เลย์เอาต์มุมมองแอปแบบเลื่อนประกอบด้วยรายการ (TransformingLazyColumn) และกล่องโต้ตอบ
เลย์เอาต์เหล่านี้ประกอบกันเป็นหน้าจอแอปส่วนใหญ่ และแสดงถึงคอลเล็กชันคอมโพเนนต์ที่ต้องปรับให้เข้ากับหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ขึ้น ตรวจสอบว่าคอมโพเนนต์ปรับเปลี่ยนตามพื้นที่โฆษณา กล่าวคือ คอมโพเนนต์มีขนาดเท่ากับความกว้างที่มีและใช้TransformingLazyColumnการปรับเมื่อความสูงของหน้าจอมีมากขึ้น เลย์เอาต์เหล่านี้สร้างขึ้นให้ปรับเปลี่ยนขนาดได้อยู่แล้ว และเรามีคำแนะนำเพิ่มเติมเพื่อใช้ประโยชน์จากพื้นที่โฆษณาที่ขยายใหญ่ขึ้น
สร้างการออกแบบที่ปรับเปลี่ยนตามอุปกรณ์และเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพ
เราได้อัปเดตลักษณะการทํางานของเลย์เอาต์และคอมโพเนนต์เพื่อให้มีลักษณะการทํางานที่ปรับเปลี่ยนตามอุปกรณ์โดยค่าเริ่มต้น รวมถึงระยะขอบและระยะห่างจากขอบแบบเปอร์เซ็นต์ เพื่อช่วยให้คุณปรับเลย์เอาต์การออกแบบให้เหมาะกับหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ได้ ในการแก้ไขปัญหานี้ เราได้อัปเดตเลย์เอาต์และคอมโพเนนต์ของไลบรารี UI ของ Android ให้มีลักษณะการทํางานแบบปรับเปลี่ยนตามอุปกรณ์โดยค่าเริ่มต้น รวมถึงระยะขอบและการเว้นวรรคตามเปอร์เซ็นต์ หากใช้คอมโพเนนต์ Compose คุณจะรับการตอบสนองนี้โดยอัตโนมัติ
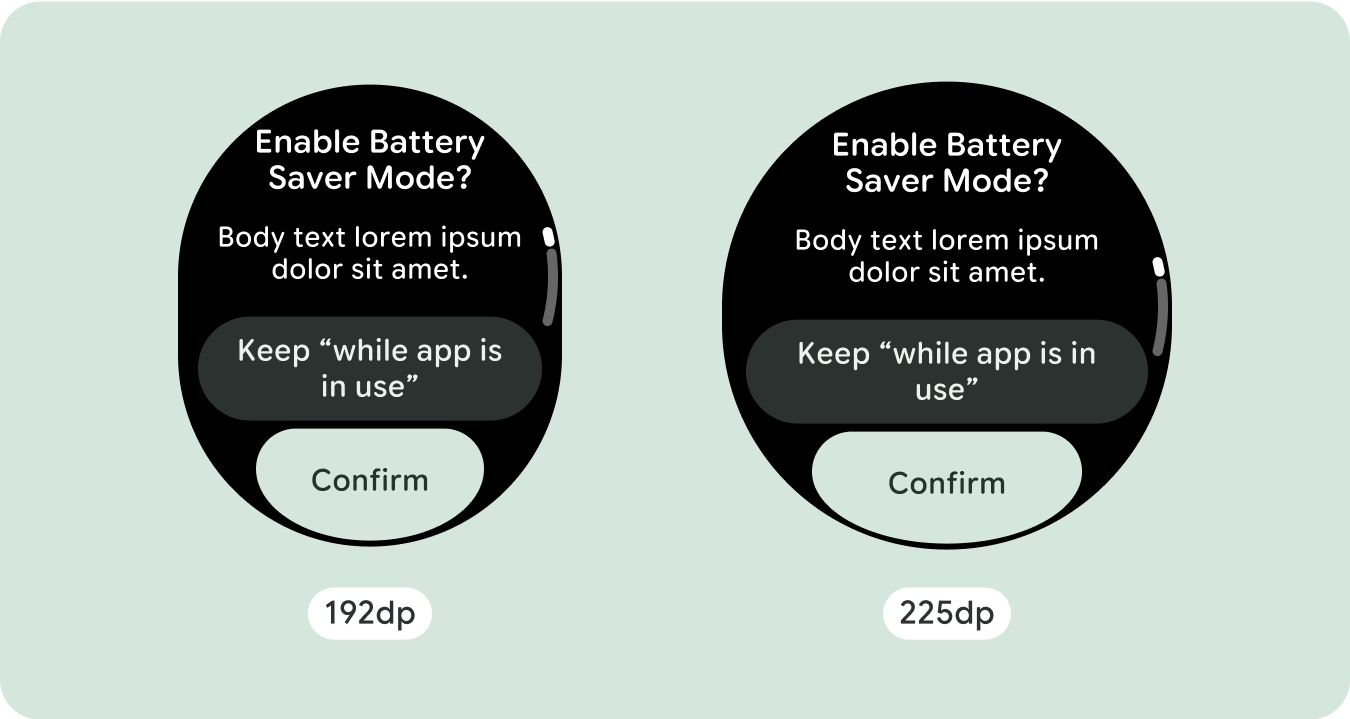
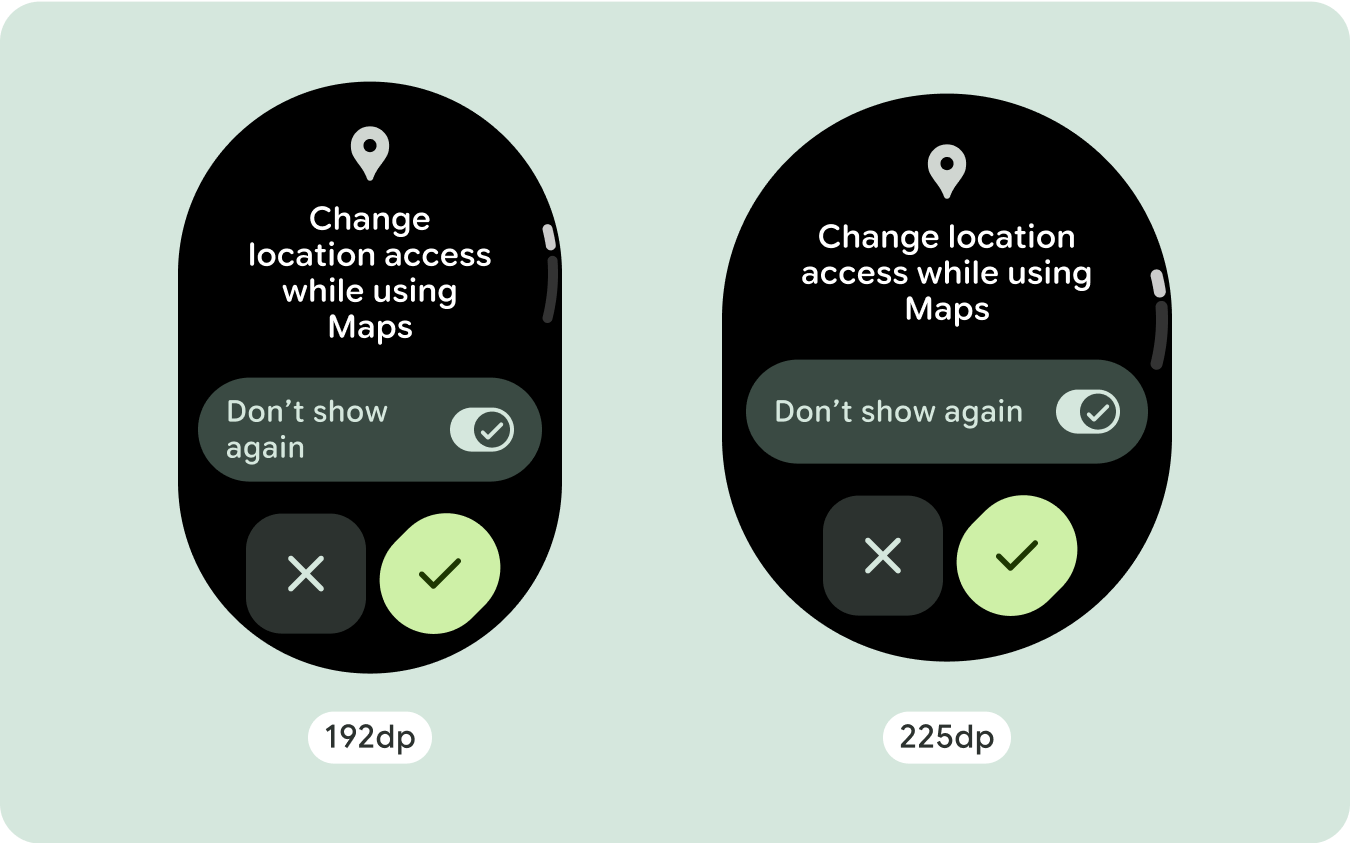
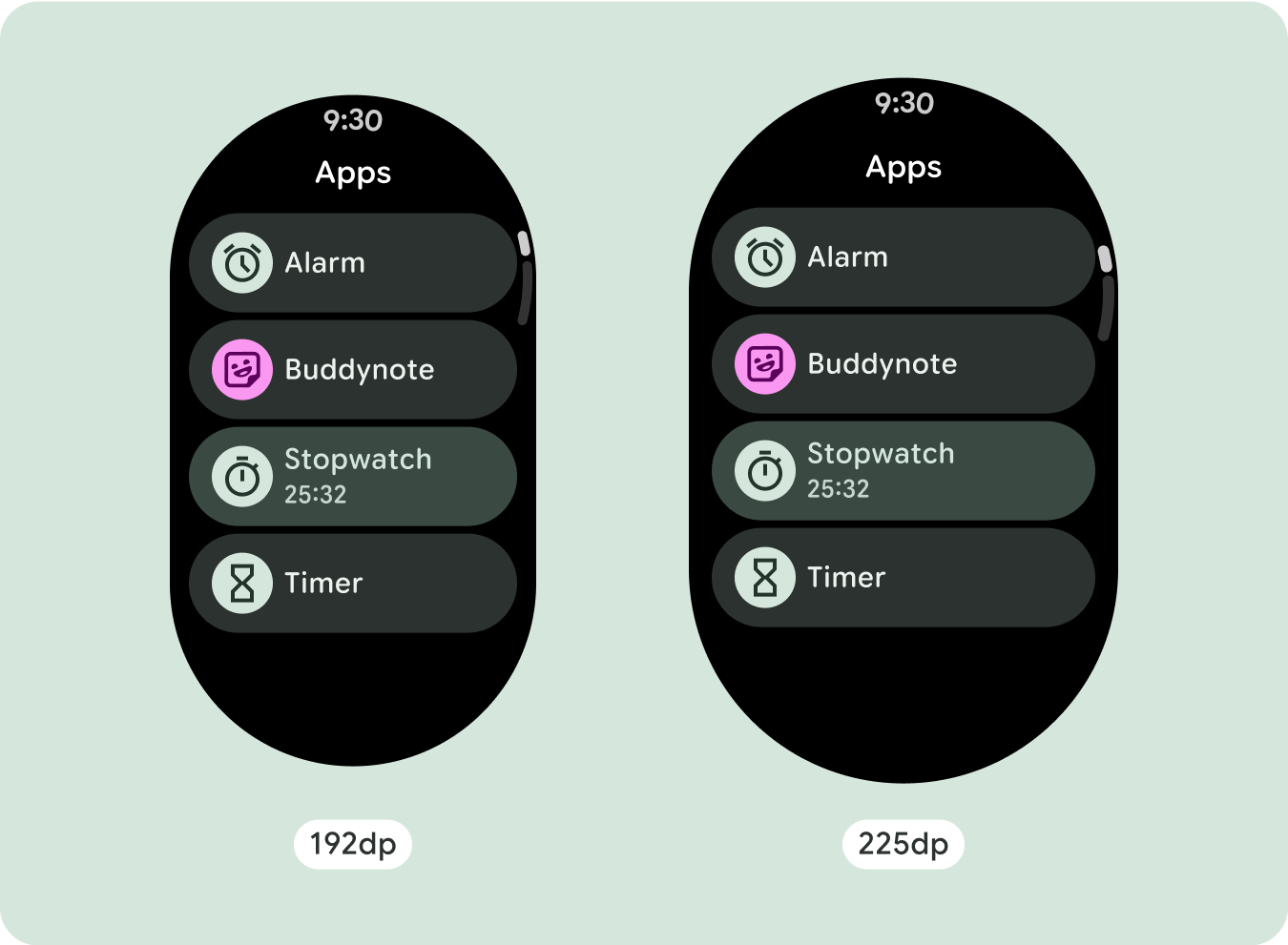
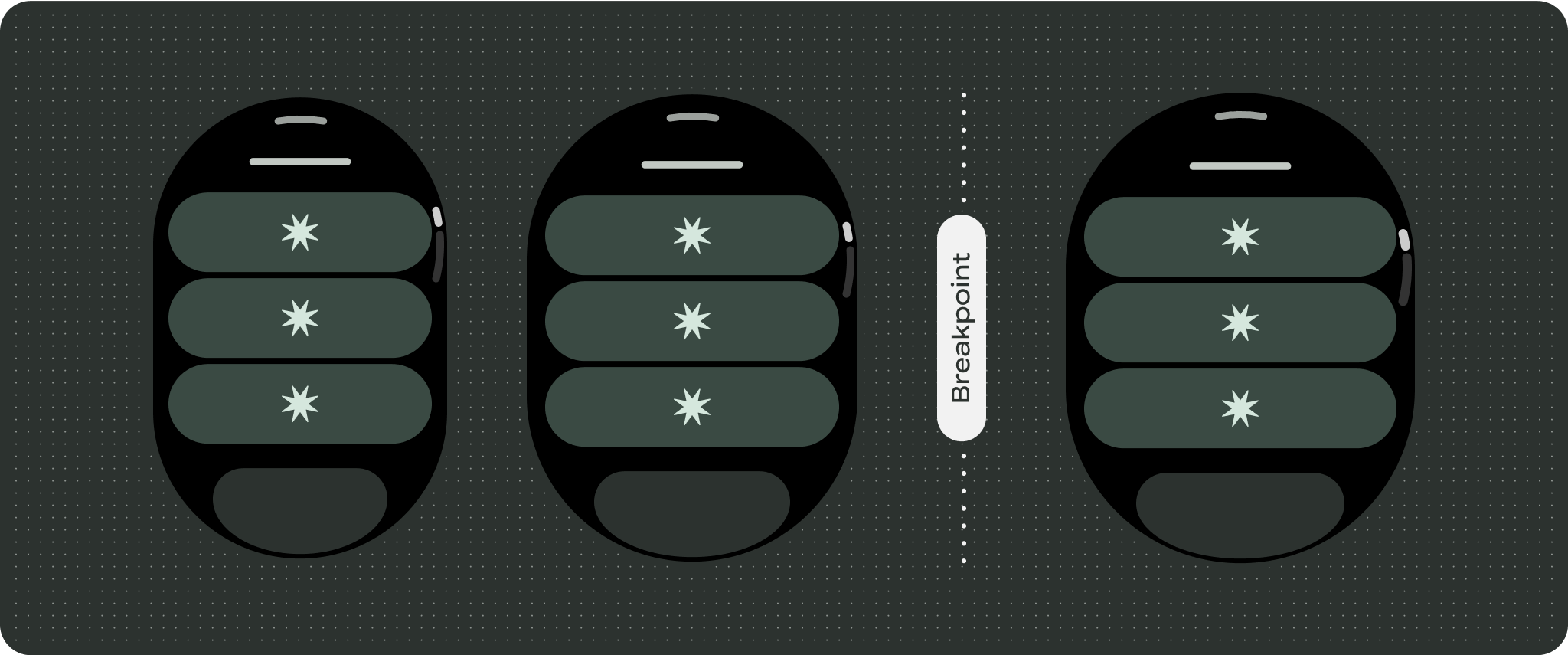
สำหรับการออกแบบหน้าจอที่ไม่ซ้ำกัน ให้ทดสอบอย่างละเอียดในหน้าจอขนาดต่างๆ เพื่อให้แน่ใจว่าคอมโพเนนต์และองค์ประกอบต่างๆ จะปรับขนาดได้อย่างราบรื่นและหลีกเลี่ยงการครอบตัดเนื้อหา ส่วนต่างของเปอร์เซ็นต์ช่วยให้ตัวเว้นวรรคปรับขนาดได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ และเราขอแนะนำให้ใช้จุดแบ่งที่ 225dp เพื่อแสดงข้อมูลเพิ่มเติมและฟังก์ชันการทำงานที่มีประสิทธิภาพมากขึ้นบนหน้าจอนาฬิกาขนาดใหญ่
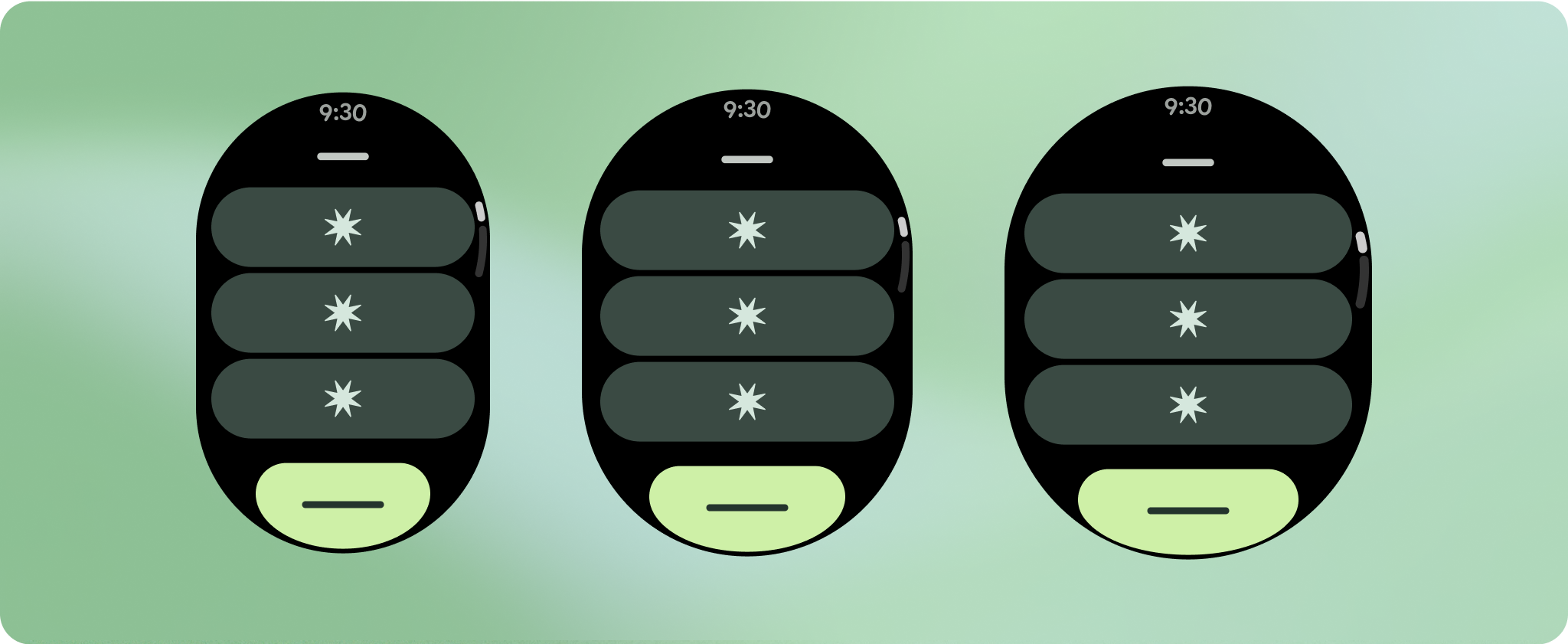
ตรวจสอบว่าคอมโพเนนต์เต็มความกว้างที่มีอยู่
ส่วนประกอบทั้งหมดสร้างขึ้นแบบตอบสนอง ซึ่งหมายความว่าจะเติมเต็มความกว้างและความสูงที่มีอยู่ ตรวจสอบว่าคุณมีระยะขอบที่จำเป็นเพื่อให้เนื้อหาไม่ถูกตัดออกโดยหน้าจอที่ปัดมุม
แสดงอักขระข้อความเพิ่มเติม
ส่วนประกอบส่วนใหญ่จะมีกล่องข้อความที่เติมเต็มความกว้างที่มีอยู่ ซึ่งหมายความว่าข้อความจะมีจำนวนอักขระเพิ่มขึ้นโดยอัตโนมัติเมื่อความกว้างของหน้าจอเพิ่มขึ้น

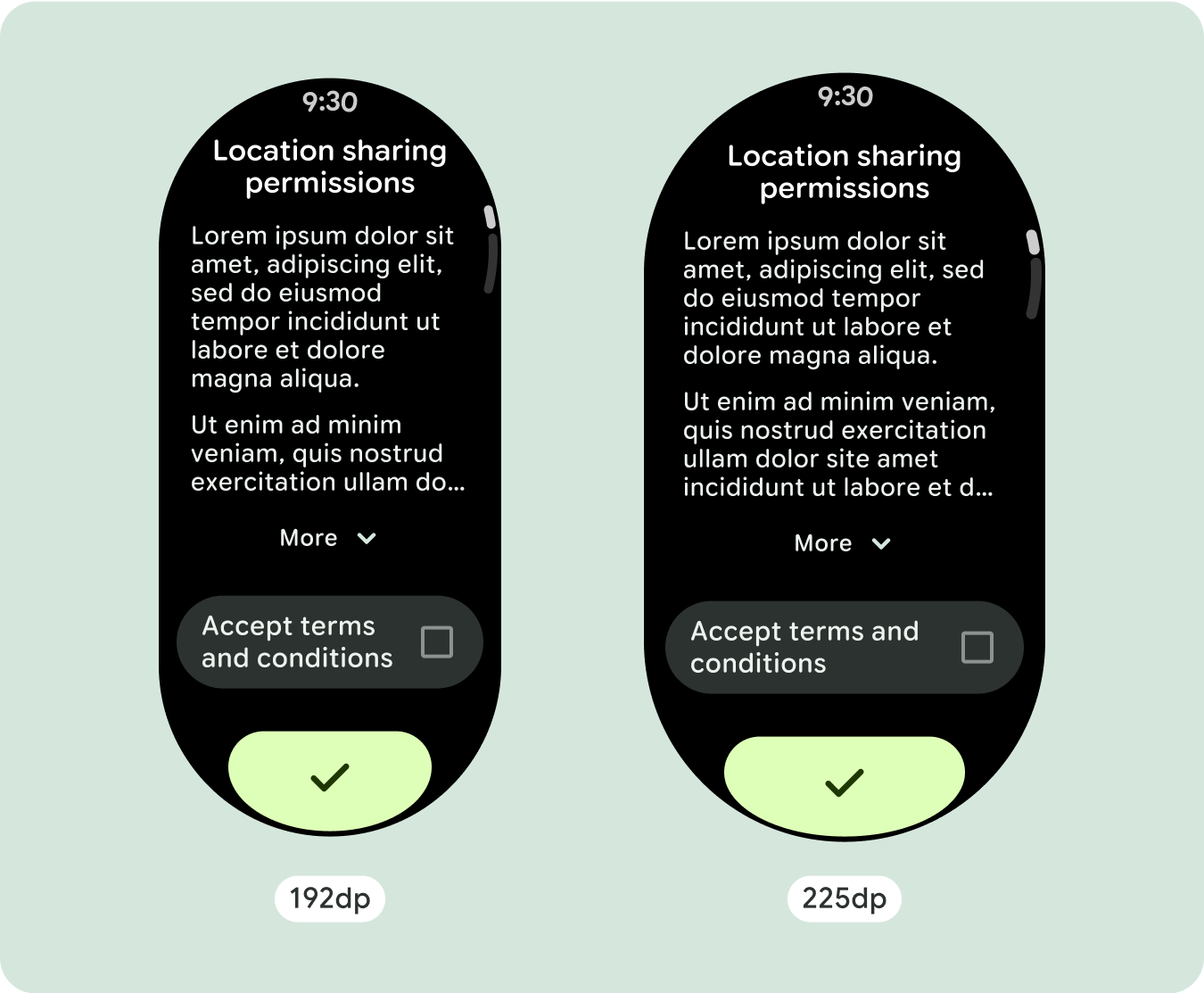
สร้างการออกแบบที่ปรับเปลี่ยนได้และมีความแตกต่างกัน
เนื่องจากเลย์เอาต์แบบเลื่อนจะแสดงเนื้อหาที่ซ่อนอยู่ก่อนหน้านี้ใต้รอยพับของหน้าจอโดยอัตโนมัติ คุณจึงไม่ต้องทำอะไรมากนักเพื่อเพิ่มมูลค่า คอมโพเนนต์แต่ละรายการจะเติมเต็มความกว้างที่มีอยู่ และในบางกรณี คอมโพเนนต์อาจมีแถวข้อความเพิ่มเติม (เช่น การ์ด) หรือคอมโพเนนต์อาจยืดออกเพื่อเติมเต็มความกว้างที่มีอยู่ (เช่น ปุ่มไอคอน)
หากต้องการใช้พื้นที่เพิ่มเติมในหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ให้คุ้มค่าที่สุด ให้เพิ่มจุดหยุดแสดงขนาดที่ 225dp จุดพักนี้ช่วยให้คุณแสดงเนื้อหาเพิ่มเติม ใส่ปุ่มหรือข้อมูลอื่นๆ หรือเปลี่ยนเลย์เอาต์ให้เหมาะกับหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ได้ ซึ่งต้องใช้การออกแบบที่แตกต่างกันสำหรับจุดพักแต่ละจุด การออกแบบหน้าจอขนาดใหญ่ (225+) อาจรวมองค์ประกอบเพิ่มเติมต่อไปนี้
เพิ่มขนาดหรือเปลี่ยนสถานะของคอมโพเนนต์ที่มีอยู่
ซึ่งอาจทำเพื่อแสดงรายละเอียดเพิ่มเติมหรือทำให้เนื้อหาดูง่ายขึ้น

เลย์เอาต์ที่เพิ่มประสิทธิภาพและมีความแตกต่างกัน
เลย์เอาต์อาจเปลี่ยนแปลงเล็กน้อยหลังจากจุดพัก 225dp เพื่อให้เนื้อหาด้านบนของหน้าจอในมุมมองเริ่มต้นได้รับการเพิ่มประสิทธิภาพ แต่เนื้อหาเดียวกันทั้งหมดที่อยู่ด้านล่างของหน้าจอควรยังคงใช้งานได้ไม่ว่าจะมีขนาดหน้าจอเท่าใดก็ตาม
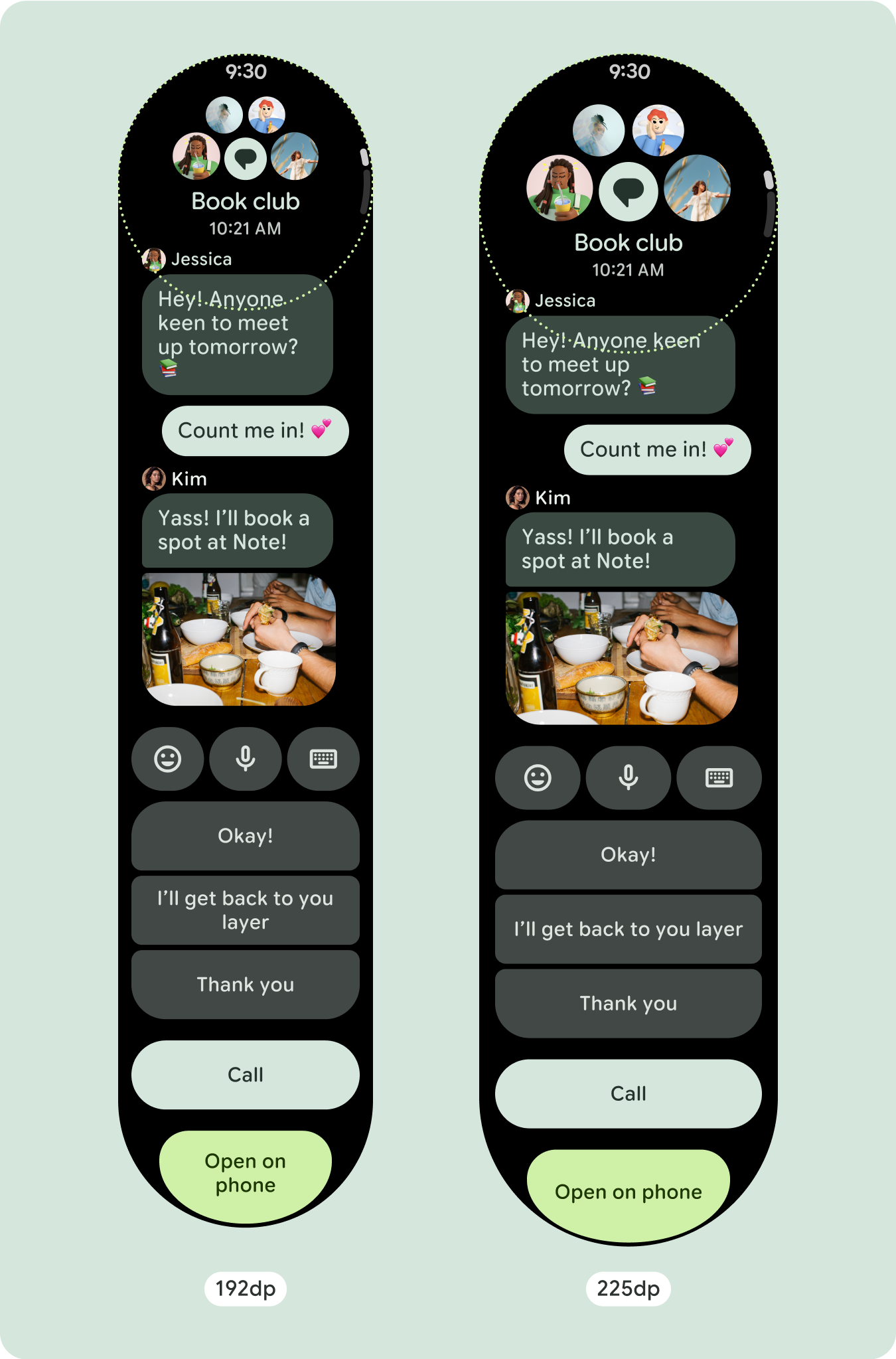
ลักษณะการทํางานที่ปรับเปลี่ยนได้
คอมโพเนนต์ทั้งหมดในไลบรารี Compose จะปรับให้เข้ากับขนาดหน้าจอที่กว้างขึ้นโดยอัตโนมัติ รวมถึงเพิ่มความกว้างและความสูง มุมมองการเลื่อนที่ใช้แนวทางการออกแบบที่ปรับเปลี่ยนตามอุปกรณ์มักจะปรับให้เหมาะกับขนาดหน้าจอที่หลากหลาย อย่างไรก็ตาม ในบางกรณีพิเศษ คุณสามารถใช้จุดหยุดพักเพื่อลบล้างมิติข้อมูลและเพิ่มเลย์เอาต์ ซึ่งจะขยายฟังก์ชันการทำงาน ปรับปรุงการมองเห็นได้อย่างรวดเร็ว หรือทำให้เนื้อหาพอดีกับหน้าจอมากขึ้น
ควรกำหนดระยะขอบด้านบน ด้านล่าง และด้านข้างทั้งหมดเป็นเปอร์เซ็นต์เพื่อหลีกเลี่ยงการตัดออกและปรับขนาดองค์ประกอบตามสัดส่วน โปรดทราบว่า PositionIndicator จะปรากฏขึ้นเมื่อผู้ใช้เลื่อน และจะแนบไปกับขอบของหน้าจอโดยอัตโนมัติไม่ว่าจะมีขนาดเท่าใดก็ตาม
เช็กลิสต์
- ใช้ระยะขอบด้านบน ด้านล่าง และด้านข้างที่แนะนํา
- กําหนดระยะขอบด้านนอกเป็นค่าเปอร์เซ็นต์เพื่อป้องกันการตัดออกที่จุดเริ่มต้นและจุดสิ้นสุดของคอนเทนเนอร์ที่เลื่อนได้
- ใช้ระยะขอบในค่า DP แบบคงที่ระหว่างองค์ประกอบ UI
- ลองใช้จุดหยุดพักที่ 225dp เพื่อแสดงเนื้อหาเพิ่มเติมหรือทำให้เนื้อหาที่มีอยู่ดูได้ง่ายขึ้นเมื่อใช้หน้าจอขนาดใหญ่
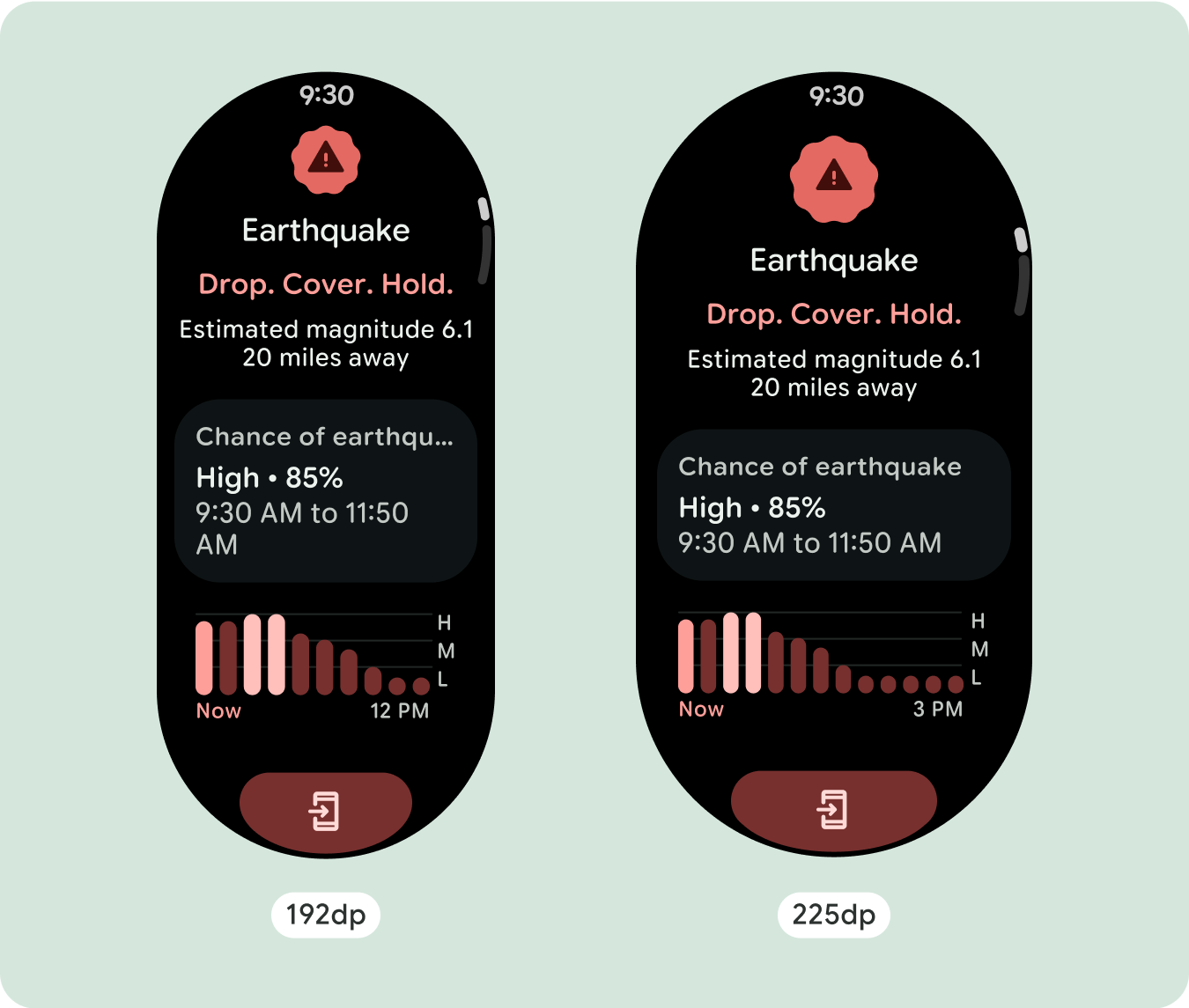
สร้างประสบการณ์ที่แตกต่าง
มุมมองการเลื่อนปรับแต่งได้เป็นอย่างมาก โดยสามารถเพิ่มคอมโพเนนต์ใดก็ได้ตามลำดับที่ต้องการ ระยะขอบด้านบนและด้านล่างอาจเปลี่ยนแปลงได้ ทั้งนี้ขึ้นอยู่กับคอมโพเนนต์ที่วางไว้ที่ด้านบนและด้านล่าง เพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้เนื้อหาถูกตัดออกโดยส่วนโค้งที่เพิ่มขึ้นของหน้าจอ

