כשמעצבים אפליקציות ל-Wear OS, צריך לשים לב לפריסות שאליהן בוחרים אותן בכל חוויה. כי Wear OS פועלת על מסכים עגולים, וחיתוך הקליפ הוא יותר ארוך. נפוצים בהשוואה למכשירים ניידים, יש שתי קטגוריות של פריסות קנוניות שכדאי לחשוב עליהן כשמתכננים את האפליקציה.
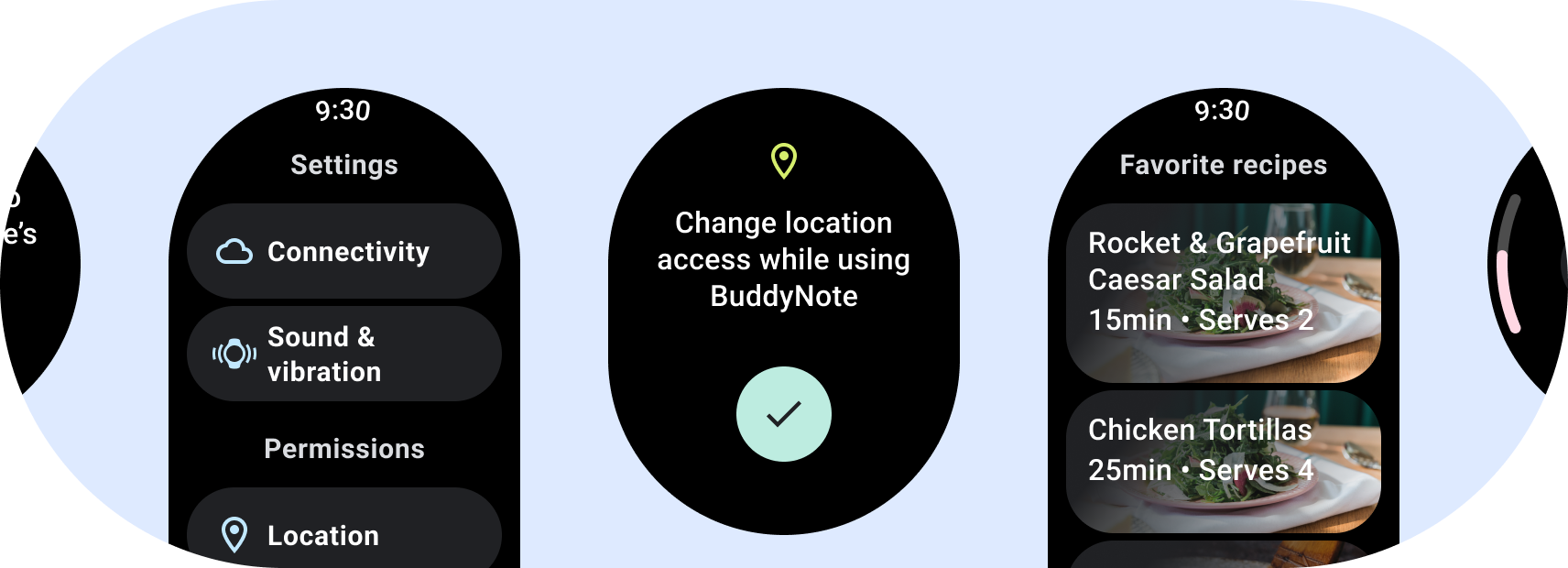
פריסות אפליקציה שלא גוללות
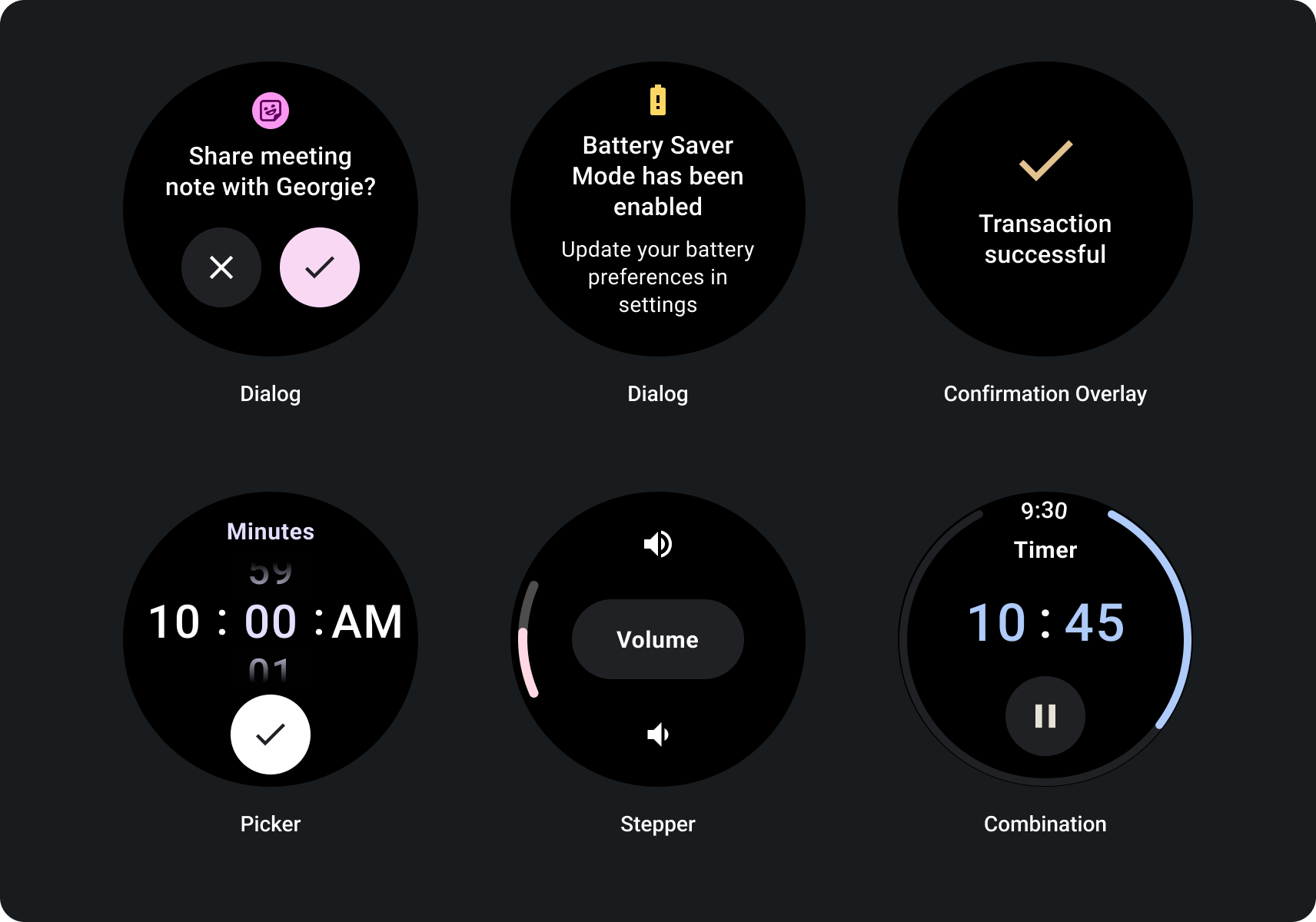
פריסות שלא גוללות מתמקדות במידע במבט מהיר ומציעות למשתמשים ערך אינטראקציה מועטה מאוד, אם בכלל. לכן הבנייה של מודל תגובה לפריסות האלה:
ממשק שמיועד לתצוגות רספונסיביות שאינן גלילה
- בדיקה על שילוב של שפות, שינוי קנה מידה של גופנים, מכשירים ומשתנים תוכן.
- יש להשתמש בפריסות שלא ניתן לגלול רק כשהתוכן מוכר או מבוקר מראש, או אם אתם חייבים להשתמש בעיצוב ספציפי.
- מחילים את השוליים העליונים, התחתונים והצדדיים המומלצים על הפריסה.
- הגדרת שוליים בערכי אחוזים במקומות שבהם התוכן עשוי היה להיות אחר להיות חתוכים.
- רצוי לארגן את הרכיבים כדי לנצל את השטח בצורה הטובה ביותר לשמור על איזון בין מכשירים בגדלים שונים.
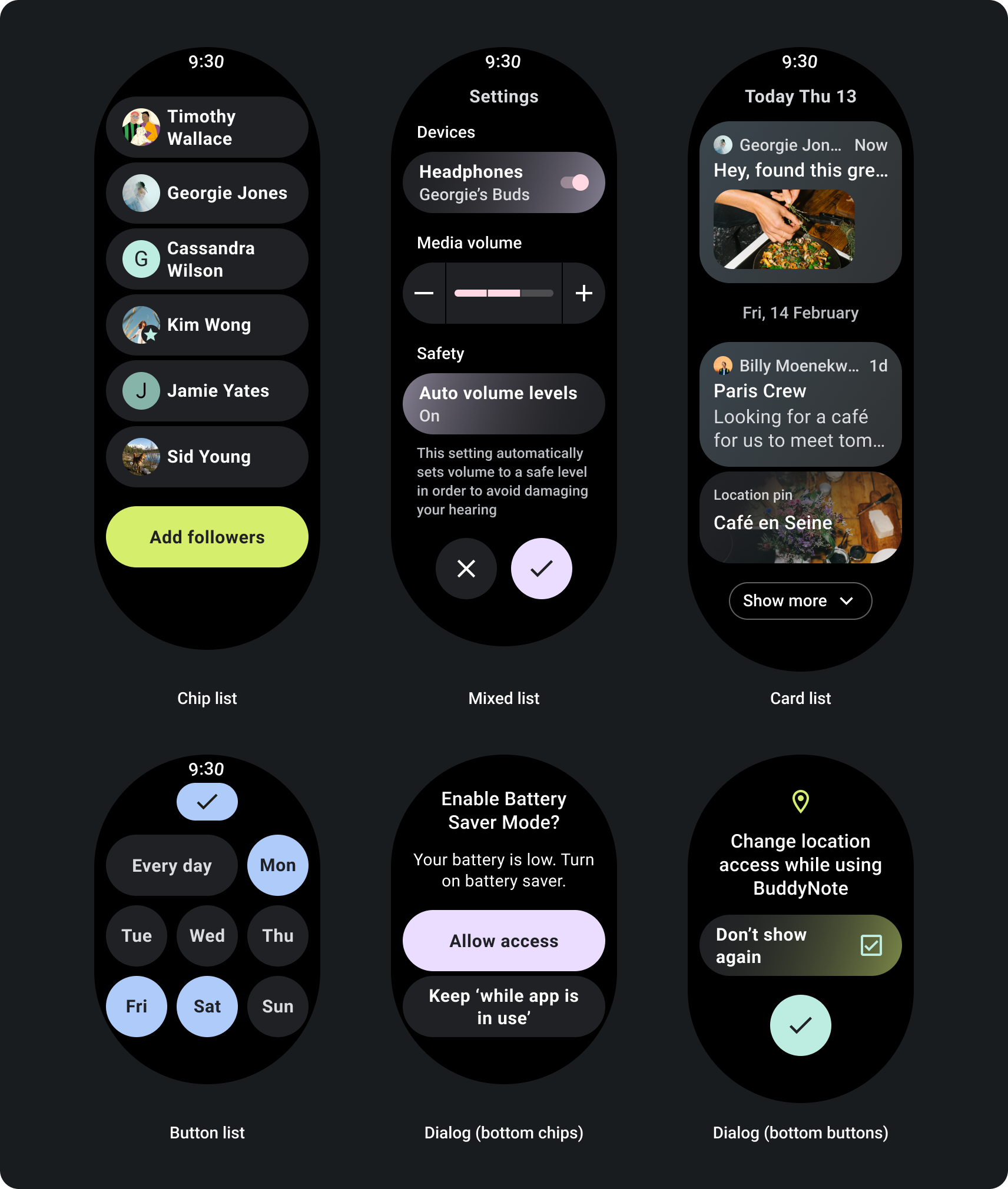
פריסות של אפליקציות לגלילה
עבור דפים שמכילים יותר מידע ממה שמתאים למסך יחיד, או שנדרשים כדי לתמוך במסלולים ארוכים וסוחפים יותר, משתמשים בגלילה צפייה.
פיתוח לתצוגות גלילה רספונסיביות
- מחילים את השוליים המומלצים לעבודה עם השוליים העליונים, התחתונים והצדדיים.
- הגדירו שוליים חיצוניים בערכי האחוזים כדי למנוע חיתוך ההתחלה והסוף של מאגר התגים שניתן לגלול.
- החלת שוליים בערכי DP קבועים בין רכיבי ממשק משתמש.
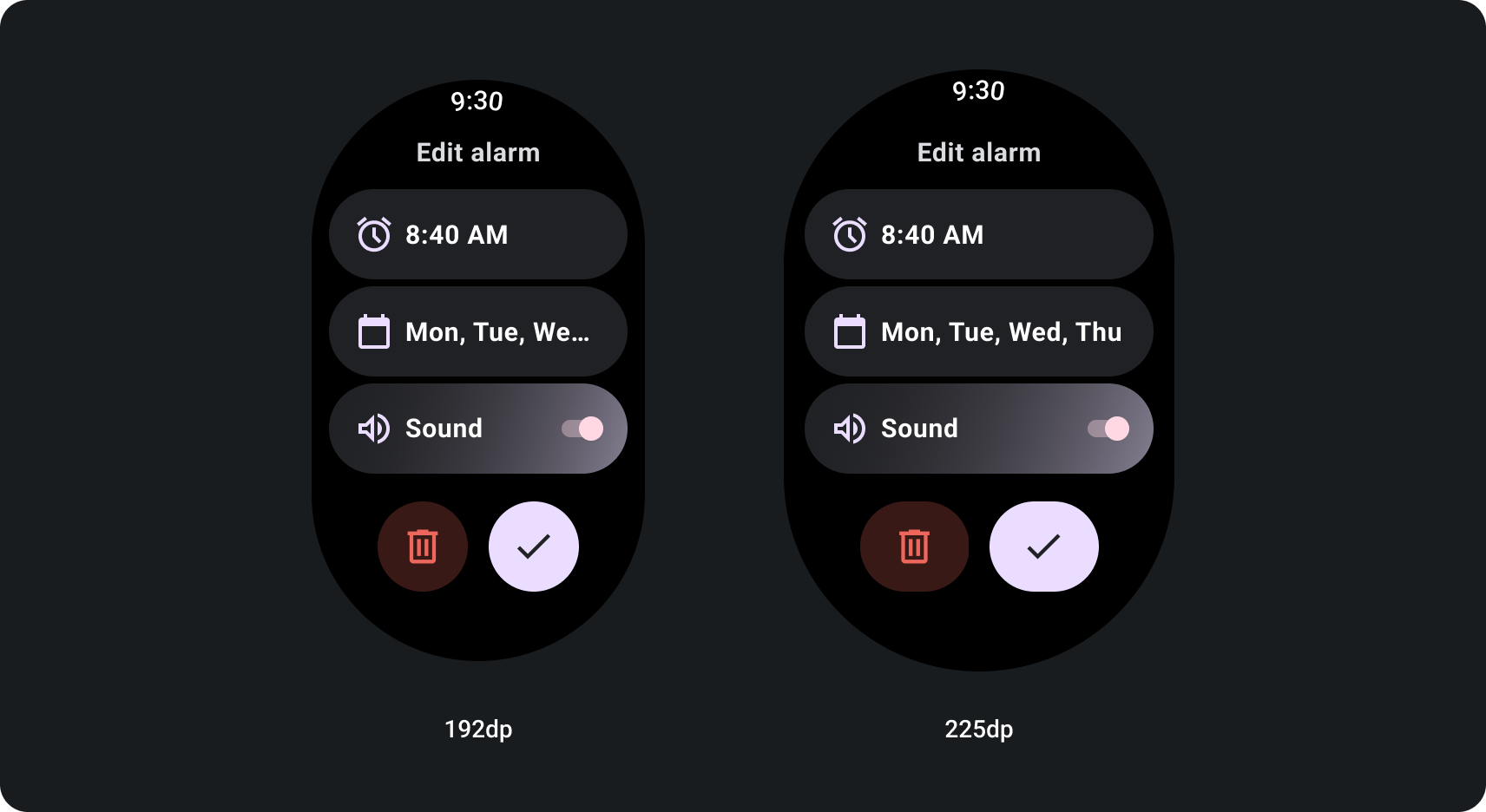
איך ליצור תצוגות גלילה מותאמות באמצעות נקודת עצירה בגודל מסך
תצוגות גלילה שמשתמשות בשיטות עיצוב רספונסיביות בדרך כלל מסתגלים בגדלים שונים. עם זאת, במקרים מיוחדים אפשר להשתמש בנקודת עצירה (breakpoint) כדי לשנות מאפיינים ולהרחיב פריסות כדי להציג אפשרויות נוספות, לשפר התכונה 'בקצרה' או כדי להתאים את התוכן למסך בצורה טובה יותר. הדוגמה הבאה מראה איך במסכים גדולים יותר מתבצע הרחבה של שני הלחצנים התחתונים:
ערכות לעיצוב פיגמה
בדף ההורדות של ערכת העיצוב אפשר לראות פריסות עיצוב עם תכונות מובנות רכיבים, אפשרויות והמלצות ליצירת אפליקציה וכרטיסי מידע שונים לפי שיטות מומלצות.

