定義要在 OpenGL ES 檢視畫面上繪製的形狀,是導入 OpenGL ES 檢視畫面的第一步 為應用程式製作高階圖像如果沒有 OpenGL ES 繪圖,或許是有點困難 瞭解 OpenGL ES 如何定義圖形物件的幾項基本資訊。
本課程將說明相對於 Android 裝置畫面的 OpenGL ES 座標系統。 定義形狀、形狀以及定義三角形和正方形的基本知識。
定義三角形
OpenGL ES 可讓您使用三維空間中的座標定義繪製的物件。所以
您必須先定義三角形的座標,才能繪製三角形。在 OpenGL 中
是定義座標浮點數的頂點陣列。上限
可將這些座標寫入 ByteBuffer,並傳遞至
以便處理的 OpenGL ES 圖形管線。
Kotlin
// number of coordinates per vertex in this array const val COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3 var triangleCoords = floatArrayOf( // in counterclockwise order: 0.0f, 0.622008459f, 0.0f, // top -0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f // bottom right ) class Triangle { // Set color with red, green, blue and alpha (opacity) values val color = floatArrayOf(0.63671875f, 0.76953125f, 0.22265625f, 1.0f) private var vertexBuffer: FloatBuffer = // (number of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(triangleCoords.size * 4).run { // use the device hardware's native byte order order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) // create a floating point buffer from the ByteBuffer asFloatBuffer().apply { // add the coordinates to the FloatBuffer put(triangleCoords) // set the buffer to read the first coordinate position(0) } } }
Java
public class Triangle { private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer; // number of coordinates per vertex in this array static final int COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3; static float triangleCoords[] = { // in counterclockwise order: 0.0f, 0.622008459f, 0.0f, // top -0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.311004243f, 0.0f // bottom right }; // Set color with red, green, blue and alpha (opacity) values float color[] = { 0.63671875f, 0.76953125f, 0.22265625f, 1.0f }; public Triangle() { // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (number of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) triangleCoords.length * 4); // use the device hardware's native byte order bb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); // create a floating point buffer from the ByteBuffer vertexBuffer = bb.asFloatBuffer(); // add the coordinates to the FloatBuffer vertexBuffer.put(triangleCoords); // set the buffer to read the first coordinate vertexBuffer.position(0); } }
根據預設,OpenGL ES 會假設有一個座標系統,其中 [0,0,0] (X,Y,Z) 會指定
GLSurfaceView 影格,
[1,1,0] 是外框的右上角
[-1,-1,0] 外框的左下角。如需此座標系統的插圖,請參閱
OpenGL ES 開發人員
指南。
請注意,這個形狀的座標是以逆時針順序定義。繪圖 順序非常重要,因為這能定義哪一邊是形狀的正面, 而您一般 以及背面,您可以選擇不使用 OpenGL ES 立體圖形繪製圖形 臉部特徵如要進一步瞭解臉部和汙染,請參閱 OpenGL ES 開發人員指南。
定義正方形
在 OpenGL 中定義三角形非常簡單,但如果您想要稍微自訂 複雜之處?例如正方形、方法有很多,但繪製這種典型的典型路徑 OpenGL ES 中的形狀是使用兩個一起繪製的三角形:
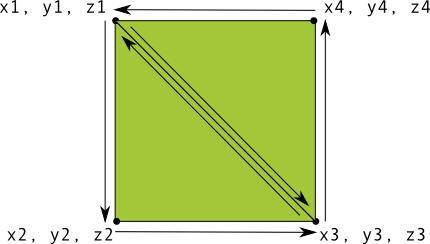
圖 1. 繪製使用兩個三角形的正方形。
同樣地,您應針對
代表這個形狀,然後將值放入 ByteBuffer 中。為避免
定義每個三角形共用的兩個座標,並使用繪圖清單
OpenGL ES 圖形管線如何繪製這些頂點。這個形狀的程式碼如下:
Kotlin
// number of coordinates per vertex in this array const val COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3 var squareCoords = floatArrayOf( -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top left -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f // top right ) class Square2 { private val drawOrder = shortArrayOf(0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3) // order to draw vertices // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates private val vertexBuffer: FloatBuffer = // (# of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(squareCoords.size * 4).run { order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) asFloatBuffer().apply { put(squareCoords) position(0) } } // initialize byte buffer for the draw list private val drawListBuffer: ShortBuffer = // (# of coordinate values * 2 bytes per short) ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(drawOrder.size * 2).run { order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) asShortBuffer().apply { put(drawOrder) position(0) } } }
Java
public class Square { private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer; private ShortBuffer drawListBuffer; // number of coordinates per vertex in this array static final int COORDS_PER_VERTEX = 3; static float squareCoords[] = { -0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f, // top left -0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom left 0.5f, -0.5f, 0.0f, // bottom right 0.5f, 0.5f, 0.0f }; // top right private short drawOrder[] = { 0, 1, 2, 0, 2, 3 }; // order to draw vertices public Square() { // initialize vertex byte buffer for shape coordinates ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (# of coordinate values * 4 bytes per float) squareCoords.length * 4); bb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); vertexBuffer = bb.asFloatBuffer(); vertexBuffer.put(squareCoords); vertexBuffer.position(0); // initialize byte buffer for the draw list ByteBuffer dlb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect( // (# of coordinate values * 2 bytes per short) drawOrder.length * 2); dlb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()); drawListBuffer = dlb.asShortBuffer(); drawListBuffer.put(drawOrder); drawListBuffer.position(0); } }
這個範例可讓您瞭解如何使用 OpenGL 建立更複雜的形狀。於 一般而言,您可以使用三角形的集合來繪製物件。在下一個課程中,您將學習如何繪製 這些形狀
