RelativeLayout 是以相對位置顯示子檢視畫面的檢視區塊群組。每個檢視畫面的位置都可以指定為相對於同層級元素 (例如
其他檢視畫面的左側或下方) 或相對於上層 RelativeLayout 區域的位置 (例如底部、左側或置中)。
注意:如要提升效能並取得更完善的工具支援,請改為使用 ConstraintLayout 建構版面配置。

RelativeLayout 是用來設計使用者介面的強大工具,讓您不須使用巢狀檢視區塊群組,因此版面配置階層能保持平坦,進而提升效能。如果您發現自己使用了多個巢狀 LinearLayout 群組,只要改用 RelativeLayout 或許就能取代這些群組。
檢視畫面位置
RelativeLayout 可讓子檢視畫面指定相對於父檢視畫面或其他子檢視畫面的位置 (以 ID 指定)。因此,您可以根據右框線對齊兩個元素,或
移到另一個下方、在畫面中央、靠左置中等等。根據預設,所有子檢視畫面均繪製在版面配置的左上角,因此您必須使用 RelativeLayout.LayoutParams 提供的各種版面配置屬性來定義每個檢視畫面的位置。
RelativeLayout 供檢視畫面使用的眾多版面配置屬性包括:
android:layout_alignParentTop- 如果為
"true",會將這個檢視畫面的上緣比對父項的上緣。 android:layout_centerVertical- 如果為
"true",會將這個子檢視畫面垂直置中於父檢視畫面中。 android:layout_below- 將這個檢視畫面的上緣置於以資源 ID 指定的檢視畫面下方。
android:layout_toRightOf- 將這個檢視畫面的左側邊緣置於以資源 ID 指定的檢視畫面右側。
以上只是其中幾種應用範例,完整的版面配置屬性列於 RelativeLayout.LayoutParams。
各個版面配置屬性的值可能為布林值,以設為相對於父項 RelativeLayout 的版面配置位置;也可能為 ID,以參照版面配置中的另一個檢視畫面來決定檢視畫面位置。
在 XML 版面配置中,能以任何順序宣告依附於版面配置中其他檢視畫面的元件。舉例來說,即使「view2」是階層中宣告的最後一個檢視畫面,您還是可以宣告「view1」置於「view2」下方。以下是這種情境的範例。
範例
用來控制每個資料檢視相對位置的屬性均另外強調。
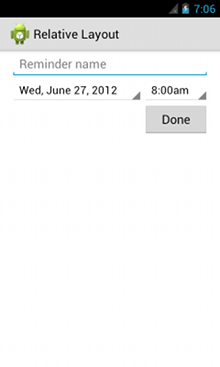
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="16dp" android:paddingRight="16dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:hint="@string/reminder" /> <Spinner android:id="@+id/dates" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_toLeftOf="@+id/times" /> <Spinner android:id="@id/times" android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/name" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" /> <Button android:layout_width="96dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@id/times" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:text="@string/done" /> </RelativeLayout>
如要進一步瞭解 RelativeLayout 每個子檢視畫面可用的版面配置屬性,請參閱 RelativeLayout.LayoutParams。

