatformStorage 和 PlayServicesStorage 时,您的应用会贡献到系统级中央索引。PlatformStorage 的索引托管在系统服务器中,PlayServicesStorage 的索引托管在 Google Play 服务的存储空间中。这些中央索引中的数据访问权限仅限于您的应用贡献的数据以及其他应用明确与您共享的数据。所有这些存储选项都使用相同的 API,并且可以根据设备的版本进行互换:
Kotlin
if (BuildCompat.isAtLeastS()) { appSearchSessionFuture.setFuture( PlatformStorage.createSearchSession( PlatformStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build() ) ) } else { if (usePlayServicesStorageBelowS) { appSearchSessionFuture.setFuture( PlayServicesStorage.createSearchSession( PlayServicesStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build() ) ) } else { appSearchSessionFuture.setFuture( LocalStorage.createSearchSession( LocalStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build() ) ) } }
Java
if (BuildCompat.isAtLeastS()) { mAppSearchSessionFuture.setFuture(PlatformStorage.createSearchSession( new PlatformStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build())); } else { if (usePlayServicesStorageBelowS) { mAppSearchSessionFuture.setFuture(PlayServicesStorage.createSearchSession( new PlayServicesStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build())); } else { mAppSearchSessionFuture.setFuture(LocalStorage.createSearchSession( new LocalStorage.SearchContext.Builder(mContext, DATABASE_NAME) .build())); } }
使用 PlatformStorage 和 PlayServicesStorage,您的应用可以安全地与其他应用共享数据,以便这些应用也能搜索您的应用数据。系统使用证书握手授予只读应用数据共享权限,以确保其他应用有权读取数据。如需详细了解此 API,请参阅 setSchemaTypeVisibilityForPackage() 文档。
此外,借助 PlatformStorage,已编入索引的数据可显示在系统界面上。应用可以选择不让其部分或全部数据显示在系统界面上。如需详细了解此 API,请参阅 setSchemaTypeDisplayedBySystem() 的文档。
| 功能 | LocalStorage(与 Android 5.0 及更高版本兼容) |
PlatformStorage(与 Android 12 及更高版本兼容) |
PlayServicesStorage(与 Android 5.0 及更高版本兼容) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 高效的全文搜索 | |||
| 多语言支持 | |||
| 缩减了二进制文件的大小 | |||
| 应用间数据共享 | |||
| 能够在系统界面上显示数据 | |||
| 可编入索引的文档大小和数量不受限制 | |||
| 加快操作速度,无需额外的 binder 延迟 |
在选择 LocalStorage 和 PlatformStorage 时,还需要考虑其他权衡因素。由于 PlatformStorage 会在 AppSearch 系统服务上封装 Jetpack API,因此与使用 LocalStorage 相比,对 APK 大小的影响微乎其微。不过,这也意味着,AppSearch 操作在调用 AppSearch 系统服务时会产生额外的 binder 延迟。借助 PlatformStorage,AppSearch 会限制应用可以编入索引的文档数量和文档大小,以确保中央索引高效运行。PlayServicesStorage 也存在与 PlatformStorage 相同的限制,并且仅适用于搭载 Google Play 服务的设备。
AppSearch 使用入门
本部分中的示例展示了如何使用 AppSearch API 与假设的记事应用集成。
编写文档类
与 AppSearch 集成的第一步是编写文档类,以描述要插入数据库中的数据。使用 @Document 注解将类标记为文档类。您可以使用文档类的实例将文档放入数据库中,以及从数据库中检索文档。
以下代码定义了一个 Note 文档类,其中包含一个带有 @Document.StringProperty 注解的字段,用于为 Note 对象的文本编制索引。
Kotlin
@Document public data class Note( // Required field for a document class. All documents MUST have a namespace. @Document.Namespace val namespace: String, // Required field for a document class. All documents MUST have an Id. @Document.Id val id: String, // Optional field for a document class, used to set the score of the // document. If this is not included in a document class, the score is set // to a default of 0. @Document.Score val score: Int, // Optional field for a document class, used to index a note's text for this // document class. @Document.StringProperty(indexingType = AppSearchSchema.StringPropertyConfig.INDEXING_TYPE_PREFIXES) val text: String )
Java
@Document public class Note { // Required field for a document class. All documents MUST have a namespace. @Document.Namespace private final String namespace; // Required field for a document class. All documents MUST have an Id. @Document.Id private final String id; // Optional field for a document class, used to set the score of the // document. If this is not included in a document class, the score is set // to a default of 0. @Document.Score private final int score; // Optional field for a document class, used to index a note's text for this // document class. @Document.StringProperty(indexingType = StringPropertyConfig.INDEXING_TYPE_PREFIXES) private final String text; Note(@NonNull String id, @NonNull String namespace, int score, @NonNull String text) { this.id = Objects.requireNonNull(id); this.namespace = Objects.requireNonNull(namespace); this.score = score; this.text = Objects.requireNonNull(text); } @NonNull public String getNamespace() { return namespace; } @NonNull public String getId() { return id; } public int getScore() { return score; } @NonNull public String getText() { return text; } }
打开数据库
您必须先创建数据库,然后才能处理文档。以下代码会创建一个名为 notes_app 的新数据库,并为 AppSearchSession 获取 ListenableFuture,该 ListenableFuture 表示与数据库的连接,并为数据库操作提供 API。
Kotlin
val context: Context = getApplicationContext() val sessionFuture = LocalStorage.createSearchSession( LocalStorage.SearchContext.Builder(context, /*databaseName=*/"notes_app") .build() )
Java
Context context = getApplicationContext(); ListenableFuture<AppSearchSession> sessionFuture = LocalStorage.createSearchSession( new LocalStorage.SearchContext.Builder(context, /*databaseName=*/ "notes_app") .build() );
设置架构
您必须先设置架构,然后才能向数据库中插入文档并从中检索文档。数据库架构由不同类型的结构化数据组成,称为“架构类型”。以下代码通过将文档类作为架构类型提供来设置架构。
Kotlin
val setSchemaRequest = SetSchemaRequest.Builder().addDocumentClasses(Note::class.java) .build() val setSchemaFuture = Futures.transformAsync( sessionFuture, { session -> session?.setSchema(setSchemaRequest) }, mExecutor )
Java
SetSchemaRequest setSchemaRequest = new SetSchemaRequest.Builder().addDocumentClasses(Note.class) .build(); ListenableFuture<SetSchemaResponse> setSchemaFuture = Futures.transformAsync(sessionFuture, session -> session.setSchema(setSchemaRequest), mExecutor);
将文档放入数据库
添加架构类型后,您可以将该类型的文档添加到数据库。以下代码使用 Note 文档类构建器构建架构类型为 Note 的文档。它会将文档命名空间 user1 设置为代表此示例的任意用户。然后,系统会将文档插入数据库,并附加监听器以处理 put 操作的结果。
Kotlin
val note = Note( namespace="user1", id="noteId", score=10, text="Buy fresh fruit" ) val putRequest = PutDocumentsRequest.Builder().addDocuments(note).build() val putFuture = Futures.transformAsync( sessionFuture, { session -> session?.put(putRequest) }, mExecutor ) Futures.addCallback( putFuture, object : FutureCallback<AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void>?> { override fun onSuccess(result: AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void>?) { // Gets map of successful results from Id to Void val successfulResults = result?.successes // Gets map of failed results from Id to AppSearchResult val failedResults = result?.failures } override fun onFailure(t: Throwable) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to put documents.", t) } }, mExecutor )
Java
Note note = new Note(/*namespace=*/"user1", /*id=*/ "noteId", /*score=*/ 10, /*text=*/ "Buy fresh fruit!"); PutDocumentsRequest putRequest = new PutDocumentsRequest.Builder().addDocuments(note) .build(); ListenableFuture<AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void>> putFuture = Futures.transformAsync(sessionFuture, session -> session.put(putRequest), mExecutor); Futures.addCallback(putFuture, new FutureCallback<AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void>>() { @Override public void onSuccess(@Nullable AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void> result) { // Gets map of successful results from Id to Void Map<String, Void> successfulResults = result.getSuccesses(); // Gets map of failed results from Id to AppSearchResult Map<String, AppSearchResult<Void>> failedResults = result.getFailures(); } @Override public void onFailure(@NonNull Throwable t) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to put documents.", t); } }, mExecutor);
搜索
您可以使用本部分介绍的搜索操作搜索已编入索引的文档。以下代码会针对属于 user1 命名空间的文档,在数据库中针对字词“fruit”执行查询。
Kotlin
val searchSpec = SearchSpec.Builder() .addFilterNamespaces("user1") .build(); val searchFuture = Futures.transform( sessionFuture, { session -> session?.search("fruit", searchSpec) }, mExecutor ) Futures.addCallback( searchFuture, object : FutureCallback<SearchResults> { override fun onSuccess(searchResults: SearchResults?) { iterateSearchResults(searchResults) } override fun onFailure(t: Throwable?) { Log.e("TAG", "Failed to search notes in AppSearch.", t) } }, mExecutor )
Java
SearchSpec searchSpec = new SearchSpec.Builder() .addFilterNamespaces("user1") .build(); ListenableFuture<SearchResults> searchFuture = Futures.transform(sessionFuture, session -> session.search("fruit", searchSpec), mExecutor); Futures.addCallback(searchFuture, new FutureCallback<SearchResults>() { @Override public void onSuccess(@Nullable SearchResults searchResults) { iterateSearchResults(searchResults); } @Override public void onFailure(@NonNull Throwable t) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to search notes in AppSearch.", t); } }, mExecutor);
遍历 SearchResults
搜索会返回 SearchResults 实例,该实例可访问 SearchResult 对象的页面。每个 SearchResult 都包含其匹配的 GenericDocument,即所有文档都转换成的文档的通用形式。以下代码会获取第一页的搜索结果,并将结果转换回 Note 文档。
Kotlin
Futures.transform( searchResults?.nextPage, { page: List<SearchResult>? -> // Gets GenericDocument from SearchResult. val genericDocument: GenericDocument = page!![0].genericDocument val schemaType = genericDocument.schemaType val note: Note? = try { if (schemaType == "Note") { // Converts GenericDocument object to Note object. genericDocument.toDocumentClass(Note::class.java) } else null } catch (e: AppSearchException) { Log.e( TAG, "Failed to convert GenericDocument to Note", e ) null } note }, mExecutor )
Java
Futures.transform(searchResults.getNextPage(), page -> { // Gets GenericDocument from SearchResult. GenericDocument genericDocument = page.get(0).getGenericDocument(); String schemaType = genericDocument.getSchemaType(); Note note = null; if (schemaType.equals("Note")) { try { // Converts GenericDocument object to Note object. note = genericDocument.toDocumentClass(Note.class); } catch (AppSearchException e) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to convert GenericDocument to Note", e); } } return note; }, mExecutor);
移除文档
当用户删除记事时,应用会从数据库中删除相应的 Note 文档。这样可以确保该记事不会再显示在搜索结果中。以下代码会明确请求按 ID 从数据库中移除 Note 文档。
Kotlin
val removeRequest = RemoveByDocumentIdRequest.Builder("user1") .addIds("noteId") .build() val removeFuture = Futures.transformAsync( sessionFuture, { session -> session?.remove(removeRequest) }, mExecutor )
Java
RemoveByDocumentIdRequest removeRequest = new RemoveByDocumentIdRequest.Builder("user1") .addIds("noteId") .build(); ListenableFuture<AppSearchBatchResult<String, Void>> removeFuture = Futures.transformAsync(sessionFuture, session -> session.remove(removeRequest), mExecutor);
持久化到磁盘
应通过调用 requestFlush() 定期将对数据库的更新持久存储到磁盘。以下代码会使用监听器调用 requestFlush(),以确定调用是否成功。
Kotlin
val requestFlushFuture = Futures.transformAsync( sessionFuture, { session -> session?.requestFlush() }, mExecutor ) Futures.addCallback(requestFlushFuture, object : FutureCallback<Void?> { override fun onSuccess(result: Void?) { // Success! Database updates have been persisted to disk. } override fun onFailure(t: Throwable) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to flush database updates.", t) } }, mExecutor)
Java
ListenableFuture<Void> requestFlushFuture = Futures.transformAsync(sessionFuture, session -> session.requestFlush(), mExecutor); Futures.addCallback(requestFlushFuture, new FutureCallback<Void>() { @Override public void onSuccess(@Nullable Void result) { // Success! Database updates have been persisted to disk. } @Override public void onFailure(@NonNull Throwable t) { Log.e(TAG, "Failed to flush database updates.", t); } }, mExecutor);
关闭会话
当应用不再调用任何数据库操作时,应关闭 AppSearchSession。以下代码会关闭之前打开的 AppSearch 会话,并将所有更新持久保存到磁盘。
Kotlin
val closeFuture = Futures.transform<AppSearchSession, Unit>(sessionFuture, { session -> session?.close() Unit }, mExecutor )
Java
ListenableFuture<Void> closeFuture = Futures.transform(sessionFuture, session -> { session.close(); return null; }, mExecutor);
其他资源
如需详细了解 AppSearch,请参阅以下其他资源:
示例
- Android AppSearch 示例 (Kotlin):这是一个记事应用,使用 AppSearch 为用户的记事编制索引,并允许用户搜索其记事。
提供反馈
通过以下资源与我们分享您的反馈和想法:
请报告 bug,以便我们进行修复。
