เมื่อออกแบบแอปสำหรับ Wear OS คุณควรแสดงเค้าโครงที่เลือกไว้อย่างตั้งใจ ในแต่ละประสบการณ์ เนื่องจาก Wear OS ทำงานบนจอแสดงผลที่เป็นวงกลมและการตัดเนื้อหาจะทำมากกว่า รูปแบบพื้นฐานมีด้วยกัน 2 หมวดหมู่ซึ่งต่างจากอุปกรณ์เคลื่อนที่ ที่คุณควรพิจารณาเมื่อออกแบบแอป
เลย์เอาต์ของแอปแบบไม่เลื่อน
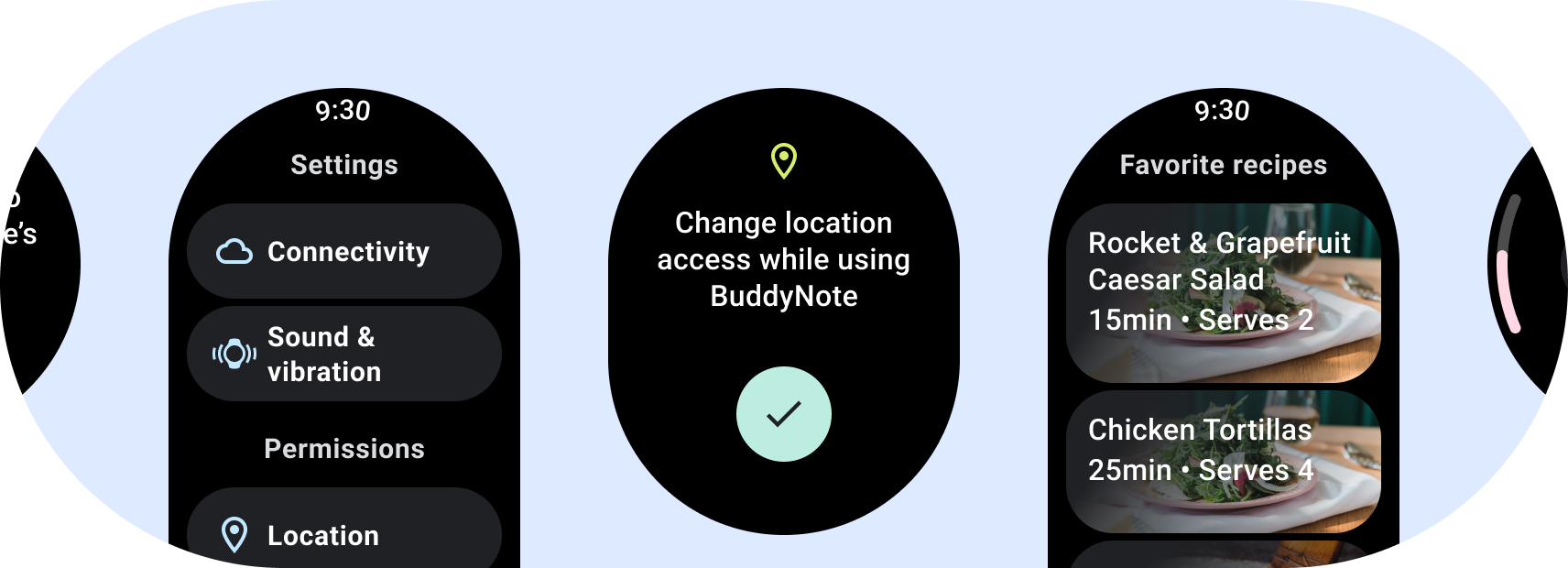
เลย์เอาต์แบบไม่เลื่อนเพื่อเน้นข้อมูลที่อ่านง่ายและมอบคุณค่าให้กับผู้ใช้ การโต้ตอบเพียงเล็กน้อยหรือไม่มีเลย ด้วยเหตุนี้ การสร้างบล็อกจึงไม่ใช่เรื่องง่าย ลักษณะการปรับเปลี่ยนตามอุปกรณ์ในเลย์เอาต์เหล่านี้
สร้างมาเพื่อมุมมองแบบไม่เลื่อนที่ปรับเปลี่ยนตามอุปกรณ์
- ทดสอบชุดค่าผสมของภาษา การปรับขนาดแบบอักษร อุปกรณ์ และตัวแปรต่างๆ เนื้อหา
- ใช้เลย์เอาต์แบบเลื่อนไม่ได้ก็ต่อเมื่อระบบรู้จักหรือควบคุมเนื้อหาแล้วเท่านั้น ล่วงหน้า หรือหากคุณต้องใช้การออกแบบที่เจาะจง
- ใช้ขอบด้านบน ด้านล่าง และด้านข้างที่แนะนำกับเลย์เอาต์
- กำหนดระยะขอบเป็นค่าเปอร์เซ็นต์ในตำแหน่งที่เนื้อหาอาจมี จะถูกตัดทอน
- จัดเรียงองค์ประกอบเพื่อให้ใช้พื้นที่ภายในองค์ประกอบได้เกิดประโยชน์สูงสุด และรักษาสมดุลระหว่างอุปกรณ์ขนาดต่างๆ
เลย์เอาต์แอปแบบเลื่อน
สำหรับหน้าที่มีข้อมูลมากเกินกว่าที่จะแสดงในหน้าจอเดียว หรือ ซึ่งจำเป็นต่อการรองรับเส้นทางที่ยาวและสมจริงมากขึ้น ให้ใช้การเลื่อน
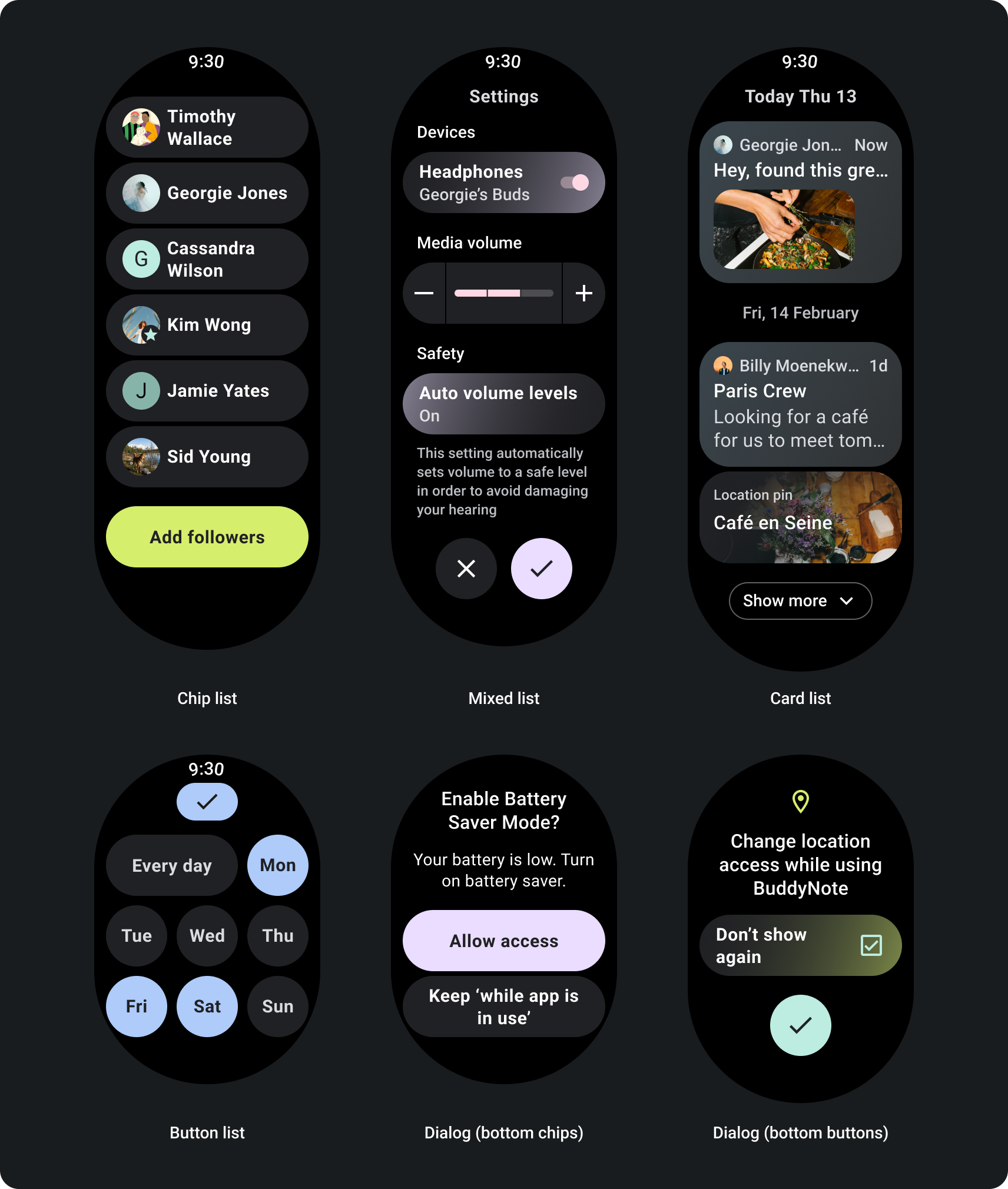
สร้างมาเพื่อมุมมองการเลื่อนที่ปรับเปลี่ยนตามอุปกรณ์
- ใช้ขอบด้านบน ด้านล่าง และด้านข้างที่แนะนำ
- ระบุระยะขอบด้านนอกเป็นค่าเปอร์เซ็นต์เพื่อป้องกันการตัดที่ จุดเริ่มต้นและจุดสิ้นสุดของคอนเทนเนอร์ที่เลื่อนได้
- ใช้ระยะขอบในค่า DP คงที่ระหว่างองค์ประกอบ UI
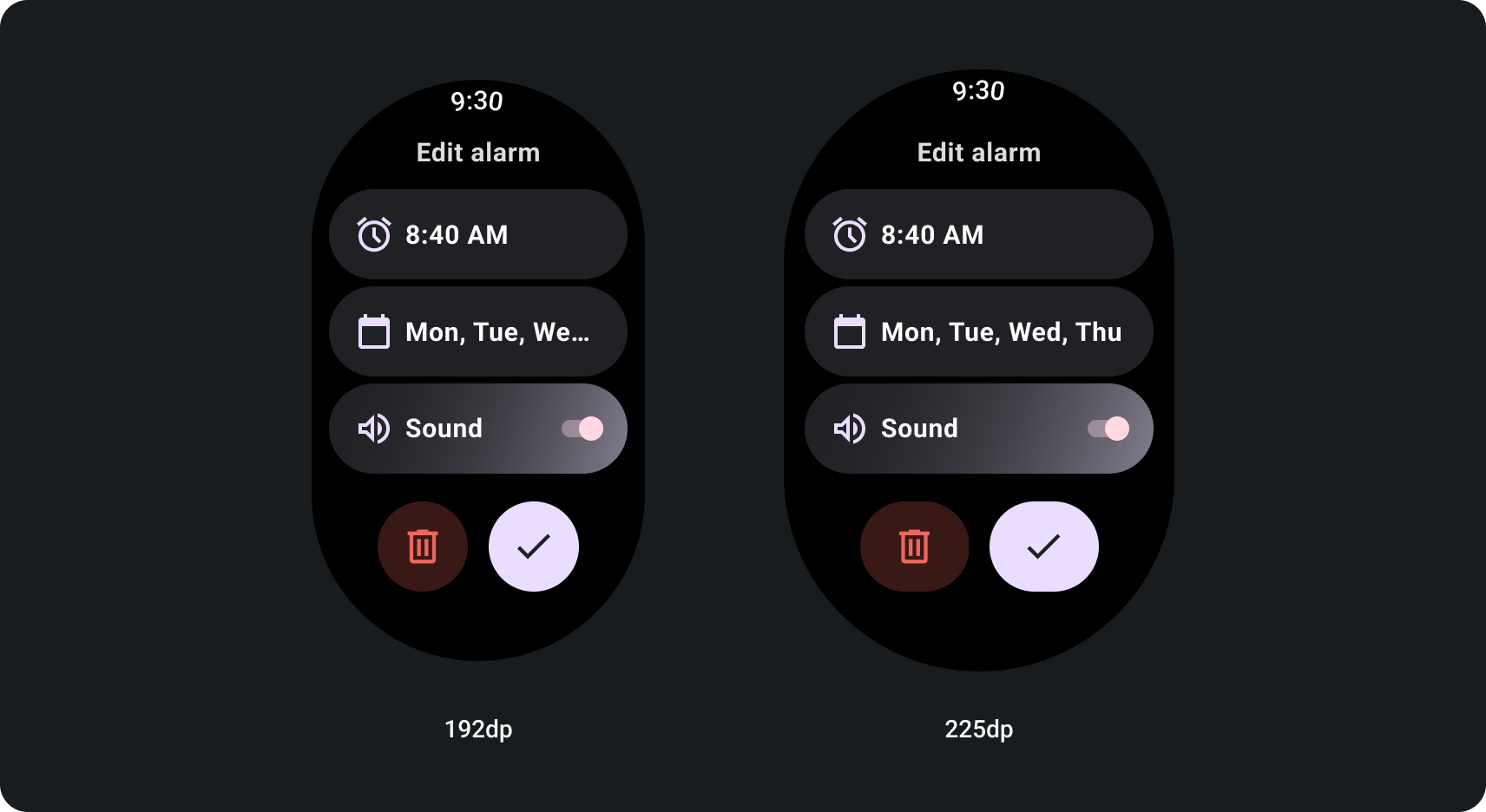
วิธีสร้างมุมมองการเลื่อนแบบปรับอัตโนมัติโดยใช้เบรกพอยท์ขนาดหน้าจอ
มุมมองการเลื่อนที่ใช้การออกแบบที่ปรับเปลี่ยนตามอุปกรณ์มักจะปรับให้เข้ากับ ขนาดหน้าจอ อย่างไรก็ตาม ในบางกรณีพิเศษ คุณสามารถใช้เบรกพอยท์เพื่อ ลบล้างมิติข้อมูลและเลย์เอาต์เสริมที่แสดงตัวเลือกเพิ่มเติม มองเห็นได้ง่ายขึ้น หรือทำให้เนื้อหาพอดีกับหน้าจอมากขึ้น ตัวอย่างต่อไปนี้ แสดงวิธีการขยายปุ่ม 2 ปุ่มด้านล่างบนหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ขึ้น ดังนี้
ชุดออกแบบ Figma
ไปที่หน้าดาวน์โหลดชุดออกแบบเพื่อสำรวจเลย์เอาต์การออกแบบที่มีในตัว คอมโพเนนต์ ตัวเลือก และคำแนะนำในการสร้างแอปและการ์ดต่างๆ การออกแบบที่เป็นไปตาม แนวทางปฏิบัติแนะนำ

