Bằng cách sử dụng WindowInsetsCompat, ứng dụng của bạn có thể truy vấn và điều khiển bàn phím ảo (còn gọi là IME) tương tự như cách ứng dụng tương tác với các thanh hệ thống. Ứng dụng của bạn cũng có thể dùng WindowInsetsAnimationCompat để tạo hiệu ứng chuyển đổi liền mạch khi bàn phím phần mềm được mở hoặc đóng.
Điều kiện tiên quyết
Trước khi thiết lập chế độ điều khiển và hiệu ứng chuyển động cho bàn phím phần mềm, hãy định cấu hình ứng dụng của bạn để hiển thị tràn viền. Cách này cho phép ứng dụng xử lý phần lồng ghép của cửa sổ hệ thống, chẳng hạn như các thanh hệ thống và bàn phím ảo.
Kiểm tra chế độ hiển thị của bàn phím phần mềm
Sử dụng WindowInsets để kiểm tra chế độ hiển thị của bàn phím phần mềm.
Kotlin
val insets = ViewCompat.getRootWindowInsets(view) ?: return val imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) val imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom
Java
WindowInsetsCompat insets = ViewCompat.getRootWindowInsets(view); boolean imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()); int imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom;
Ngoài ra, bạn có thể sử dụng ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener để theo dõi các thay đổi về khả năng hiển thị của bàn phím phần mềm.
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view) { _, insets -> val imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) val imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom insets }
Java
ViewCompat.setOnApplyWindowInsetsListener(view, (v, insets) -> { boolean imeVisible = insets.isVisible(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()); int imeHeight = insets.getInsets(WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()).bottom; return insets; });
Đồng bộ hoá hiệu ứng chuyển động với bàn phím phần mềm
Khi người dùng nhấn vào một trường nhập dữ liệu, bàn phím sẽ trượt vào vị trí từ cuối màn hình, như minh hoạ trong ví dụ sau:
Ví dụ được gắn nhãn "Không đồng bộ" trong hình 2 minh hoạ hành vi mặc định trong Android 10 (API cấp 29), trong đó trường văn bản và nội dung của ứng dụng xuất hiện ngay lập tức thay vì đồng bộ hoá với hiệu ứng chuyển động của bàn phím – hành vi này có thể gây khó chịu về mặt thị giác.
Trong Android 11 (API cấp 30) trở lên, bạn có thể dùng
WindowInsetsAnimationCompatđể đồng bộ hoá hiệu ứng chuyển đổi của ứng dụng với cách bàn phím trượt lên và xuống từ cuối màn hình. Điều này trông mượt mà hơn, như minh hoạ trong ví dụ có nhãn "Được đồng bộ hoá" trong hình 2.
Định cấu hình WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback bằng khung hiển thị cần đồng bộ hoá với hiệu ứng chuyển động của bàn phím.
Kotlin
ViewCompat.setWindowInsetsAnimationCallback( view, object : WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback(DISPATCH_MODE_STOP) { // Override methods. } )
Java
ViewCompat.setWindowInsetsAnimationCallback( view, new WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback( WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback.DISPATCH_MODE_STOP ) { // Override methods. });
Có một số phương thức để ghi đè trong WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.Callback, cụ thể là onPrepare(), onStart(), onProgress() và onEnd().
Hãy bắt đầu bằng cách gọi onPrepare() trước khi có bất kỳ thay đổi nào về bố cục.
onPrepare được gọi khi một hiệu ứng chuyển động của phần lồng ghép bắt đầu và trước khi các khung hiển thị được bố trí lại do hiệu ứng chuyển động. Bạn có thể dùng phương thức đó để lưu trạng thái bắt đầu, trong trường hợp này là toạ độ dưới cùng của khung hiển thị.
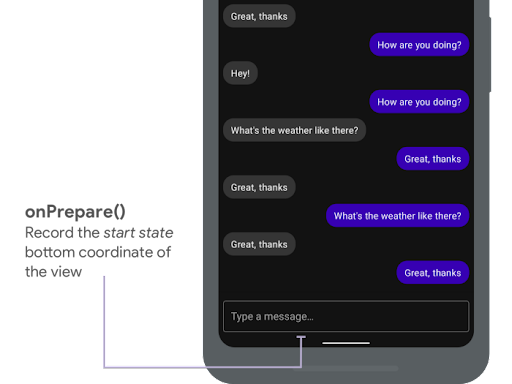
onPrepare() để ghi lại trạng thái bắt đầu.
Đoạn mã sau đây cho thấy một lệnh gọi mẫu đến onPrepare:
Kotlin
var startBottom = 0f override fun onPrepare( animation: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat ) { startBottom = view.bottom.toFloat() }
Java
float startBottom; @Override public void onPrepare( @NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation ) { startBottom = view.getBottom(); }
onStart được gọi khi một hiệu ứng chuyển động của phần lồng ghép bắt đầu. Bạn có thể dùng lệnh này để đặt tất cả các thuộc tính khung hiển thị thành trạng thái kết thúc của các thay đổi về bố cục. Nếu bạn đã đặt lệnh gọi lại OnApplyWindowInsetsListener cho bất kỳ khung hiển thị nào, thì lệnh gọi lại đó sẽ được gọi tại thời điểm này. Đây là thời điểm thích hợp để lưu trạng thái kết thúc của các thuộc tính khung hiển thị.
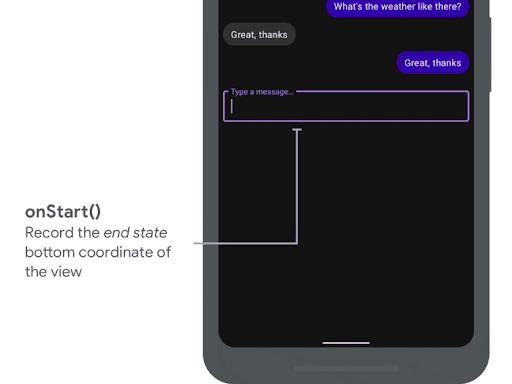
onStart() để ghi lại trạng thái kết thúc.
Đoạn mã sau đây cho thấy một lệnh gọi mẫu đến onStart:
Kotlin
var endBottom = 0f override fun onStart( animation: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat, bounds: WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat ): WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat { // Record the position of the view after the IME transition. endBottom = view.bottom.toFloat() return bounds }
Java
float endBottom; @NonNull @Override public WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat onStart( @NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation, @NonNull WindowInsetsAnimationCompat.BoundsCompat bounds ) { endBottom = view.getBottom(); return bounds; }
onProgress được gọi khi phần lồng ghép thay đổi trong quá trình chạy hiệu ứng chuyển động, vì vậy, bạn có thể ghi đè phần này và được thông báo trên mọi khung hình trong quá trình tạo hiệu ứng chuyển động cho bàn phím. Cập nhật các thuộc tính của khung hiển thị để khung hiển thị chuyển động đồng bộ với bàn phím.
Tại đây, mọi thay đổi về bố cục đều đã hoàn tất. Ví dụ: nếu bạn dùng View.translationY để dịch chuyển khung hiển thị, giá trị sẽ giảm dần cho mỗi lần gọi phương thức này và cuối cùng đạt đến 0 cho vị trí bố cục ban đầu.
onProgress() để đồng bộ hoá các hiệu ứng chuyển động.
Đoạn mã sau đây cho thấy một lệnh gọi mẫu đến onProgress:
Kotlin
override fun onProgress( insets: WindowInsetsCompat, runningAnimations: MutableList<WindowInsetsAnimationCompat> ): WindowInsetsCompat { // Find an IME animation. val imeAnimation = runningAnimations.find { it.typeMask and WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime() != 0 } ?: return insets // Offset the view based on the interpolated fraction of the IME animation. view.translationY = (startBottom - endBottom) * (1 - imeAnimation.interpolatedFraction) return insets }
Java
@NonNull @Override public WindowInsetsCompat onProgress( @NonNull WindowInsetsCompat insets, @NonNull List<WindowInsetsAnimationCompat> runningAnimations ) { // Find an IME animation. WindowInsetsAnimationCompat imeAnimation = null; for (WindowInsetsAnimationCompat animation : runningAnimations) { if ((animation.getTypeMask() & WindowInsetsCompat.Type.ime()) != 0) { imeAnimation = animation; break; } } if (imeAnimation != null) { // Offset the view based on the interpolated fraction of the IME animation. view.setTranslationY((startBottom - endBottom) * (1 - imeAnimation.getInterpolatedFraction())); } return insets; }
Bạn có thể ghi đè onEnd (không bắt buộc). Phương thức này được gọi sau khi hiệu ứng chuyển động kết thúc. Đây là thời điểm thích hợp để xoá mọi thay đổi tạm thời.
Tài nguyên khác
- WindowInsetsAnimation trên GitHub.

