Việc làm cho các đối tượng di chuyển theo một chương trình đặt trước như tam giác xoay sẽ hữu ích cho
thu hút được sự chú ý, nhưng nếu bạn muốn người dùng tương tác với đồ hoạ OpenGL ES của mình thì sao?
Chìa khoá để tạo ra tính tương tác cảm ứng cho ứng dụng OpenGL ES là mở rộng việc triển khai
GLSurfaceView để ghi đè
onTouchEvent() để theo dõi các sự kiện chạm.
Bài học này sẽ hướng dẫn bạn cách theo dõi các sự kiện chạm để cho phép người dùng xoay một đối tượng OpenGL ES.
Thiết lập trình nghe thao tác chạm
Để ứng dụng OpenGL ES của bạn phản hồi các sự kiện chạm, bạn phải triển khai
Phương thức onTouchEvent() trong
Lớp GLSurfaceView. Quy trình triển khai mẫu bên dưới cho biết cách lắng nghe
Các sự kiện MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE và dịch các sự kiện đó sang
góc quay của hình dạng.
Kotlin
private const val TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR: Float = 180.0f / 320f ... private var previousX: Float = 0f private var previousY: Float = 0f override fun onTouchEvent(e: MotionEvent): Boolean { // MotionEvent reports input details from the touch screen // and other input controls. In this case, you are only // interested in events where the touch position changed. val x: Float = e.x val y: Float = e.y when (e.action) { MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE -> { var dx: Float = x - previousX var dy: Float = y - previousY // reverse direction of rotation above the mid-line if (y > height / 2) { dx *= -1 } // reverse direction of rotation to left of the mid-line if (x < width / 2) { dy *= -1 } renderer.angle += (dx + dy) * TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR requestRender() } } previousX = x previousY = y return true }
Java
private final float TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR = 180.0f / 320; private float previousX; private float previousY; @Override public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) { // MotionEvent reports input details from the touch screen // and other input controls. In this case, you are only // interested in events where the touch position changed. float x = e.getX(); float y = e.getY(); switch (e.getAction()) { case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: float dx = x - previousX; float dy = y - previousY; // reverse direction of rotation above the mid-line if (y > getHeight() / 2) { dx = dx * -1 ; } // reverse direction of rotation to left of the mid-line if (x < getWidth() / 2) { dy = dy * -1 ; } renderer.setAngle( renderer.getAngle() + ((dx + dy) * TOUCH_SCALE_FACTOR)); requestRender(); } previousX = x; previousY = y; return true; }
Lưu ý rằng sau khi tính góc xoay, phương thức này sẽ gọi
requestRender() để cho
trình kết xuất đồ hoạ rằng đã đến lúc kết xuất khung hình. Đây là phương pháp hiệu quả nhất trong ví dụ này
vì không cần vẽ lại khung trừ khi có thay đổi về phép xoay. Tuy nhiên, việc này
không có bất kỳ ảnh hưởng nào đến hiệu quả trừ khi bạn cũng yêu cầu trình kết xuất chỉ vẽ lại khi
dữ liệu thay đổi bằng cách sử dụng setRenderMode()
, vì vậy hãy đảm bảo không nhận xét dòng này trong trình kết xuất:
Kotlin
class MyGlSurfaceView(context: Context) : GLSurfaceView(context) { init { // Render the view only when there is a change in the drawing data renderMode = GLSurfaceView.RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY } }
Java
public MyGLSurfaceView(Context context) { ... // Render the view only when there is a change in the drawing data setRenderMode(GLSurfaceView.RENDERMODE_WHEN_DIRTY); }
Hiển thị góc xoay
Mã ví dụ ở trên yêu cầu bạn hiển thị góc xoay qua trình kết xuất bằng cách
thêm thành viên công khai. Vì mã kết xuất đang chạy trên một luồng riêng biệt với người dùng chính
luồng giao diện của ứng dụng, bạn phải khai báo biến công khai này dưới dạng volatile.
Dưới đây là mã để khai báo biến và hiển thị cặp phương thức getter và setter:
Kotlin
class MyGLRenderer4 : GLSurfaceView.Renderer { @Volatile var angle: Float = 0f }
Java
public class MyGLRenderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer { ... public volatile float mAngle; public float getAngle() { return mAngle; } public void setAngle(float angle) { mAngle = angle; } }
Áp dụng chế độ xoay
Để áp dụng chế độ xoay được tạo bằng phương thức nhập bằng cách chạm, hãy ghi chú mã tạo ra một góc và thêm một biến chứa góc đã tạo bằng phương thức nhập bằng cách chạm:
Kotlin
override fun onDrawFrame(gl: GL10) { ... val scratch = FloatArray(16) // Create a rotation for the triangle // long time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() % 4000L; // float angle = 0.090f * ((int) time); Matrix.setRotateM(rotationMatrix, 0, angle, 0f, 0f, -1.0f) // Combine the rotation matrix with the projection and camera view // Note that the mvpMatrix factor *must be first* in order // for the matrix multiplication product to be correct. Matrix.multiplyMM(scratch, 0, mvpMatrix, 0, rotationMatrix, 0) // Draw triangle triangle.draw(scratch) }
Java
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) { ... float[] scratch = new float[16]; // Create a rotation for the triangle // long time = SystemClock.uptimeMillis() % 4000L; // float angle = 0.090f * ((int) time); Matrix.setRotateM(rotationMatrix, 0, mAngle, 0, 0, -1.0f); // Combine the rotation matrix with the projection and camera view // Note that the vPMatrix factor *must be first* in order // for the matrix multiplication product to be correct. Matrix.multiplyMM(scratch, 0, vPMatrix, 0, rotationMatrix, 0); // Draw triangle mTriangle.draw(scratch); }
Khi bạn đã hoàn tất các bước được mô tả ở trên, hãy chạy chương trình và kéo ngón tay trên màn hình để xoay tam giác:
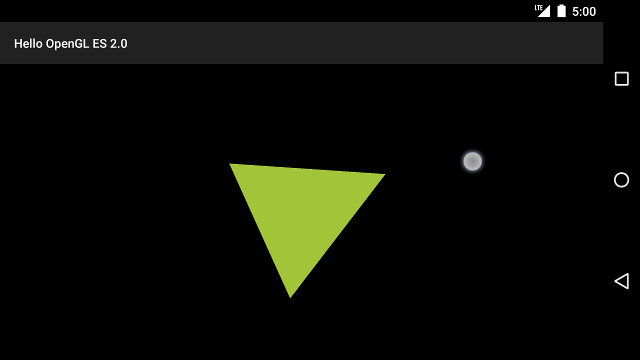
Hình 1. Hình tam giác đang xoay khi nhập bằng cách chạm (hình tròn hiển thị cử chỉ chạm vị trí).
