นาฬิกา Wear OS อาจมีการกําหนดค่าปุ่มฮาร์ดแวร์ที่แตกต่างกัน คู่มือนี้จะอธิบายกรณีการใช้งานที่ดีที่สุดสำหรับปุ่มแต่ละประเภท
ประเภทปุ่ม
ปุ่มประเภทต่างๆ ที่พบบ่อยที่สุดในอุปกรณ์ Wear OS มีดังนี้
ปุ่มระบบปฏิบัติการ

ปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชัน

กดสถานะ
คุณสามารถโต้ตอบกับปุ่มของ Wear OS ได้ด้วยวิธีต่อไปนี้
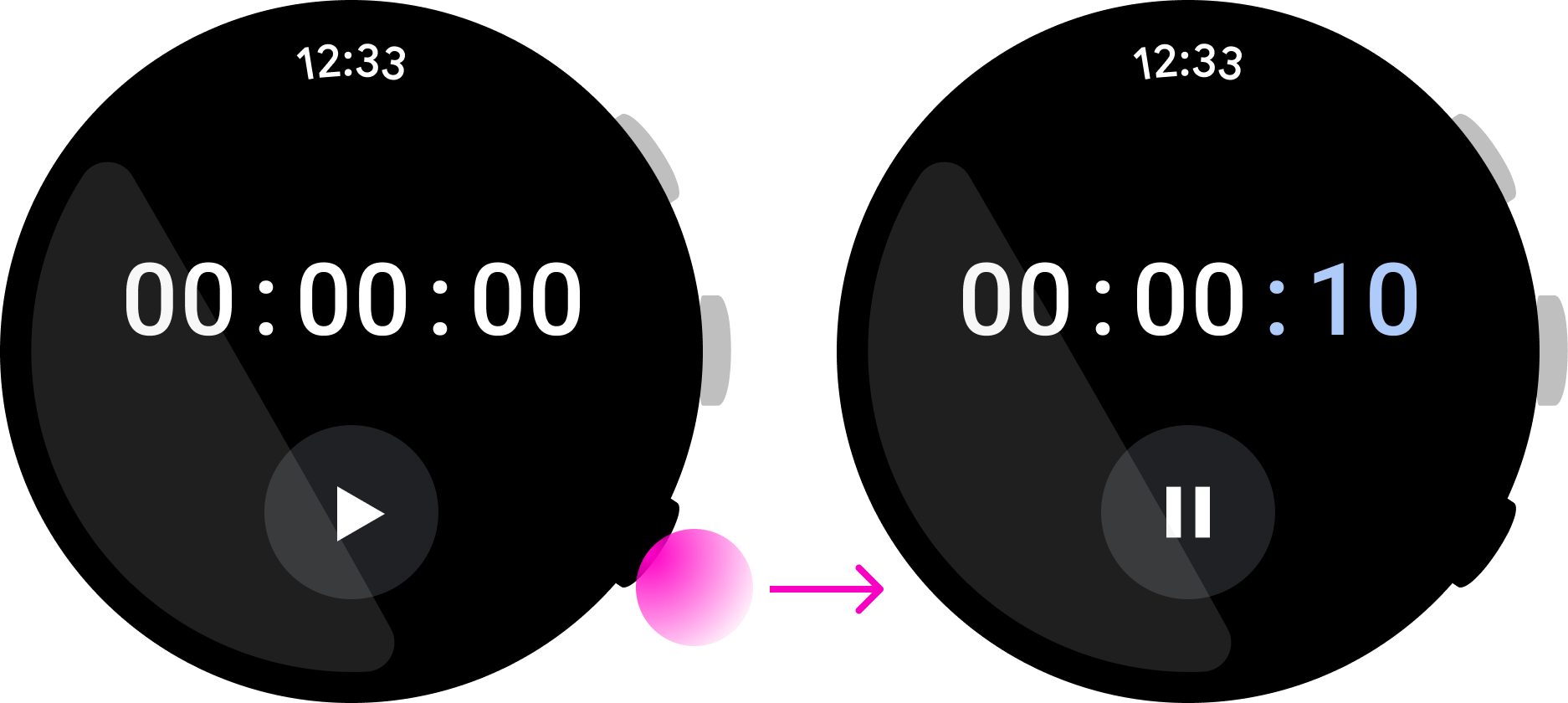
การกดครั้งเดียว

รูปที่ 1 ผู้ใช้กดปุ่มแล้วปล่อยอย่างรวดเร็ว
กดค้าง

รูปที่ 2 ผู้ใช้กดปุ่มค้างไว้นานกว่า 500 มิลลิวินาที
การแมปปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชัน
แอปสามารถกำหนดปุ่มมัลติฟังก์ชันให้กับการดำเนินการได้หากการดำเนินการดังกล่าวเหมาะกับ Use Case ของแอป แอปไม่จำเป็นต้องกำหนดการดำเนินการให้กับปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชัน
ใช้ปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชันในแอปหากเป็นไปตามเงื่อนไขข้อใดข้อหนึ่งต่อไปนี้
- แอปของคุณมีการดำเนินการแบบ 2 ค่าที่ชัดเจน (เช่น เล่น/หยุดชั่วคราว)
- ผู้ใช้ใช้แอปของคุณเป็นหลักโดยไม่ได้มองที่จอแสดงผล

รูปที่ 3 แอปฟิตเนสนี้กำหนดการดำเนินการหยุดชั่วคราว/เล่นต่อให้กับปุ่มมัลติฟังก์ชัน ซึ่งช่วยให้ผู้ใช้ดำเนินการได้โดยไม่ต้องมองที่หน้าจอ
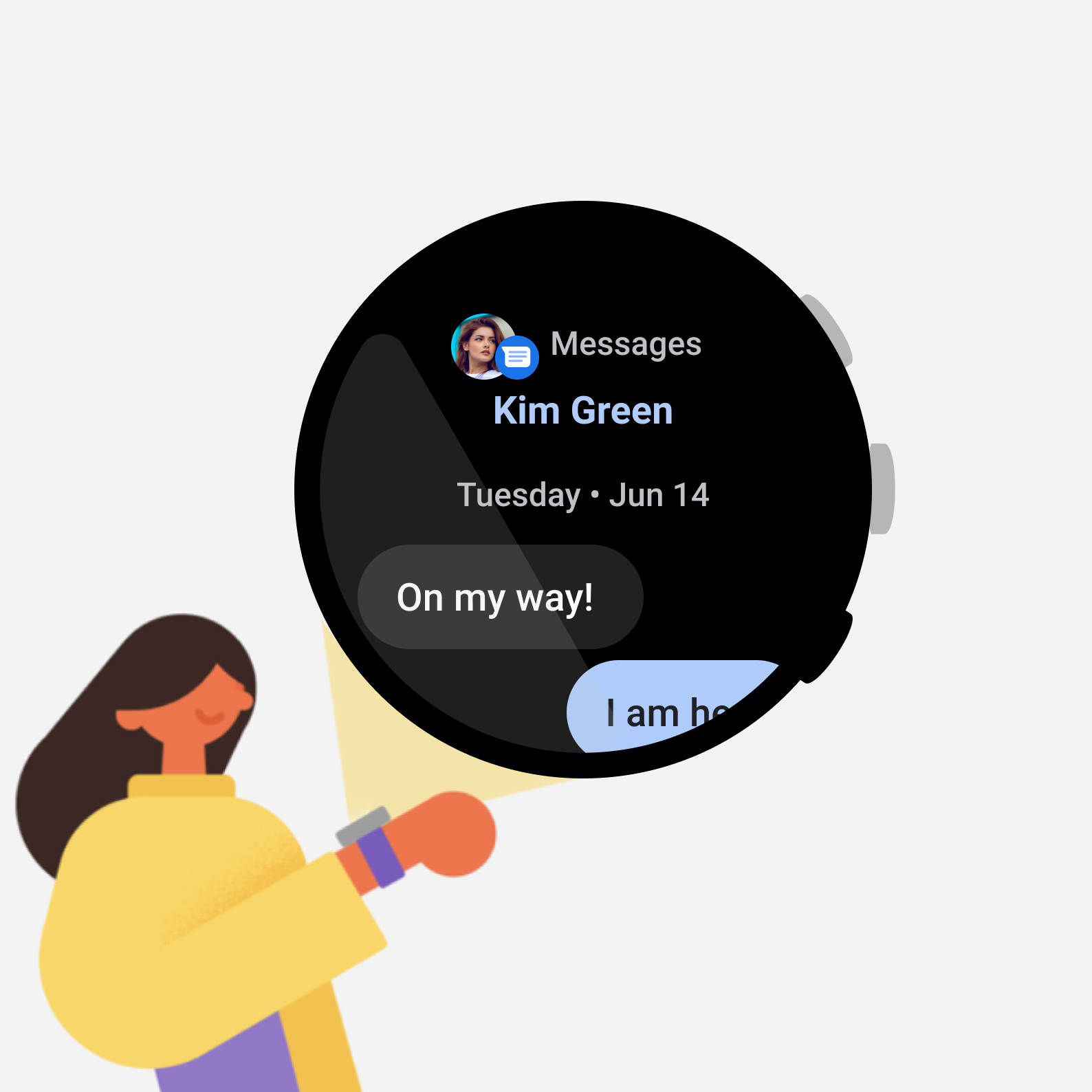
รูปที่ 4 แอปรับส่งข้อความนี้มีการดำเนินการตอบกลับ ซึ่งต้องใช้หลายขั้นตอนและดำเนินการให้เสร็จสมบูรณ์ด้วยการกดปุ่มเพียงปุ่มเดียวไม่ได้
การดำเนินการแบบไบนารี
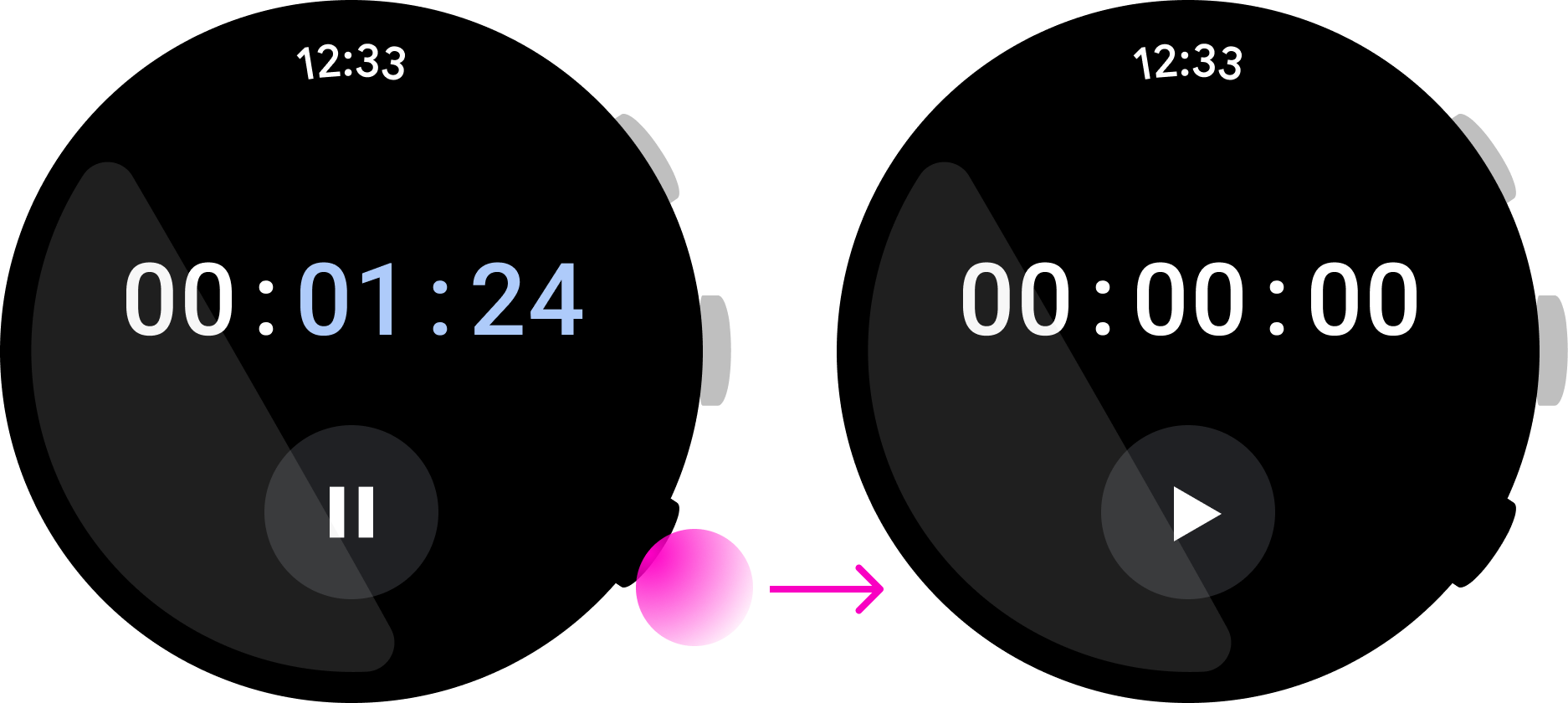
การดำเนินการแบบ 2 ค่าช่วยให้ผู้ใช้เข้าใจสิ่งที่จะเกิดขึ้นทุกครั้งที่กดปุ่ม เช่น "เริ่ม" และ "หยุด" ในนาฬิกาจับเวลาถือเป็นการดำเนินการแบบ 2 ค่า และแสดงถึง Use Case ที่ดีสำหรับปุ่มมัลติฟังก์ชัน
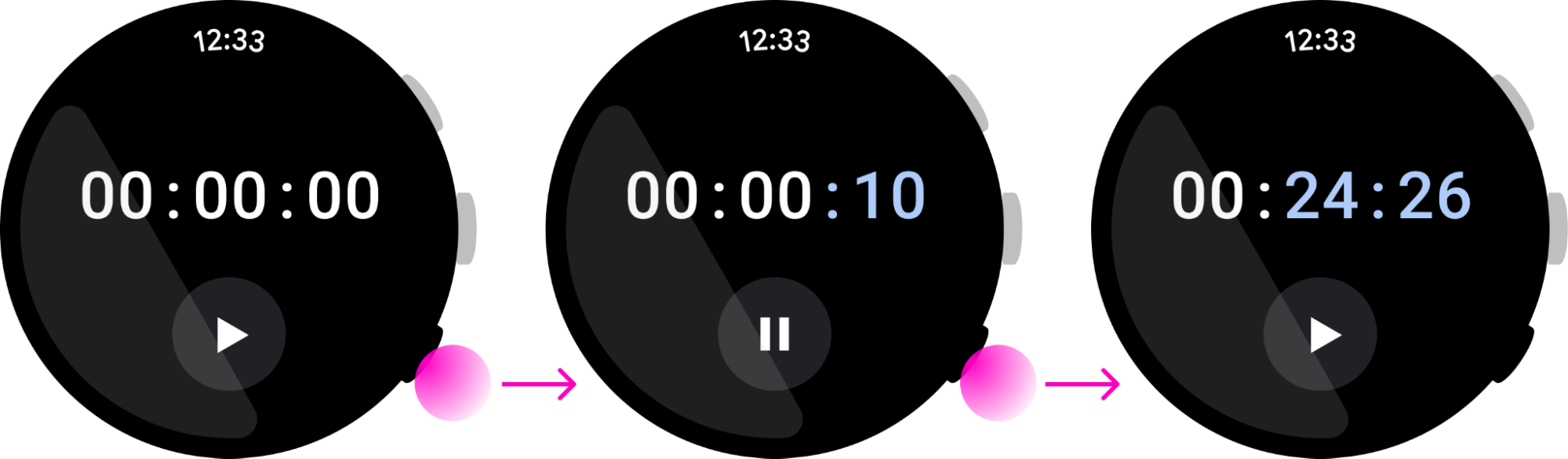
ปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชันเป็นทางเลือก
ทำให้การดำเนินการของปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชันเข้าถึงได้ผ่านองค์ประกอบ UI บนหน้าจอ เนื่องจากนาฬิกาบางรุ่นไม่มีปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชัน แต่คุณใช้ปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชันแทนปุ่มบนหน้าจอได้
อย่าใช้ปุ่มมัลติฟังก์ชันสำหรับการดำเนินการที่ดำเนินการโดยใช้องค์ประกอบ UI บนหน้าจอไม่ได้
เน้นความเรียบง่ายและเข้าถึงได้ทันที
การกดปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชันจะดำเนินการที่กำหนดไว้ทันที หากไม่ต้องการให้ผู้ใช้ต้องมองที่หน้าจอ ให้ใช้ปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชันสำหรับการดำเนินการที่ทําได้ด้วยการกดเพียงครั้งเดียว
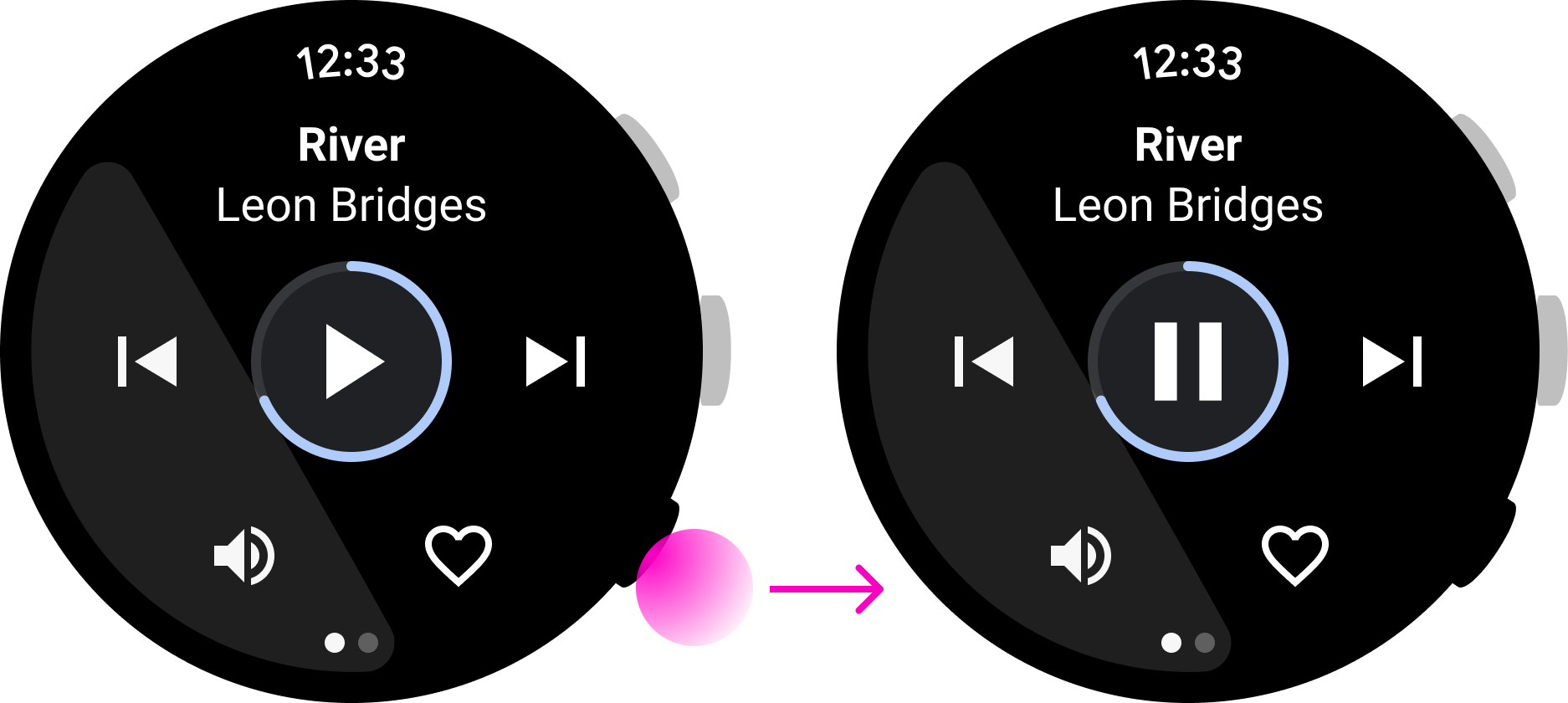
ควรทำ
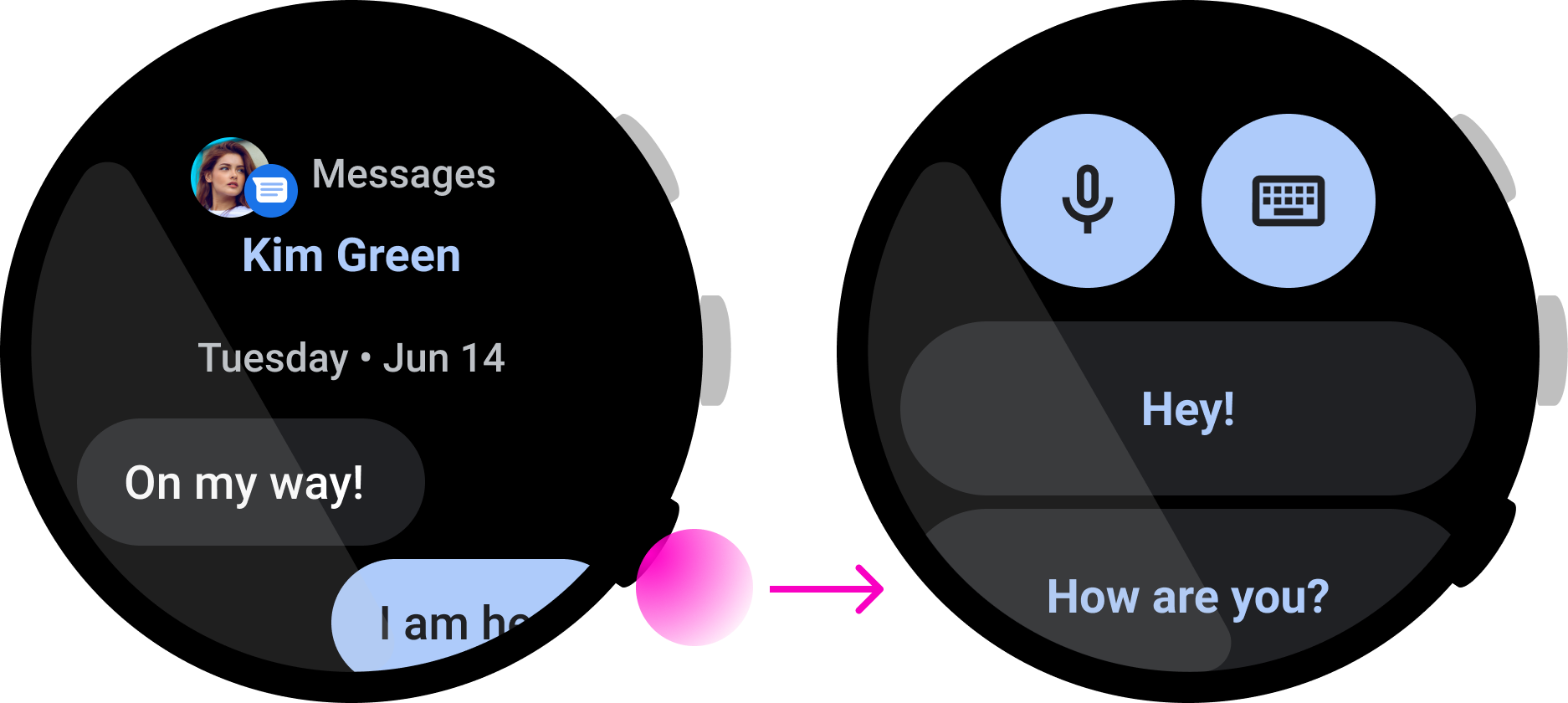
ไม่ควรทำ
ในแอปเพลงนี้ ผู้ใช้สามารถหยุดเพลงชั่วคราวได้อย่างรวดเร็ว ซึ่งเป็นตัวอย่างที่ดีของการใช้ปุ่มมัลติฟังก์ชัน อย่างไรก็ตาม ในแอปการรับส่งข้อความนี้ การกดปุ่มจะเป็นการเริ่มการตอบ แต่ผู้ใช้อาจต้องตรวจสอบข้อความก่อนดำเนินการให้เสร็จสมบูรณ์ ซึ่งหมายความว่านี่ไม่ใช่การโต้ตอบที่ดีสำหรับปุ่มหลายฟังก์ชัน
ใช้ได้ 2 ด้าน
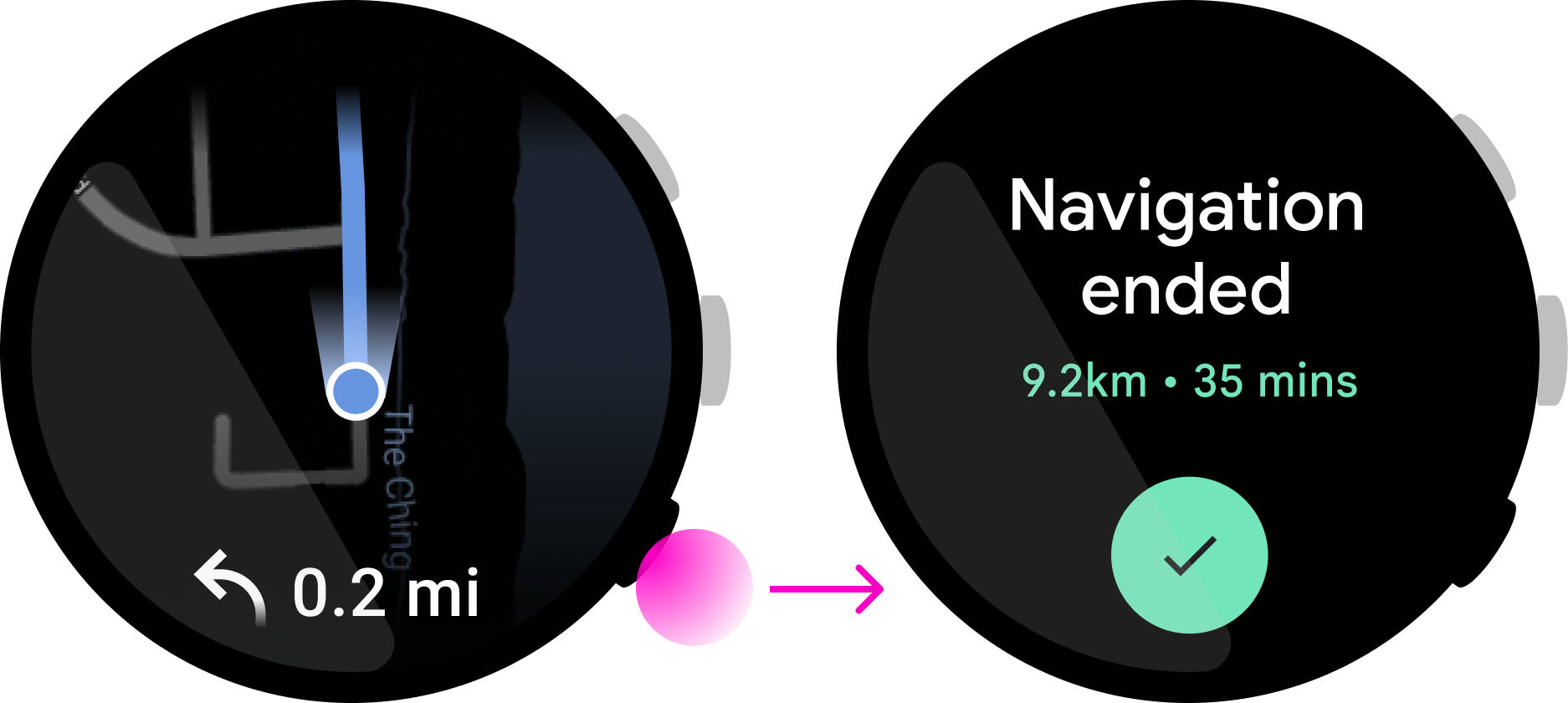
ทําให้การดำเนินการของปุ่มย้อนกลับได้ อย่าใช้ปุ่มมัลติฟังก์ชันเพื่อเรียกใช้การดำเนินการที่ก่อให้เกิดความเสียหาย เช่น การลบข้อมูลหรือการหยุดกิจกรรมที่กำลังดำเนินอยู่ เช่น การกดปุ่มมัลติฟังก์ชันในแอปแผนที่นี้จะดำเนินการเพื่อ "หยุดการนําทาง" ซึ่งอาจทําให้ผู้ใช้เสียเส้นทางในเวลาสําคัญ